Solar Eclipse Prime Page
Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25
Fred Espenak
Key to Solar Eclipse Figure (below)
Introduction
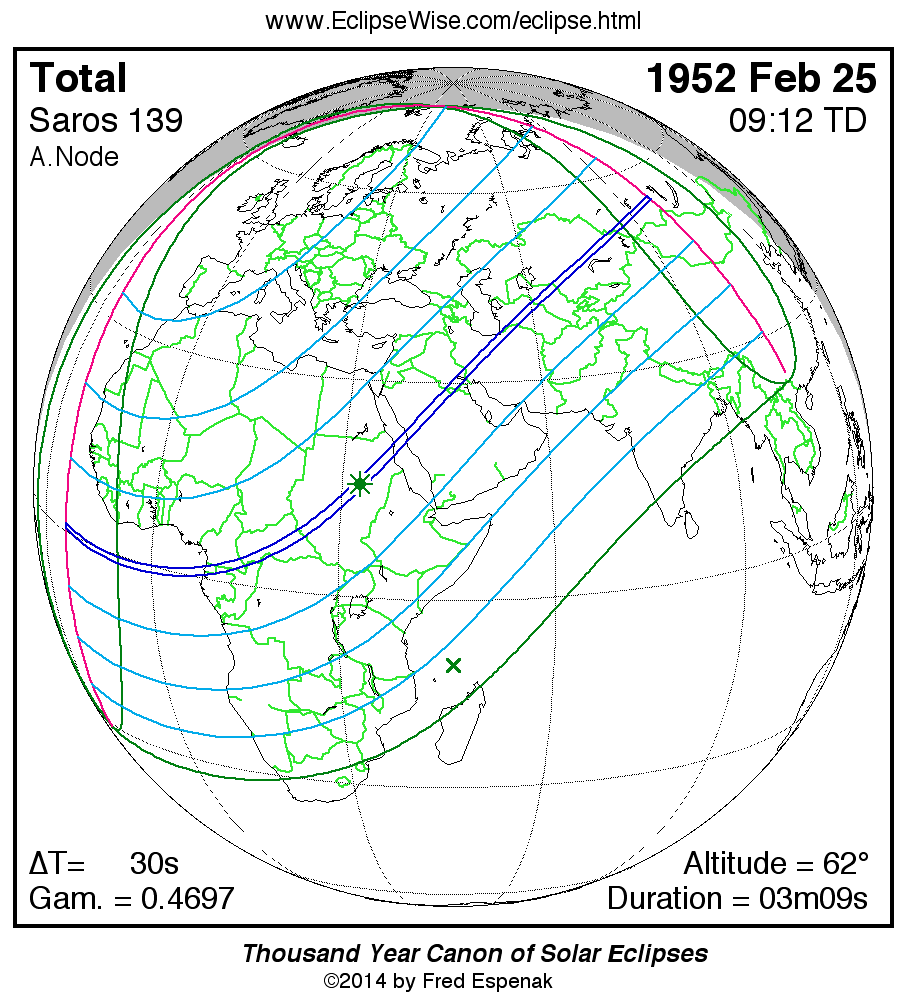
The Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 is visible from the following geographic regions:
- Partial Eclipse: Europe, Africa, Asia
- Total Eclipse: Gabon, Central African Rep., Sudan, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Russia
The map to the right depicts the geographic regions of eclipse visibility. Click on the map to enlarge it. For an explanation of the features appearing in the map, see Key to Solar Eclipse Maps.
The instant of greatest eclipse takes place on 1952 Feb 25 at 09:11:35 TD (09:11:05 UT1). This is 1.4 days after the Moon reaches perigee. During the eclipse, the Sun is in the constellation Aquarius. The synodic month in which the eclipse takes place has a Brown Lunation Number of 361.
The eclipse belongs to Saros 139 and is number 26 of 71 eclipses in the series. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node. The Moon moves southward with respect to the node with each succeeding eclipse in the series and gamma decreases.
The total solar eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 is preceded two weeks earlier by a partial lunar eclipse on 1952 Feb 11.
These eclipses all take place during a single eclipse season.
The eclipse predictions are given in both Terrestrial Dynamical Time (TD) and Universal Time (UT1). The parameter ΔT is used to convert between these two times (i.e., UT1 = TD - ΔT). ΔT has a value of 30.0 seconds for this eclipse.
The following links provide maps and data for the eclipse.
