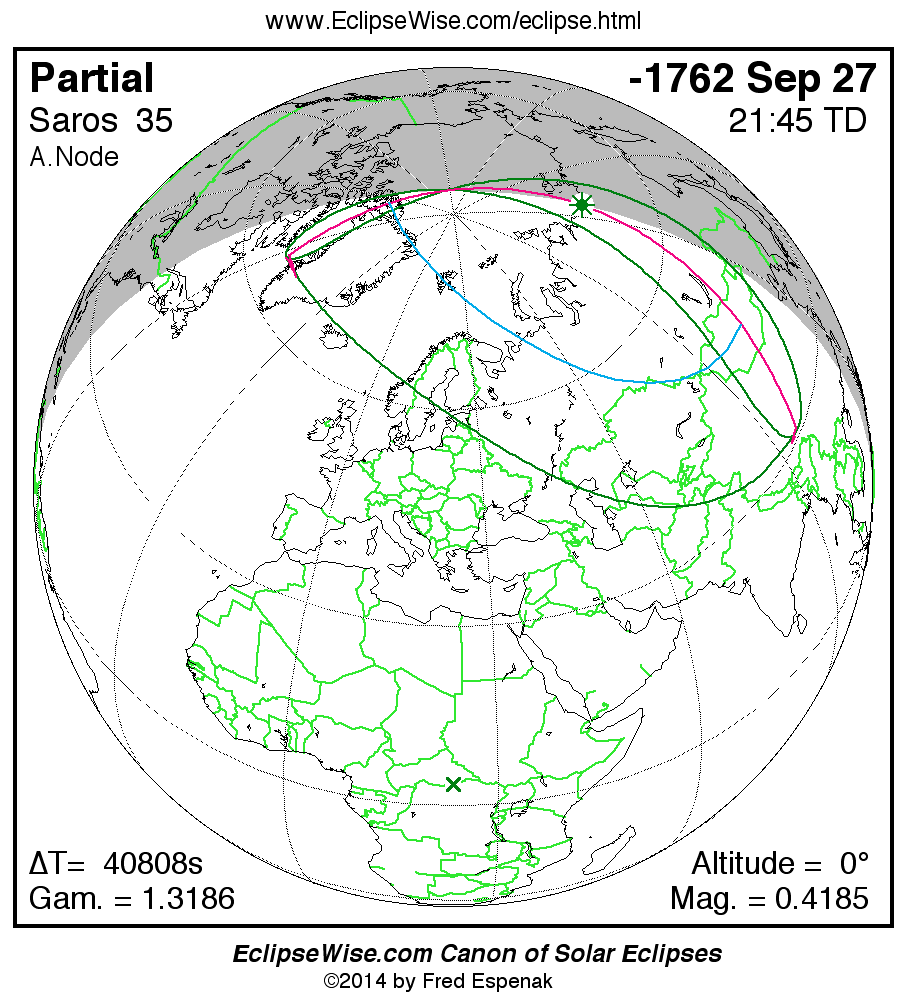
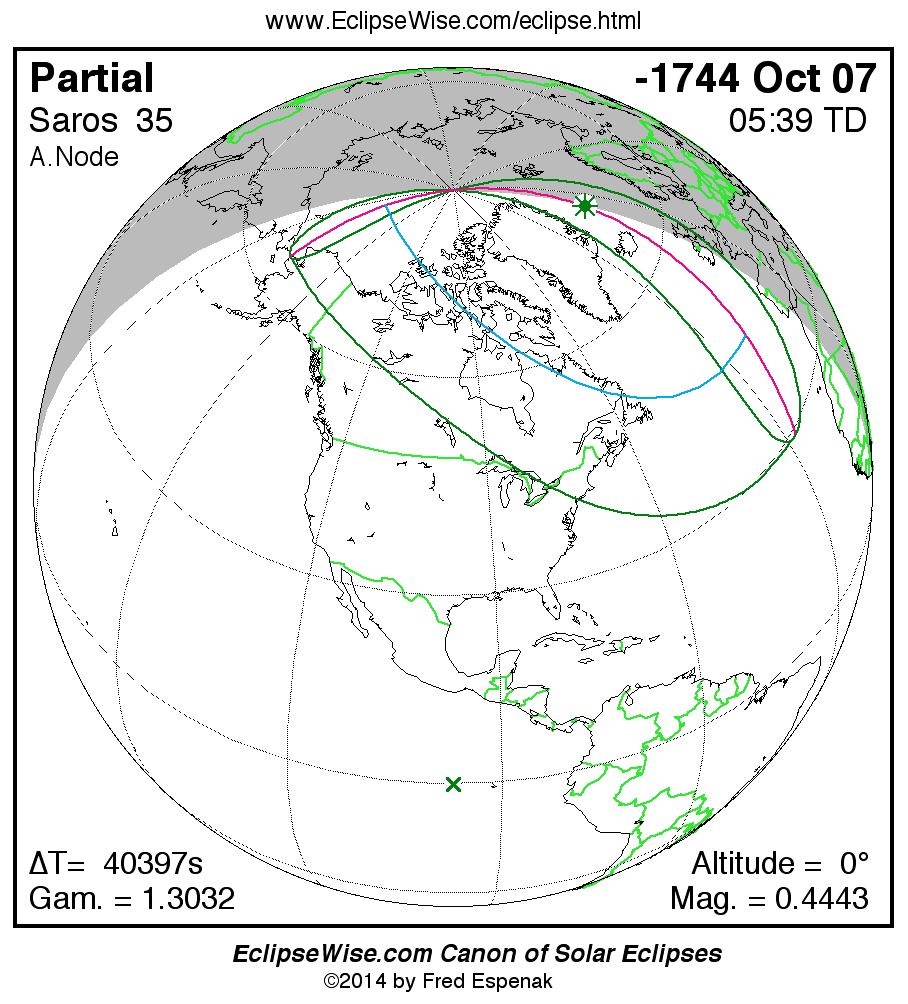
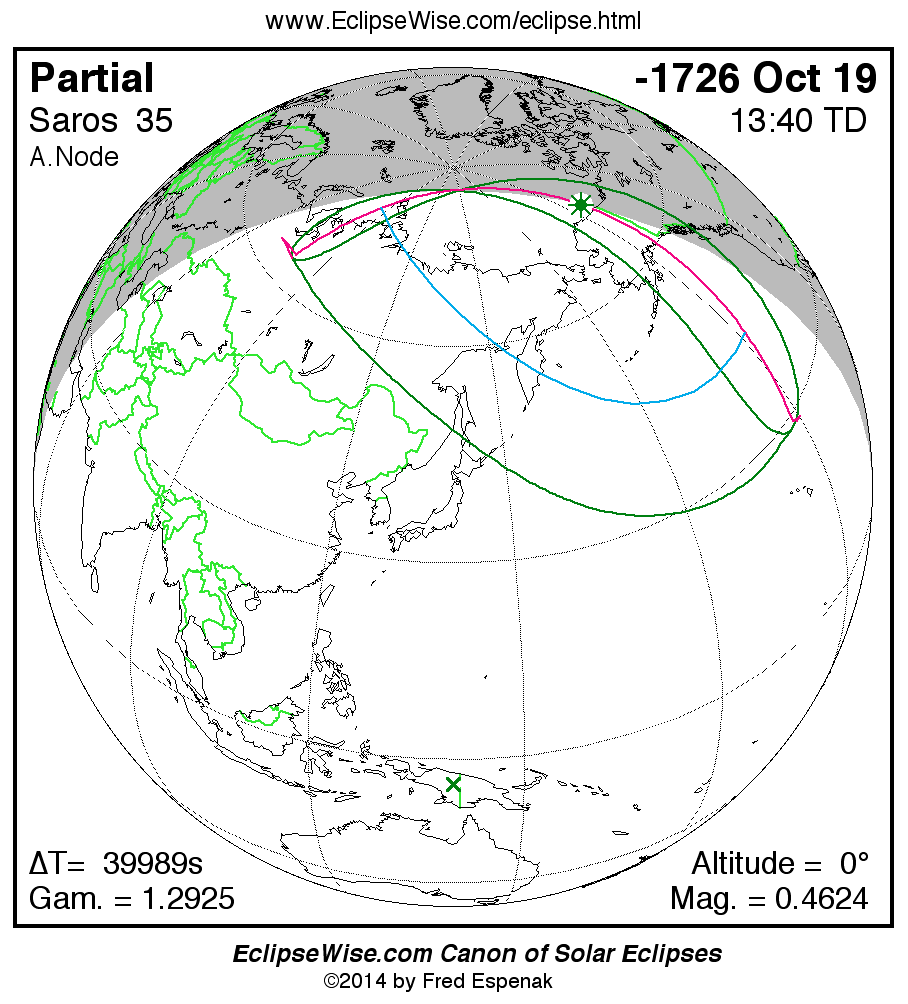
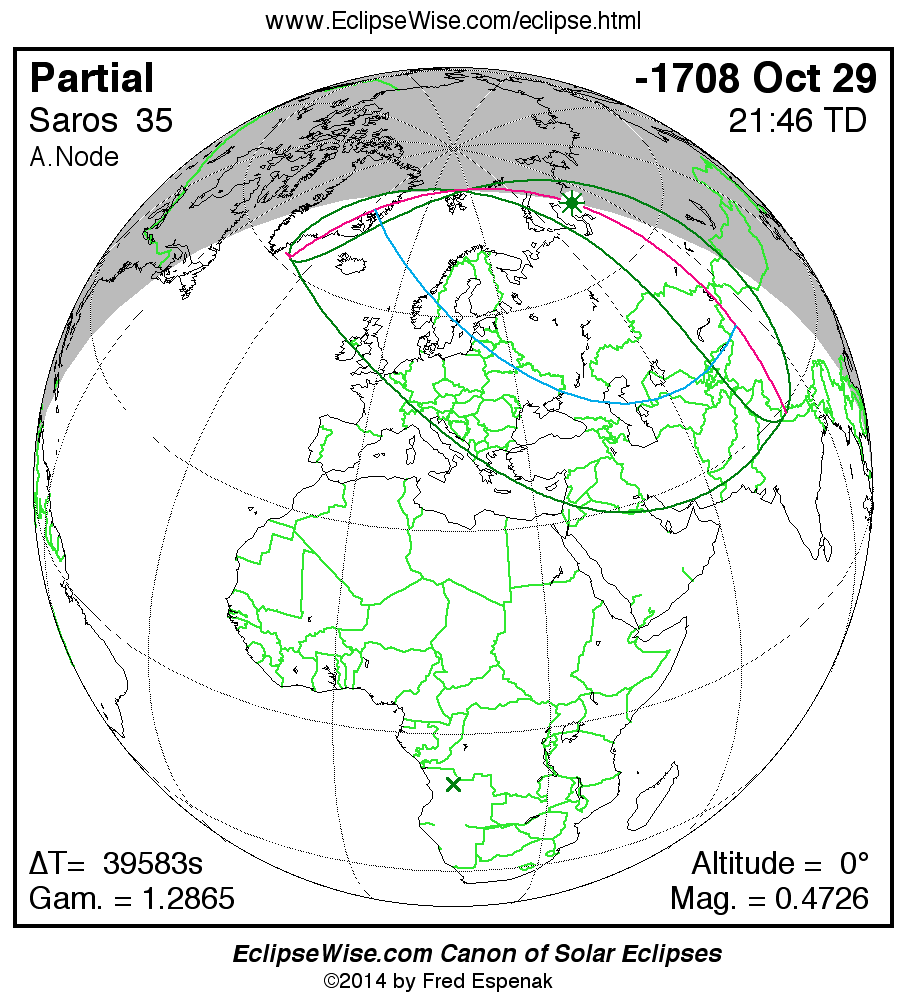
