Solar Eclipse Prime Page
Hybrid Solar Eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 (1453 Jan 28 BCE)
Fred Espenak
Introduction
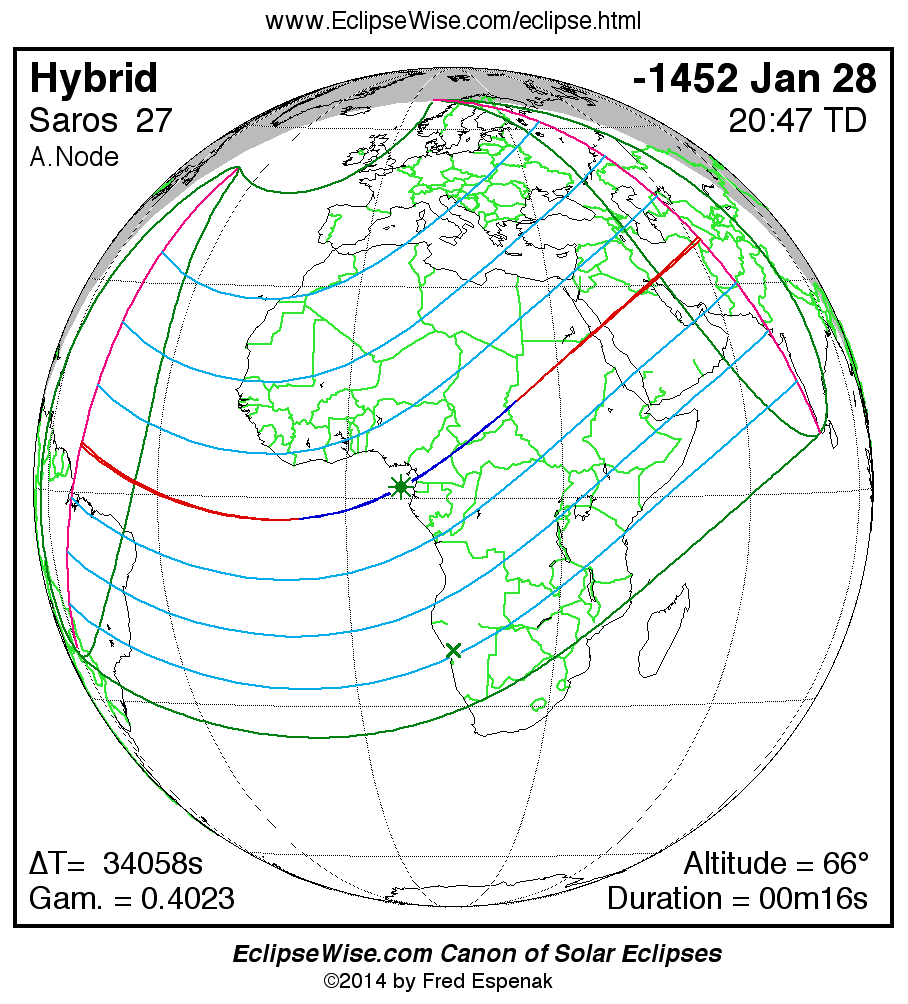
The Hybrid Solar Eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 (1453 Jan 28 BCE) is visible from the geographic regions shown on the map to the right. Click on the map to enlarge it. For an explanation of the features appearing in the map, see Key to Solar Eclipse Maps.
The instant of greatest eclipse takes place on -1452 Jan 28 at 20:47:07 TD (11:19:34 UT1). This is 4.1 days before the Moon reaches perigee. During the eclipse, the Sun is in the constellation Aquarius. The synodic month in which the eclipse takes place has a Brown Lunation Number of -41742.
The eclipse belongs to Saros 27 and is number 31 of 72 eclipses in the series. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node. The Moon moves southward with respect to the node with each succeeding eclipse in the series and gamma decreases.
The solar eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 is one of the rare hybrid solar eclipses. In this particular case the eclipse path starts out as annular. Further down the track it changes to total and then back to annular before the path ends. It is a very short hybrid eclipse with a duration at greatest eclipse of 00m16s. The eclipse magnitude is 1.0025, while Gamma has a value of 0.4023.
The hybrid solar eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 is preceded two weeks earlier by a penumbral lunar eclipse on -1452 Jan 13.
These eclipses all take place during a single eclipse season.
The eclipse predictions are given in both Terrestrial Dynamical Time (TD) and Universal Time (UT1). The parameter ΔT is used to convert between these two times (i.e., UT1 = TD - ΔT). ΔT has a value of 34053.6 seconds for this eclipse. The uncertainty in ΔT is 1752.6 seconds corresponding to a standard error in longitude of the eclipse path of ± 7.32°.
The following links provide maps and data for the eclipse.
- Orthographic Map: Hybrid Solar Eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 - global map of eclipse visibility
- Google Map: Hybrid Solar Eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 - interactive map of the eclipse path
- Path Table: Hybrid Solar Eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 - coordinates of the central line and path limits
- Circumstances Table: Hybrid Solar Eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 - eclipse times for hundreds of cities
- Saros 27 Table - data for all eclipses in the Saros series
The tables below contain detailed predictions and additional information on the Hybrid Solar Eclipse of -1452 Jan 28 .