- Orthographic Map: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - detailed global map of eclipse visibility (Key to Figure)
- Google Map: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - interactive map of the eclipse path
- Path Table: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - coordinates of the central line and path limits
- Circumstances Table: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - eclipse times for hundreds of cities
- Saros 139 Table - data for all eclipses in the Saros series
- Additional Tables and Data - for this event
Eclipse Data: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25
| Eclipse Characteristics | |
| Parameter | Value |
| Eclipse Magnitude | 1.03660 |
| Eclipse Obscuration | 1.07454 |
| Gamma | 0.46973 |
| Conjunction Times | ||
| Event | Calendar Date and Time | Julian Date |
| Greatest Eclipse | 1952 Feb 25 at 09:11:34.8 TD (09:11:04.8 UT1) | 2434067.882695 |
| Ecliptic Conjunction | 1952 Feb 25 at 09:16:27.1 TD (09:15:57.1 UT1) | 2434067.886077 |
| Equatorial Conjunction | 1952 Feb 25 at 09:36:51.1 TD (09:36:21.0 UT1) | 2434067.900244 |
| Geocentric Coordinates of Sun and Moon | ||
| 1952 Feb 25 at 09:11:34.8 TD (09:11:04.8 UT1) | ||
| Coordinate | Sun | Moon |
| Right Ascension | 22h30m04.0s | 22h29m11.4s |
| Declination | -09°25'03.8" | -08°59'49.8" |
| Semi-Diameter | 16'09.4" | 16'30.0" |
| Eq. Hor. Parallax | 08.9" | 1°00'33.5" |
| Geocentric Libration of Moon | |
| Angle | Value |
| l | 2.7° |
| b | -0.6° |
| c | -20.0° |
| Prediction Parameters | |
| Paramater | Value |
| Ephemerides | JPL DE405 |
| ΔT | 30.0 s |
| k (penumbra) | 0.2725076 |
| k (umbra) | 0.2722810 |
| Saros Series | 139 (26/71) |
Penumbral Shadow Contacts and Extremes: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25
| Contacts of Penumbral Shadow with Earth | |||||
| Contact Event | Contact | Time TD |
Time UT1 |
Latitude | Longitude |
| First External Contact | P1 | 06:38:16.5 | 06:37:46.5 | 09°24.1'S | 007°41.3'W |
| Last External Contact | P4 | 11:44:46.4 | 11:44:16.3 | 44°26.3'N | 087°55.8'E |
| Extreme Northern and Southern Path Limits of Penumbra | |||||
| Contact Event | Contact | Time TD |
Time UT1 |
Latitude | Longitude |
| North Extreme Path Limit 1 | N1 | 07:31:30.9 | 07:31:00.9 | 30°54.2'S | 025°08.0'W |
| South Extreme Path Limit 1 | S1 | 10:51:43.8 | 10:51:13.7 | 23°03.3'N | 106°28.7'E |
Explanation of Penumbral Shadow Contacts and Extremes Tables
Umbral Shadow Contacts and Extremes: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25
| Contacts of Umbral Shadow with Earth | |||||
| Contact Event | Contact | Time TD |
Time UT1 |
Latitude | Longitude |
| First External Contact | U1 | 07:38:39.4 | 07:38:09.4 | 00°36.6'N | 021°06.2'W |
| First Internal Contact | U2 | 07:39:59.5 | 07:39:29.4 | 00°57.1'N | 021°22.9'W |
| Last Internal Contact | U3 | 10:42:56.4 | 10:42:26.3 | 54°33.6'N | 099°16.2'E |
| Last External Contact | U4 | 10:44:13.4 | 10:43:43.4 | 54°14.5'N | 099°06.5'E |
| Extreme Northern and Southern Path Limits of Umbra | |||||
| Contact Event | Contact | Time TD |
Time UT1 |
Latitude | Longitude |
| North Extreme Path Limit 1 | N1 | 07:39:36.0 | 07:39:05.9 | 01°08.6'N | 021°15.1'W |
| South Extreme Path Limit 1 | S1 | 07:39:03.3 | 07:38:33.2 | 00°25.1'N | 021°14.2'W |
| North Extreme Path Limit 2 | N2 | 10:43:18.8 | 10:42:48.8 | 54°44.2'N | 099°05.2'E |
| South Extreme Path Limit 2 | S2 | 10:43:50.6 | 10:43:20.6 | 54°03.8'N | 099°17.5'E |
Central Line Extremes and Duration: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25
| Extreme Limits of the Central Line | |||||
| Contact Event | Contact | Time TD |
Time UT1 |
Latitude | Longitude |
| Extreme Central Line Limit 1 | C1 | 07:39:19.4 | 07:38:49.4 | 00°46.8'N | 021°14.6'W |
| Extreme Central Line Limit 2 | C2 | 10:43:34.9 | 10:43:04.9 | 54°24.0'N | 099°11.4'E |
Explanation of Central Line Extremes Table
| Greatest Eclipse and Greatest Duration | ||||||||
| Event | Time TD |
Time UT1 |
Latitude | Longitude | Sun Altitude |
Sun Azimuth |
Path Width | Central Duration |
| Greatest Eclipse | 09:11:34.8 | 09:11:04.8 | 15°37.5'N | 032°39.8'E | 61.9° | 152.1° | 137.8 km | 03m09.43s |
| Greatest Duration | 09:07:12.9 | 09:06:42.9 | 14°30.4'N | 031°33.5'E | 61.8° | 147.1° | 138.8 km | 03m09.62s |
Polynomial Besselian Elements: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25
| Polynomial Besselian Elements | ||||||
| 1952 Feb 25 at 09:00:00.0 TD (=t0) | ||||||
| n | x | y | d | l1 | l2 | μ |
| 0 | -0.31351 | 0.36693 | -9.4216 | 0.54062 | -0.00551 | 311.6712 |