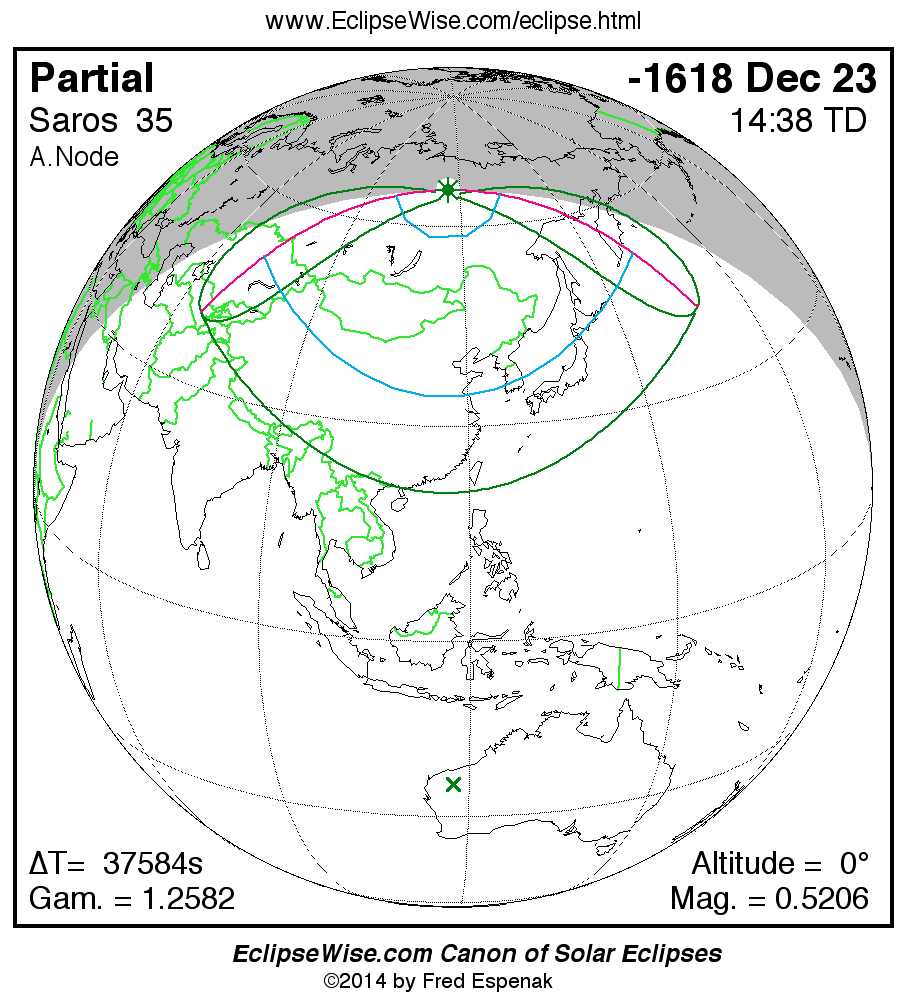
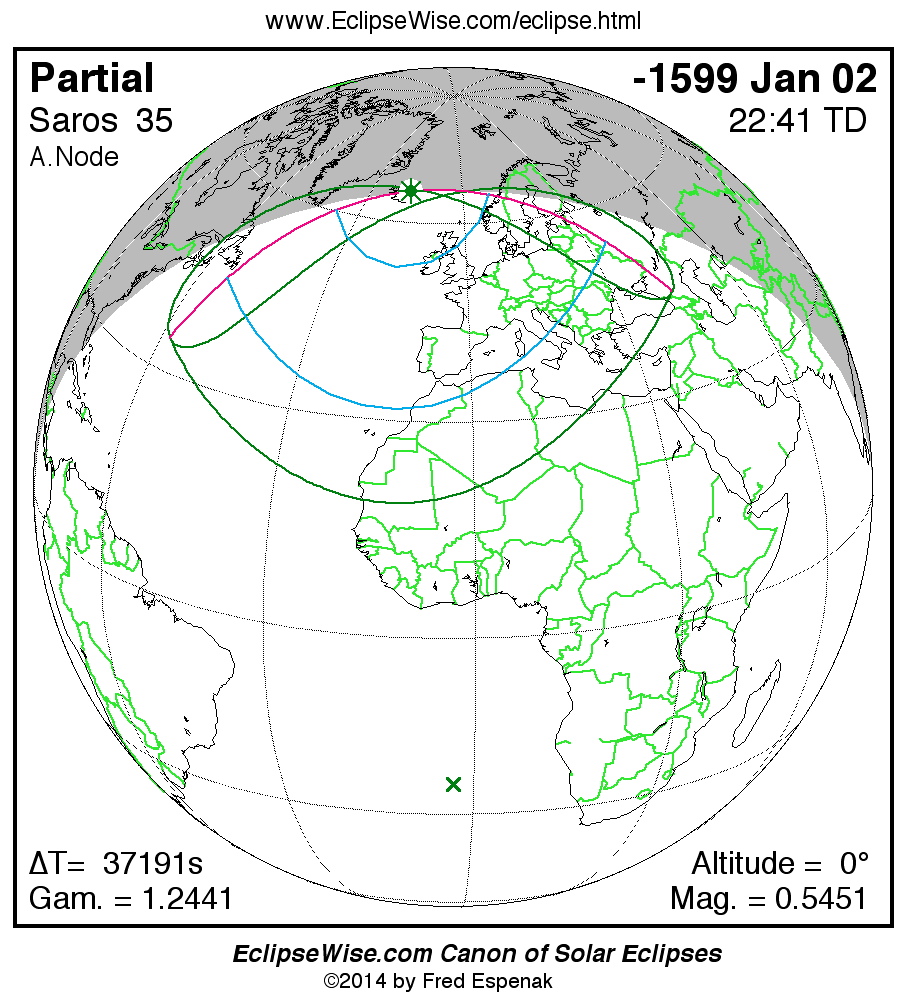
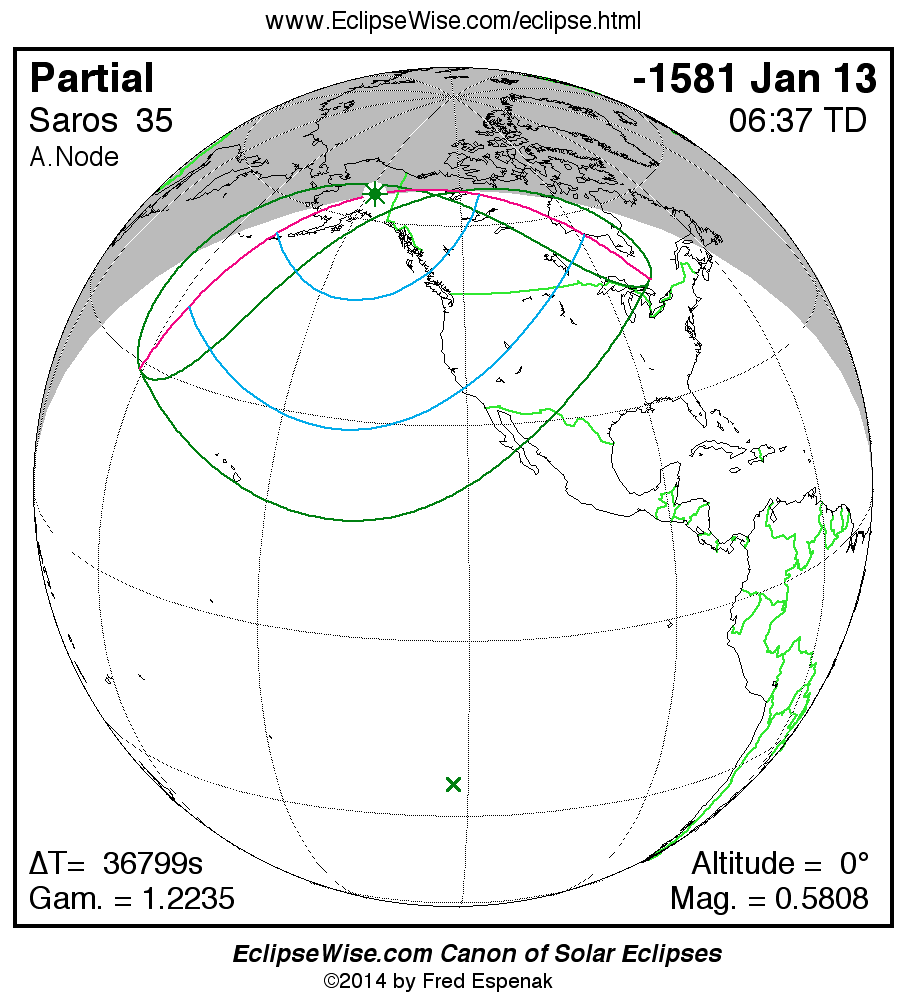
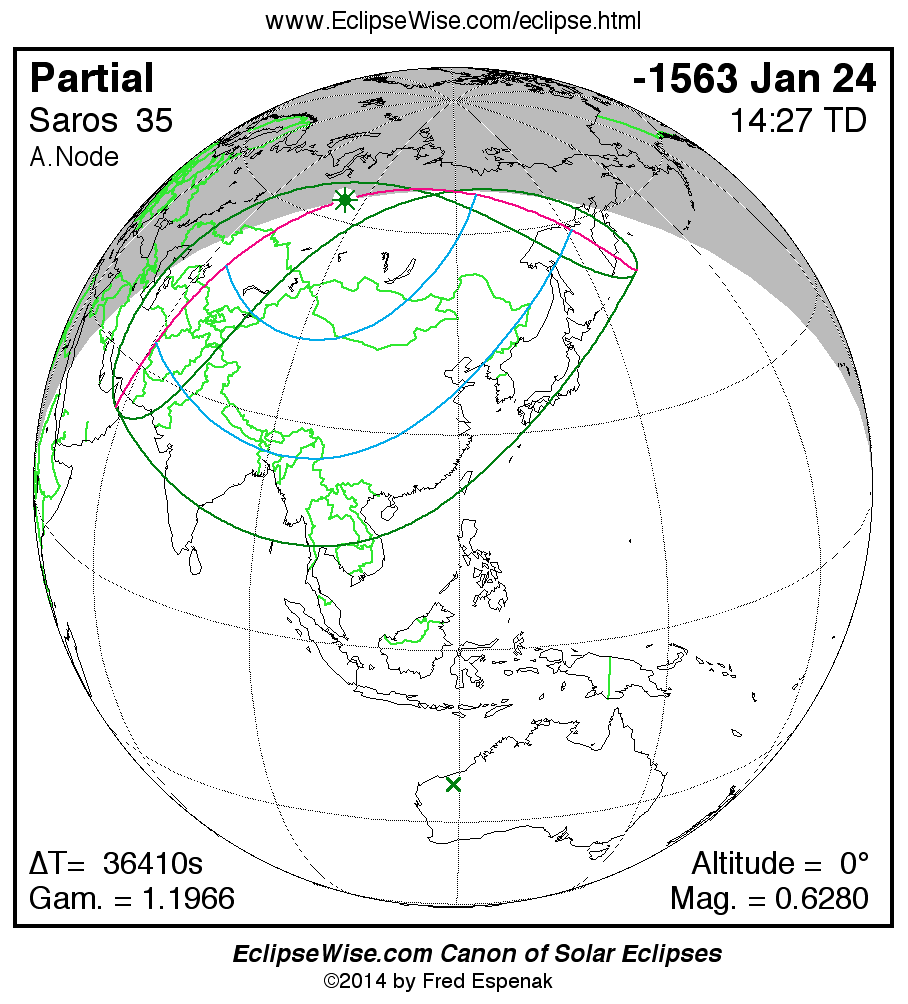
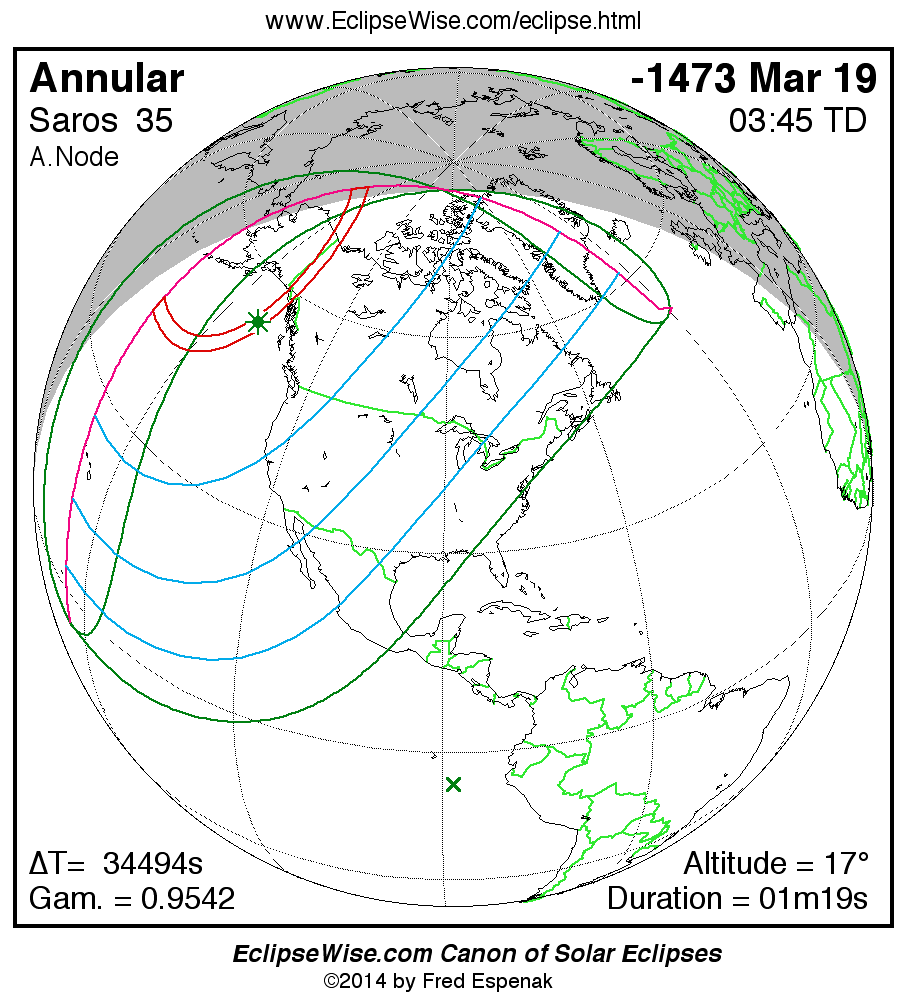
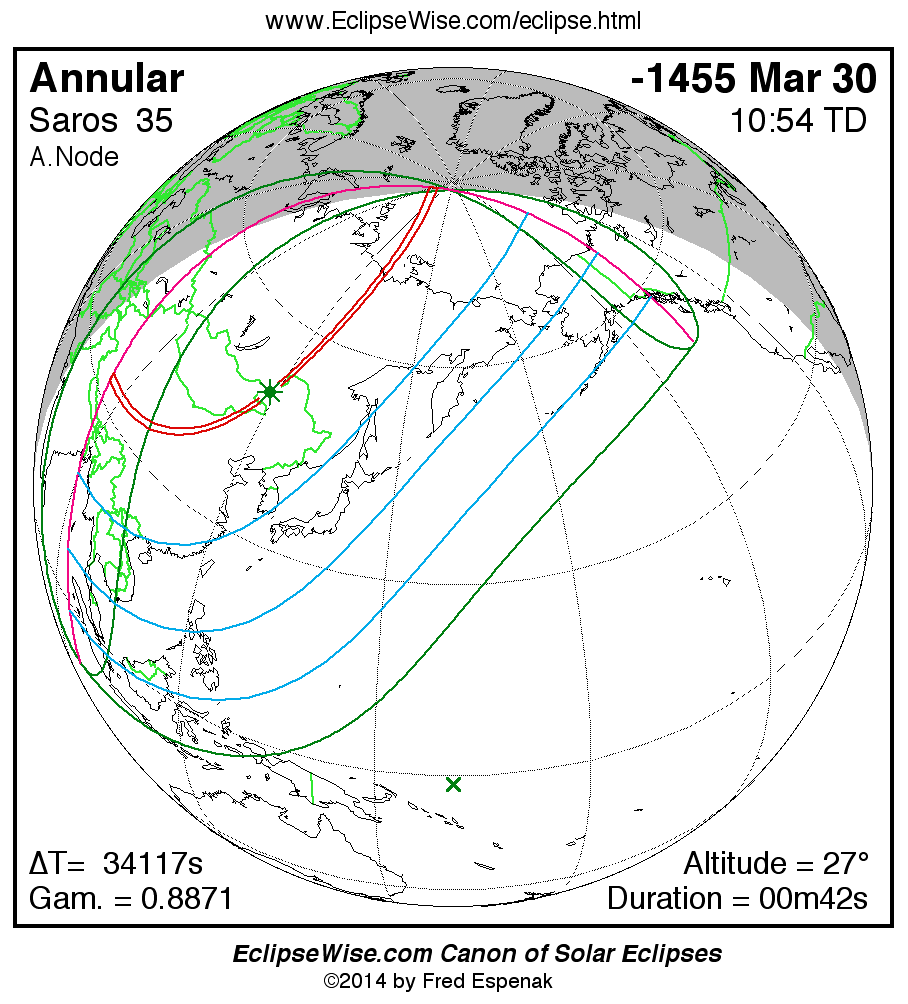
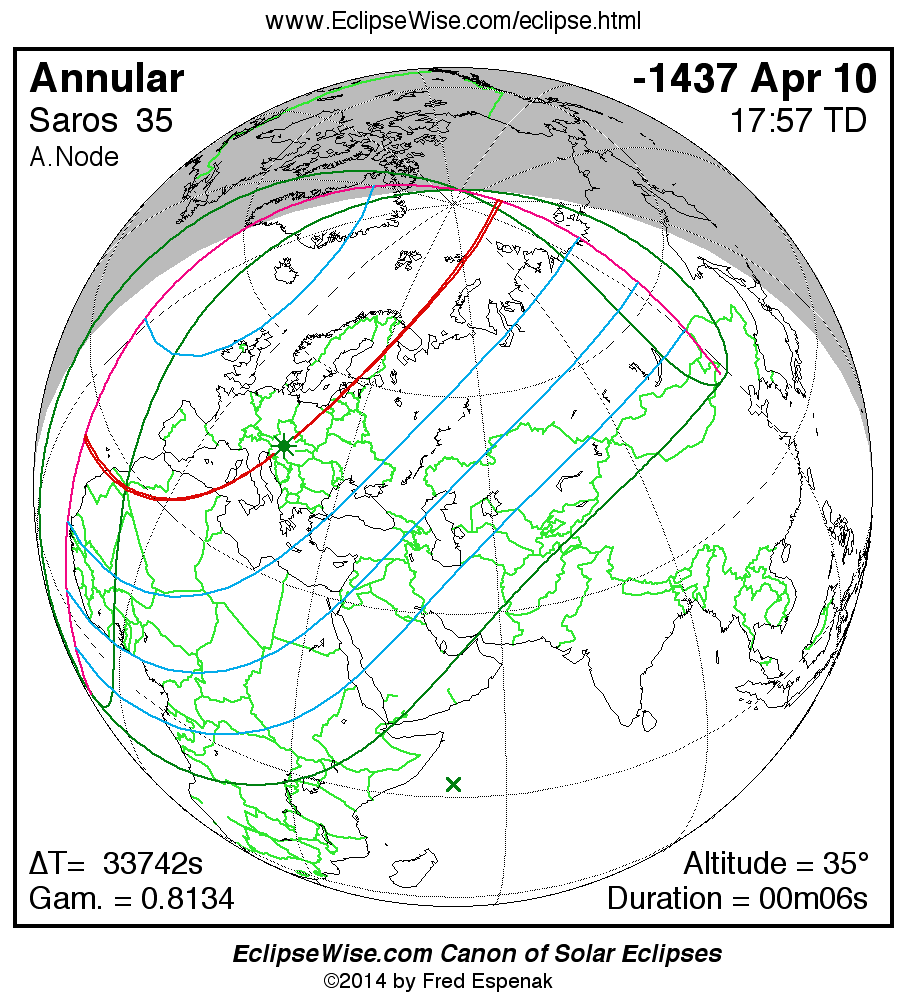