| 1 | 0.51046 | 0.26275 | 0.0148 | 0.00008 | 0.00008 | 15.0028 |
| 2 | -0.00002 | 0.00003 | 0.0000 | -0.00001 | -0.00001 | 0.0000 |
| 3 | -0.00001 | -0.00000 | - | - | - | - |
| Tan ƒ1 | 0.0047231 |
| Tan ƒ2 | 0.0046996 |
At time t1 (decimal hours), each besselian element is evaluated by:
x = x0 + x1*t + x2*t2 + x3*t3 (or x = Σ [xn*tn]; n = 0 to 3)
where: t = t1 - t0 (decimal hours) and t0 = 9.000
Links for the Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25
- Orthographic Map: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - detailed global map of eclipse visibility (Key to Figure)
- Google Map: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - interactive map of the eclipse path
- Path Table: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - coordinates of the central line and path limits
- Circumstances Table: Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - eclipse times for hundreds of cities
- Saros 139 Table - data for all eclipses in the Saros series
- Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 - Google search for links to this eclipse
Links to Additional Solar Eclipse Information
- Home - home page of EclipseWise with predictions for both solar and lunar eclipses
- Solar Eclipses - primary page for solar eclipse predictions
- Solar Eclipse Links - detailed directory of links
- Solar Eclipse Basics - the fundamentals about solar eclipses
- Periodicity of Solar Eclipses - eclipse seasons, Saros and Inex
- Solar Eclipses and the Saros - details on the Saros cycle
- Solar Eclipse Predictions and the Mean Lunar Radius
• Decade Tables of Solar Eclipses:
|
1901 - 1910 |
1911 - 1919 |
1921 - 1930 |
1931 - 1940 |
1941 - 1950 |
|
1951 - 1960 |
1961 - 1970 |
1971 - 1980 |
1981 - 1990 |
1991 - 2000 |
|
2001 - 2010 |
2011 - 2020 |
2021 - 2030 |
2031 - 2040 |
2041 - 2050 |
|
2051 - 2060 |
2061 - 2070 |
2071 - 2080 |
2081 - 2090 |
2091 - 2100 |
- Six Millennium Catalog of Solar Eclipses - covers the years -2999 to +3000 (3000 BCE to 3000 CE)
- Global Map Animations of Solar Eclipses: 2001 - 2100 - animated maps of every solar eclipse of the 21st Century
- Saros Catalog of Solar Eclipses - covers Saros series -30 through 190
- World Atlas of Solar Eclipse Maps - index page
- Solar Eclipse Search Engine - search for solar eclipses from -1999 to +3000
- Javascript Solar Eclipse Explorer - calculate all solar eclipses visible from a city
- MrEclipse.com - Eclipse resources and tips on photography
- MrEclipse: Solar Eclipses for Beginners - a primer on solar eclipse basics
- How to Photograph a Solar Eclipse - instructions for imaging an eclipse of the Sun
- MrEclipse Photo Index - an index of solar eclipse photographs
Solar Eclipse Publications
- Eclipse Almanac: 2021 to 2030 - overview of all solar and lunar eclipses for the decade
- 21st Century Canon of Solar Eclipses - coveres every solar eclipse from 2001 through 2100
- Thousand Year Canon of Solar Eclipses 1501 to 2500 - basic details about every solar eclipse for 1000 years
- Five Millennium Canon of Solar Eclipses: -1999 to +3000 - the ultimate reference with maps and diagrams
- Five Millennium Catalog of Solar Eclipses: -1999 to +3000 - the ultimate reference containing comprehensive tables
- Atlas of Central Solar Eclipses in the USA - 2,000 years of solar eclipses through North America
- Road Atlas of the Annular Solar Eclipse of 2023 October 14 - detailed maps of the annular eclipse path
- Road Atlas of the Total Solar Eclipse of 2024 April 08 - detailed maps of the total eclipse path
Eclipse Predictions
Predictions for the Total Solar Eclipse of 1952 Feb 25 were generated using the JPL DE405 solar and lunar ephemerides. The lunar coordinates were calculated with respect to the Moon's Center of Mass. The predictions are given in both Terrestrial Dynamical Time (TD) and Universal Time (UT1). The parameter ΔT is used to convert between these two times (i.e., UT1 = TD - ΔT). ΔT has a value of 30.0 seconds for this eclipse.
Acknowledgments
Some of the content on this website is based on the books 21st Century Canon of Solar Eclipses and Thousand Year Canon of Solar Eclipses 1501 to 2500. All eclipse calculations are by Fred Espenak, and he assumes full responsibility for their accuracy.
Permission is granted to reproduce eclipse data when accompanied by a link to this page and an acknowledgment:
"Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, www.EclipseWise.com"
The use of diagrams and maps is permitted provided that they are NOT altered (except for re-sizing) and the embedded credit line is NOT removed or concealed.