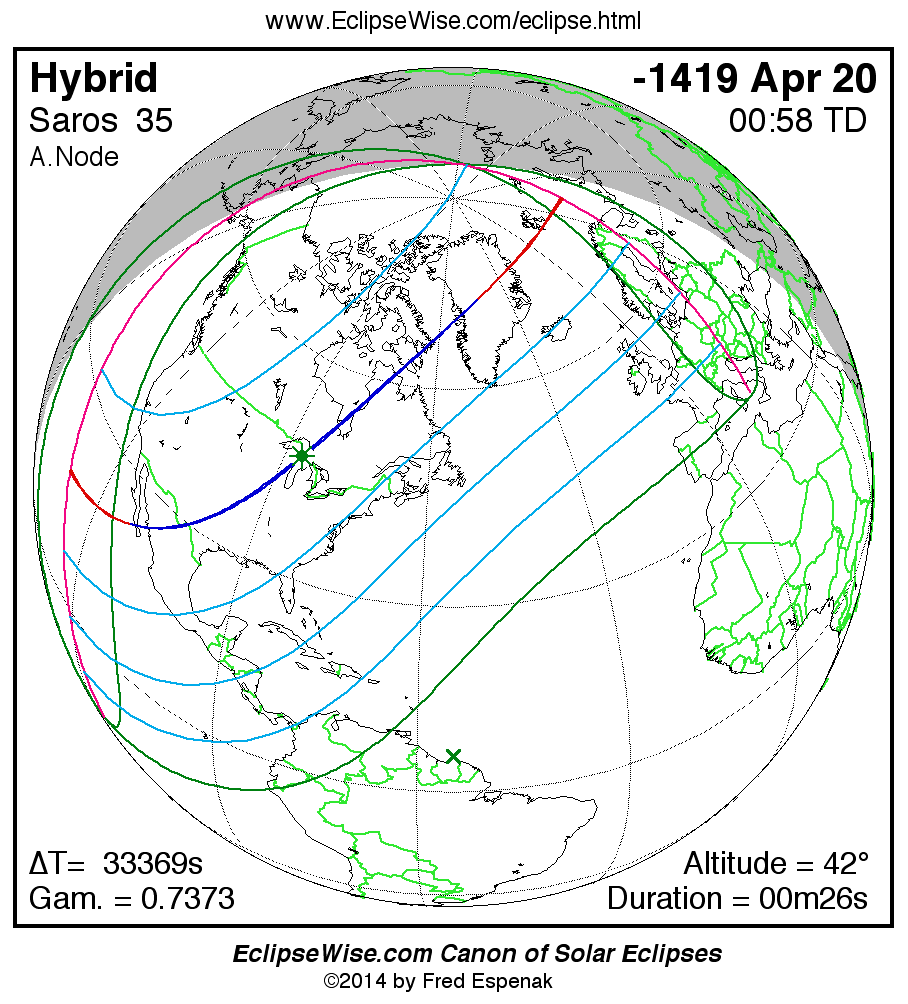
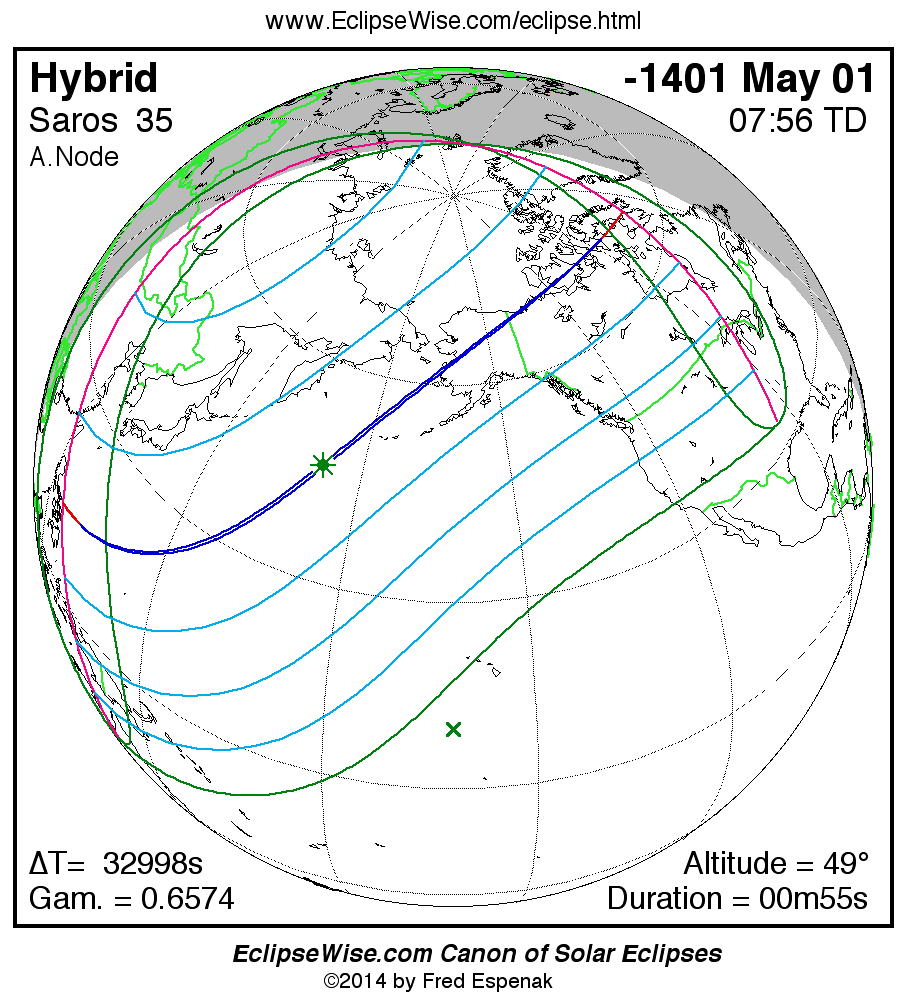
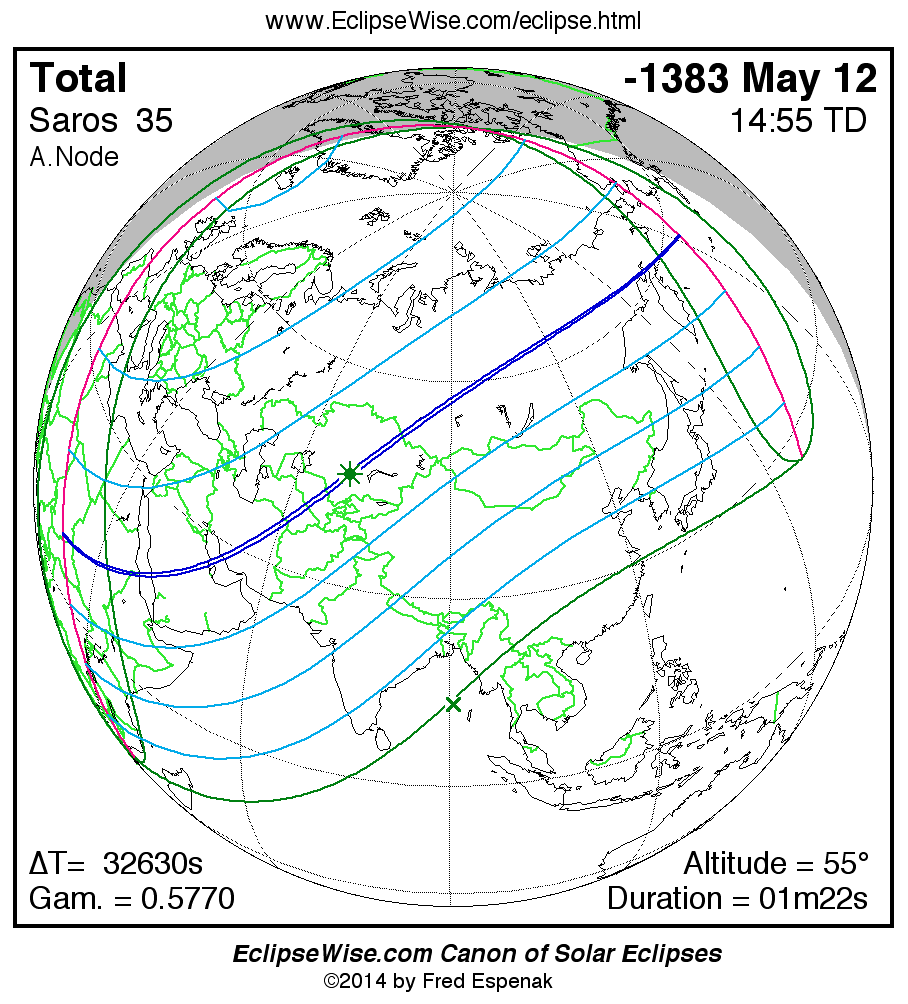
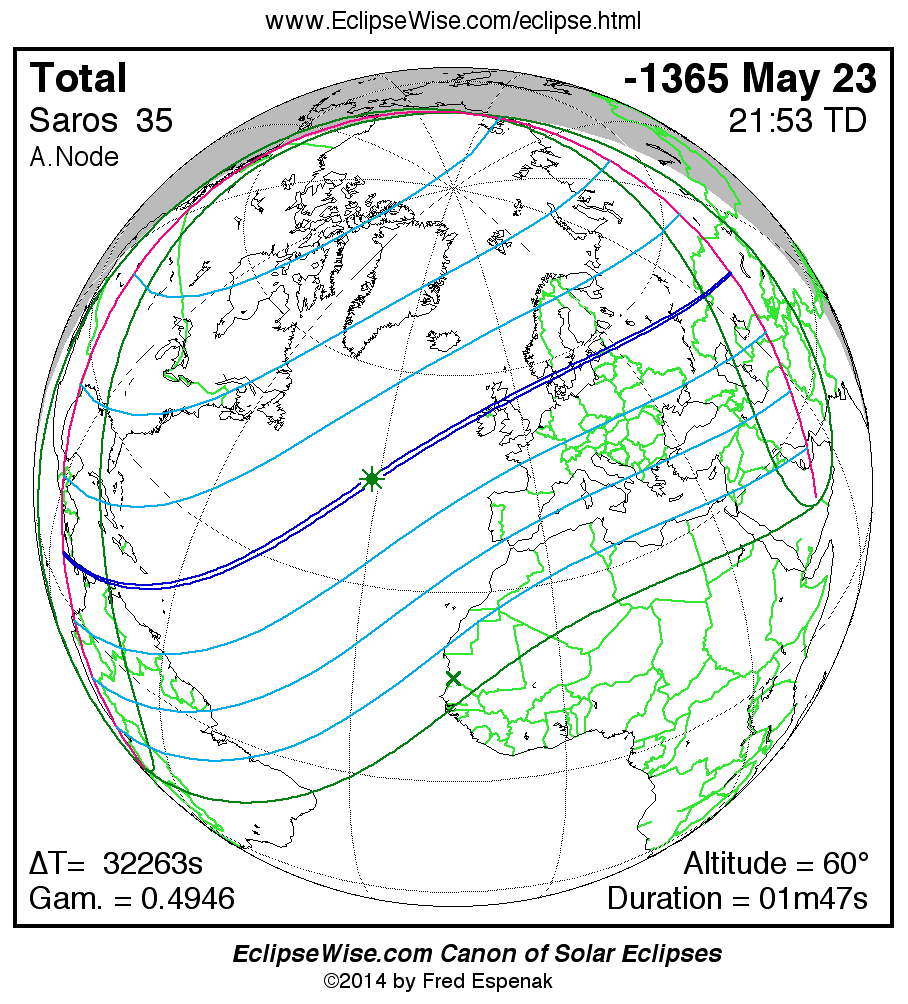
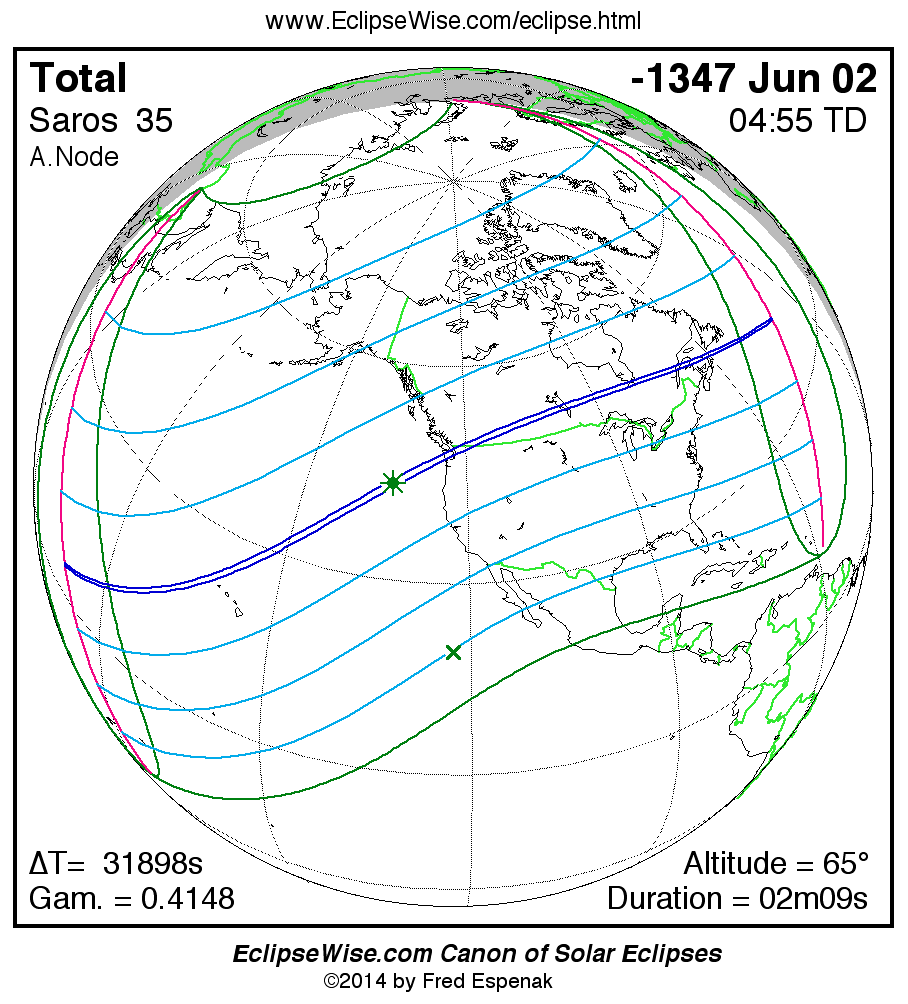
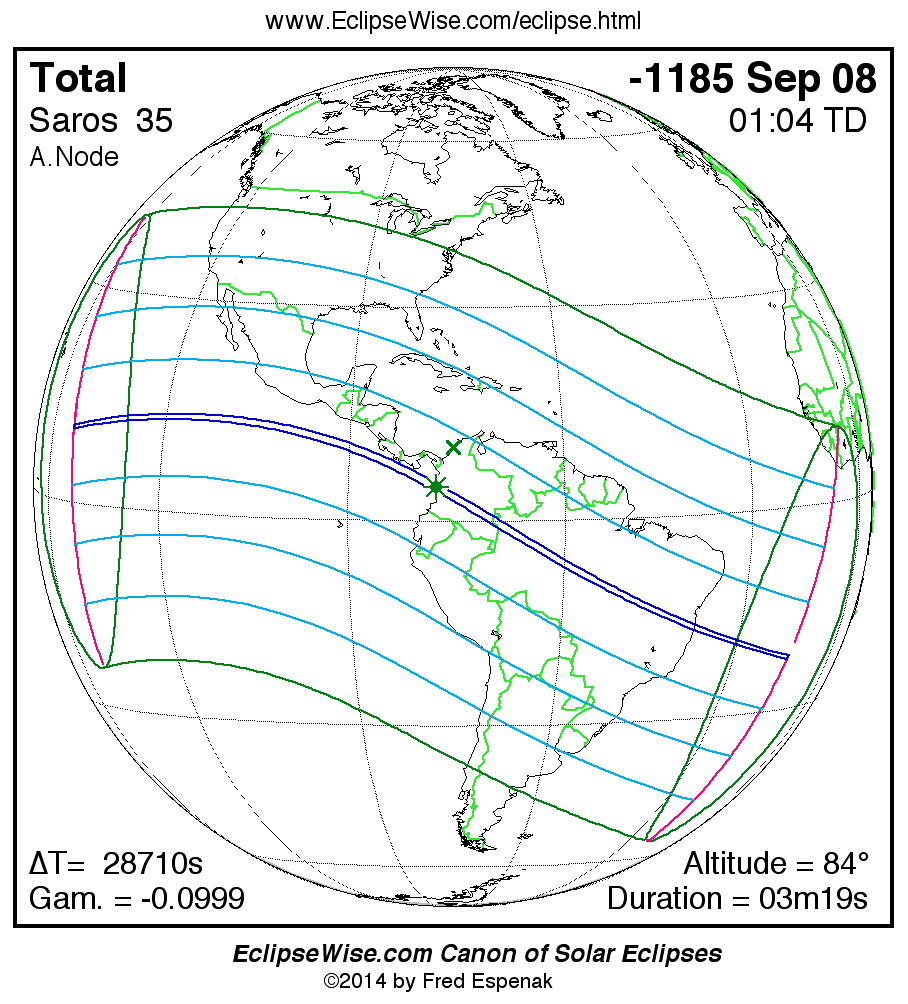
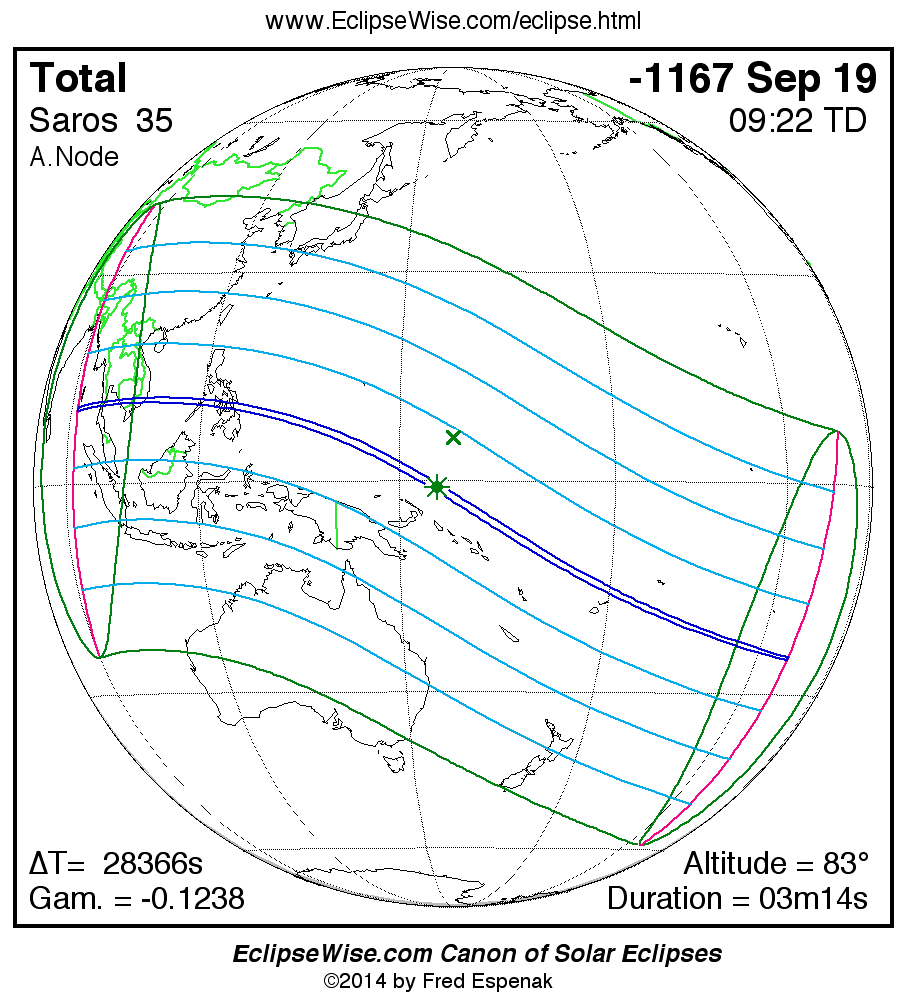
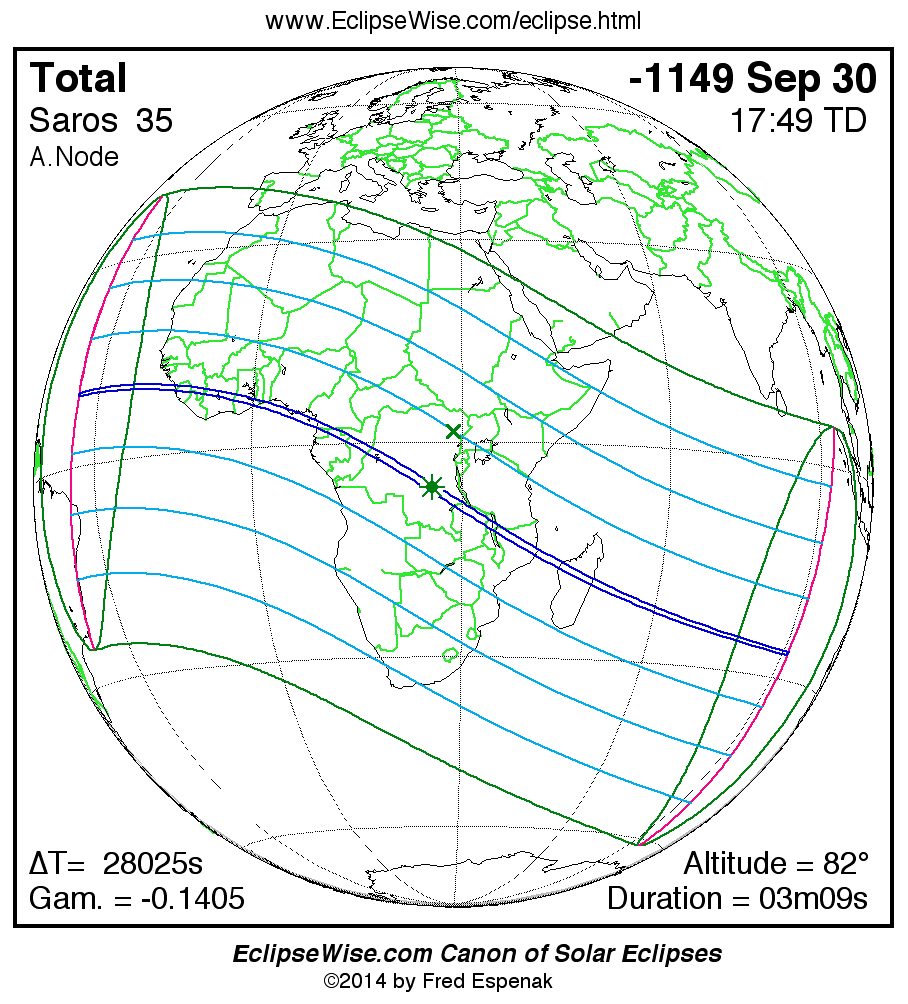
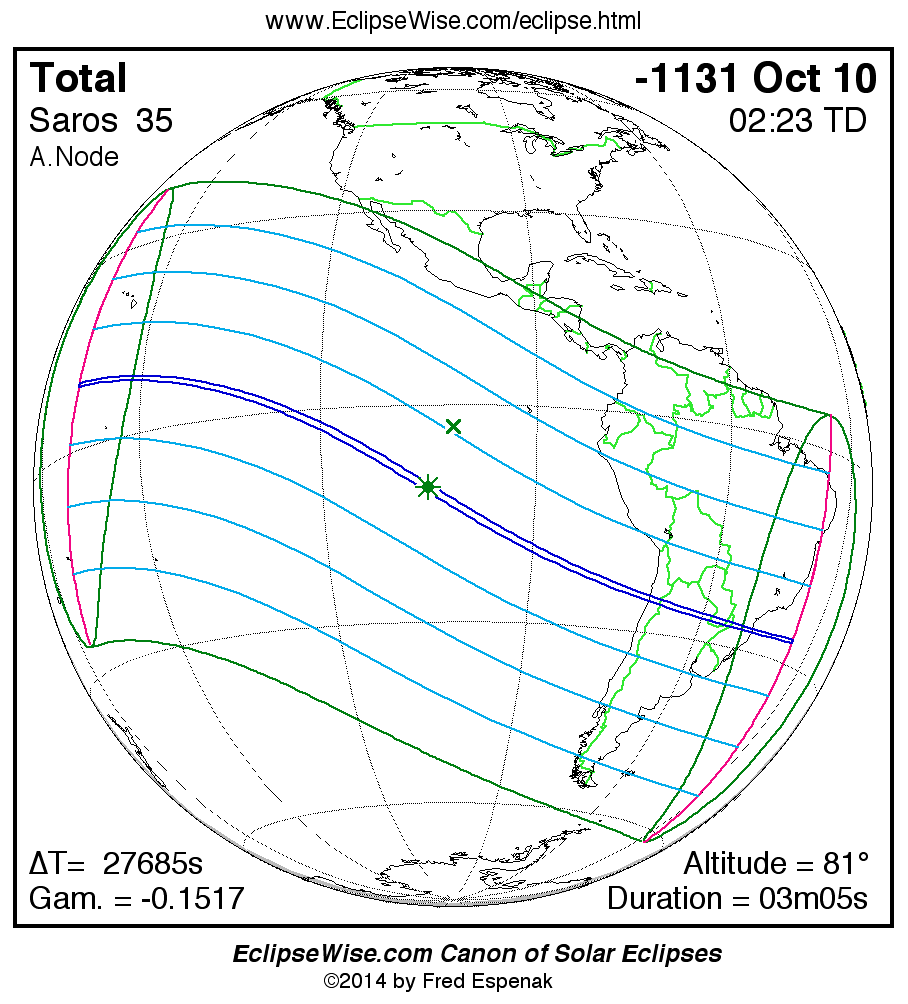
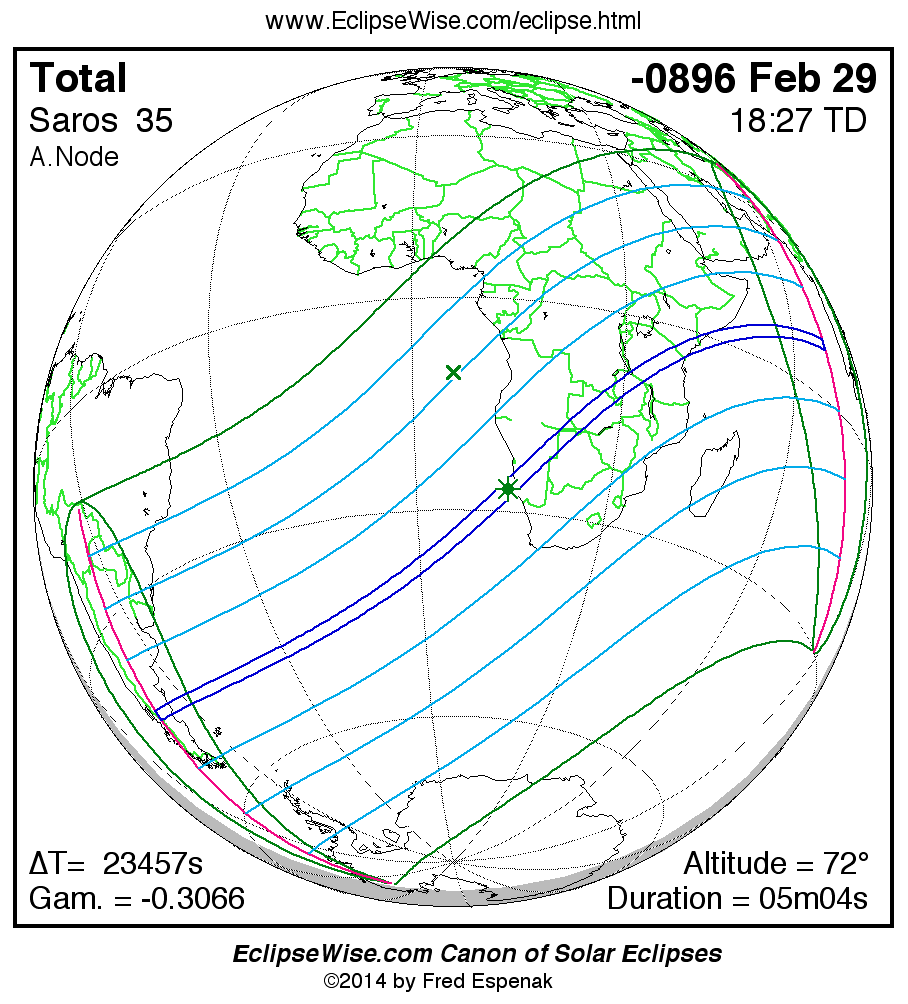
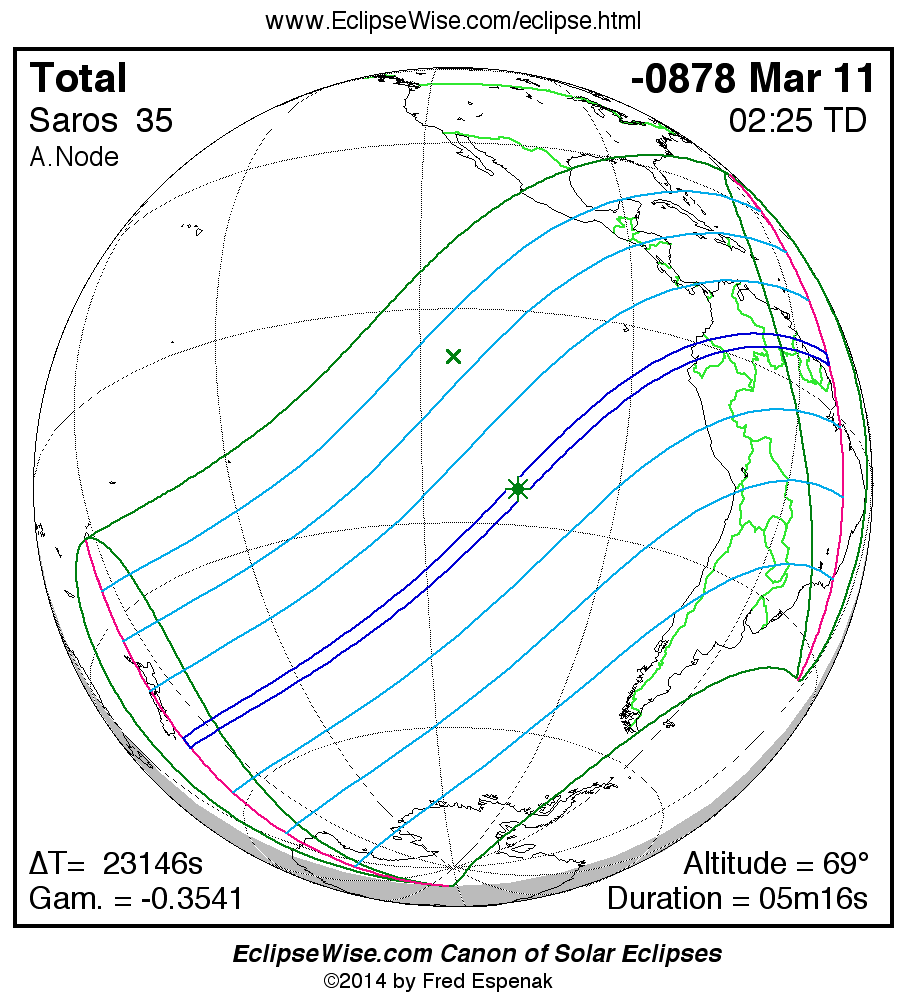
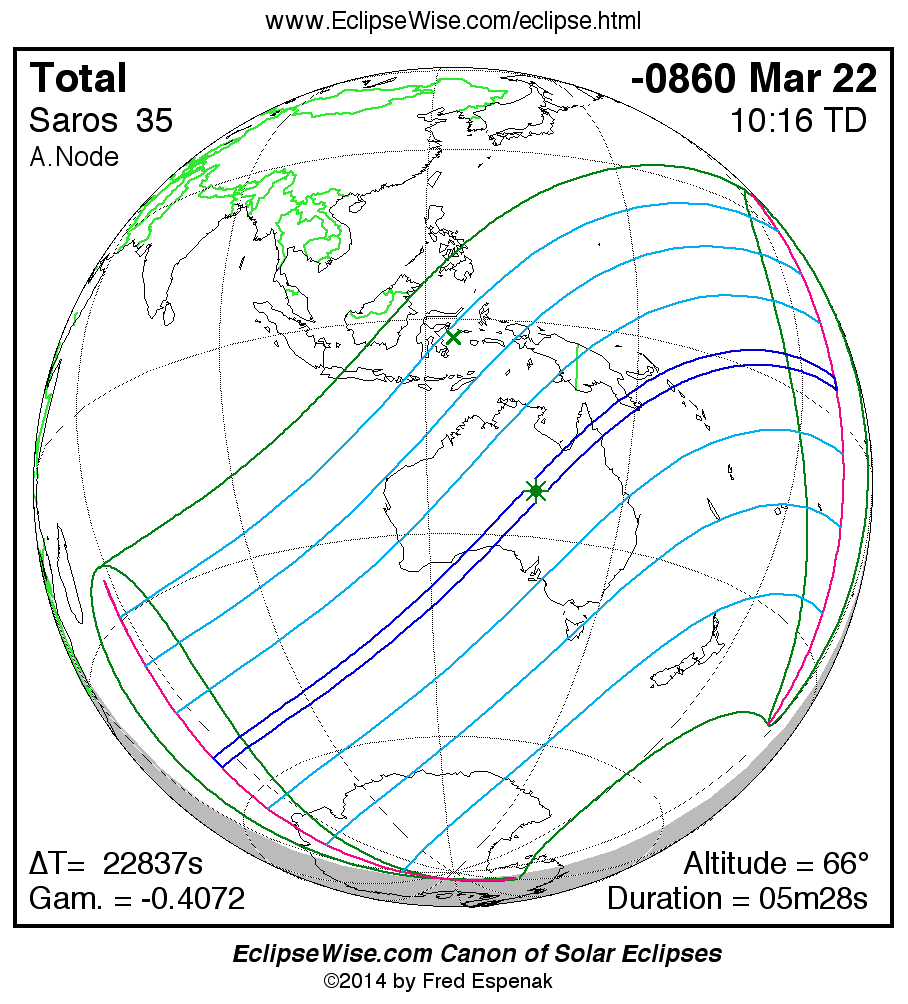
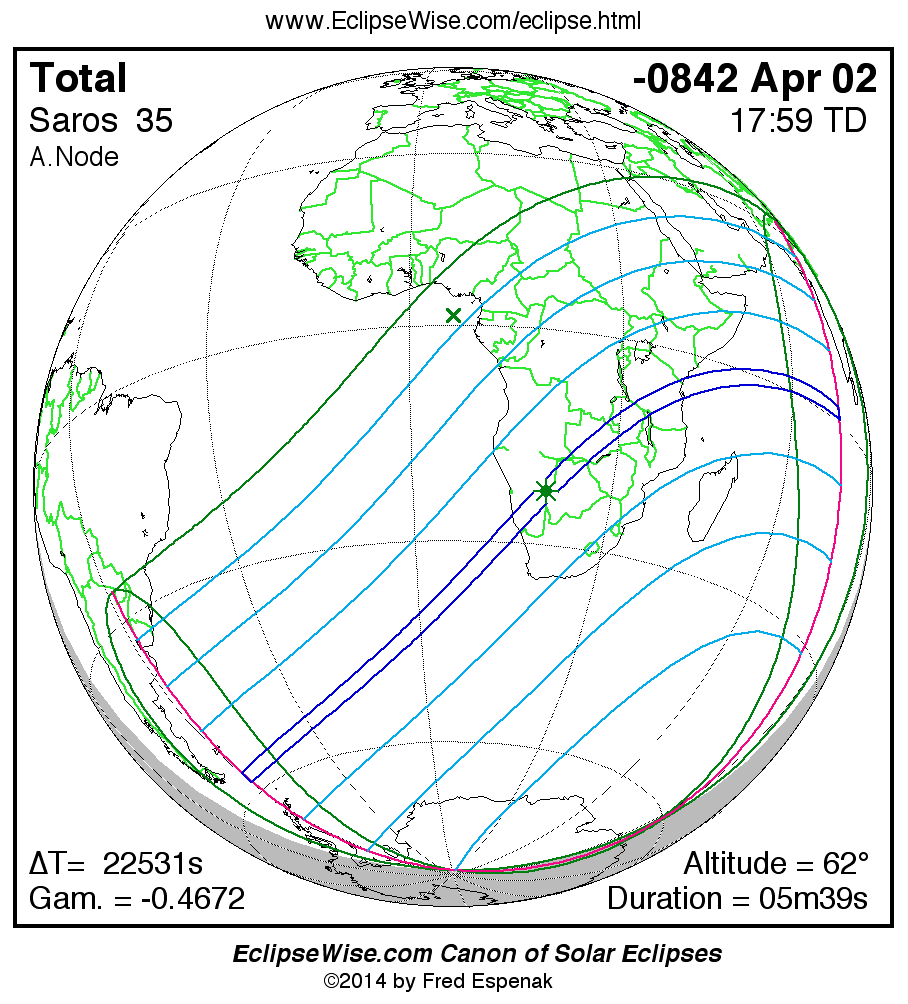
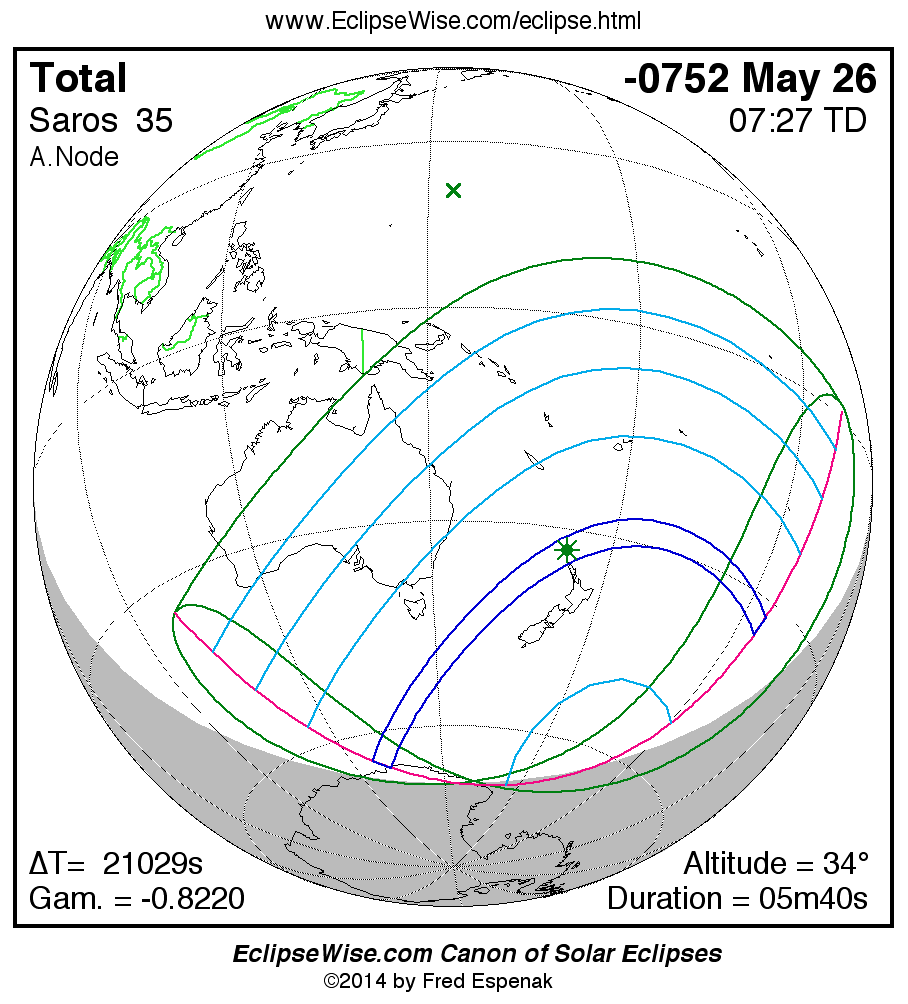
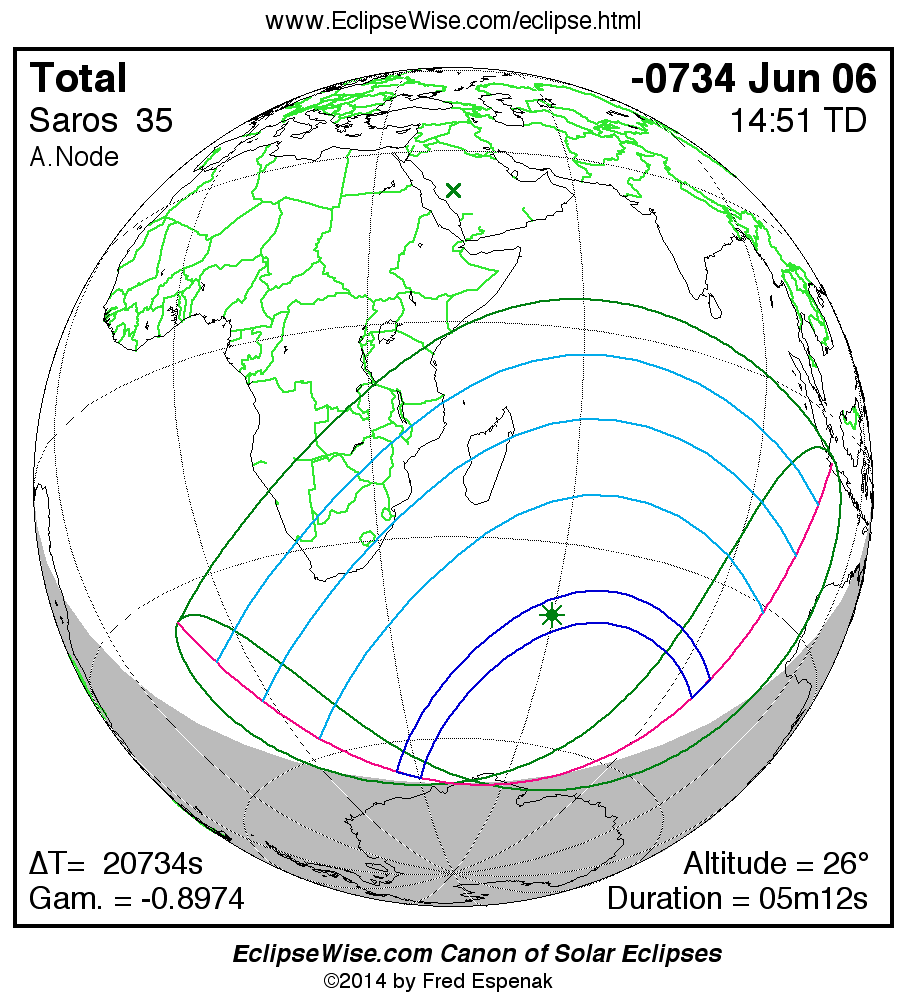
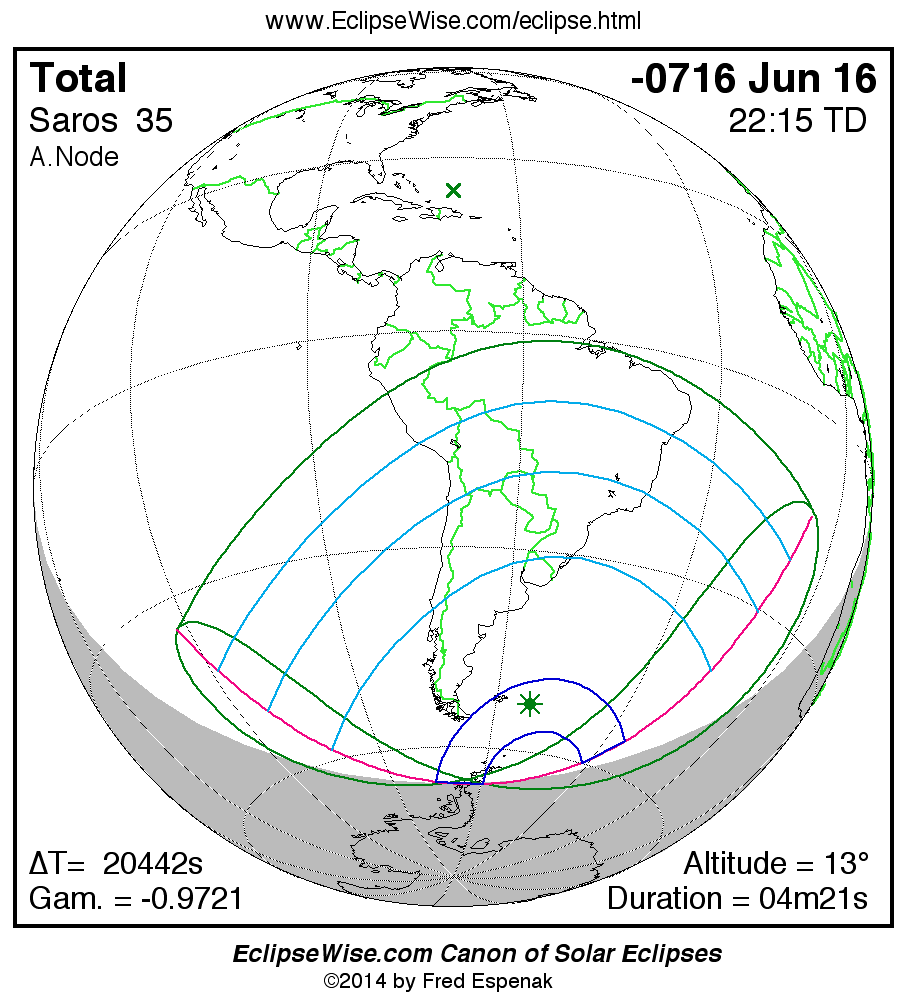
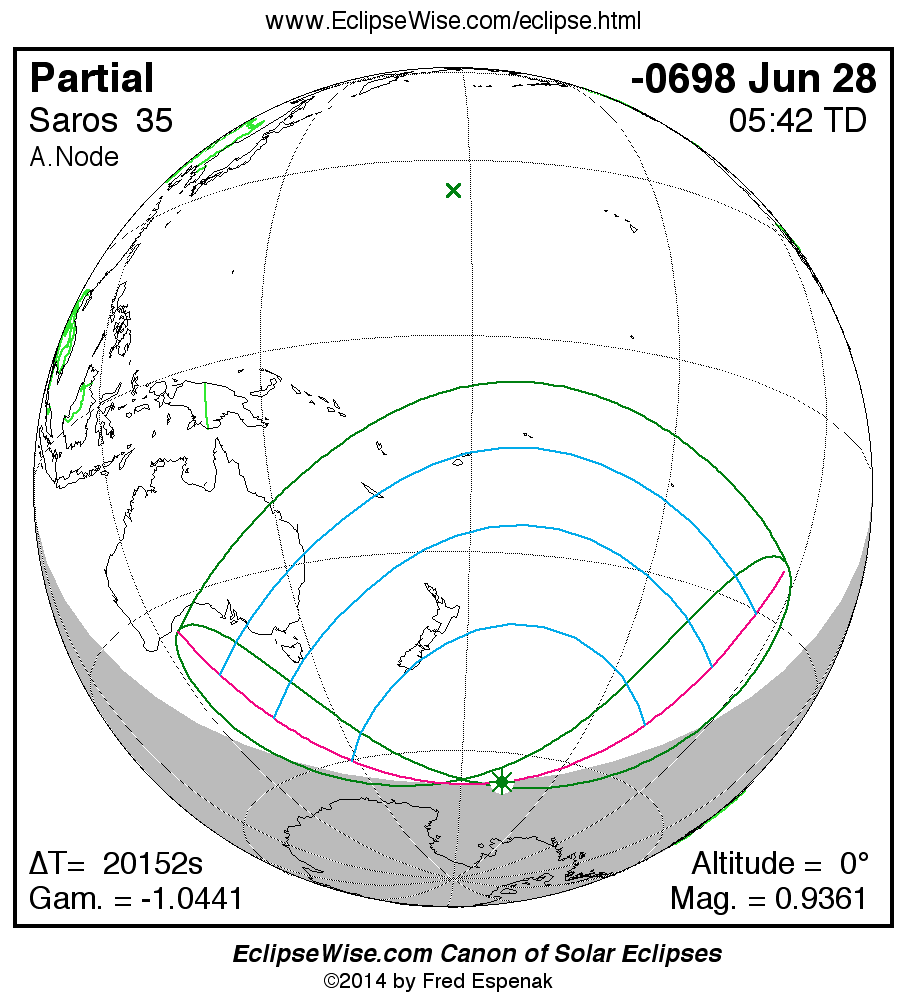
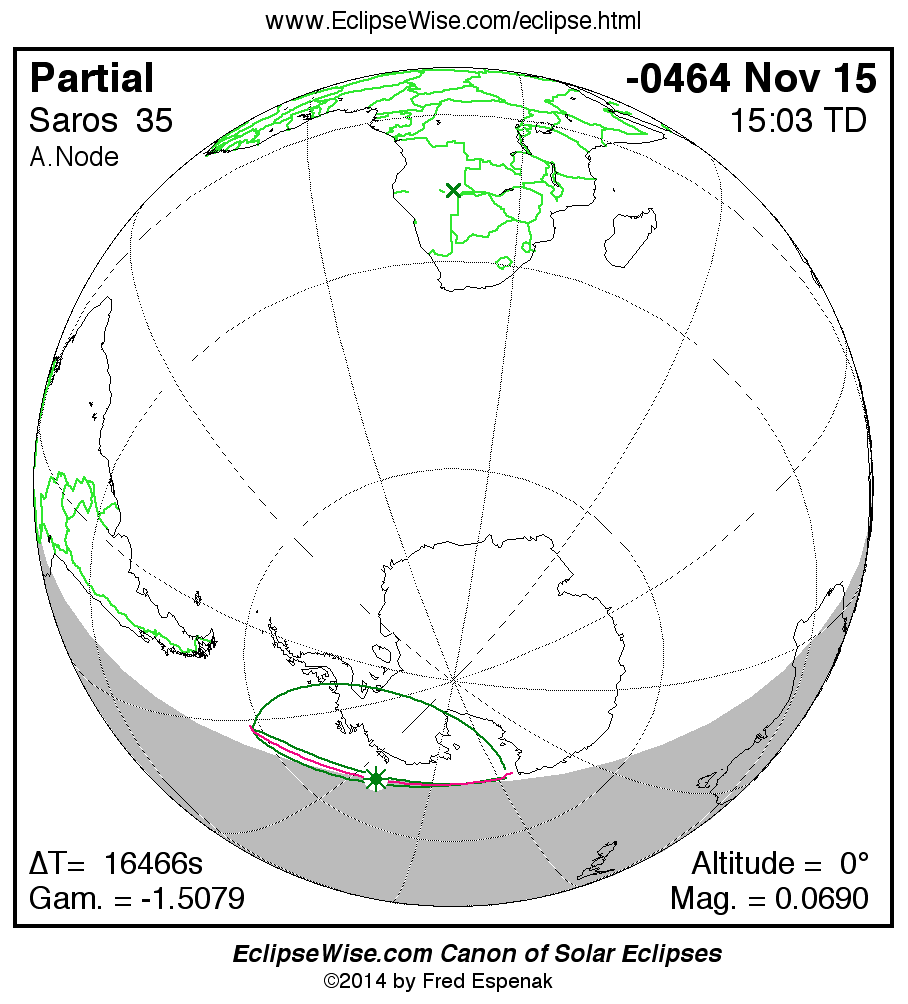
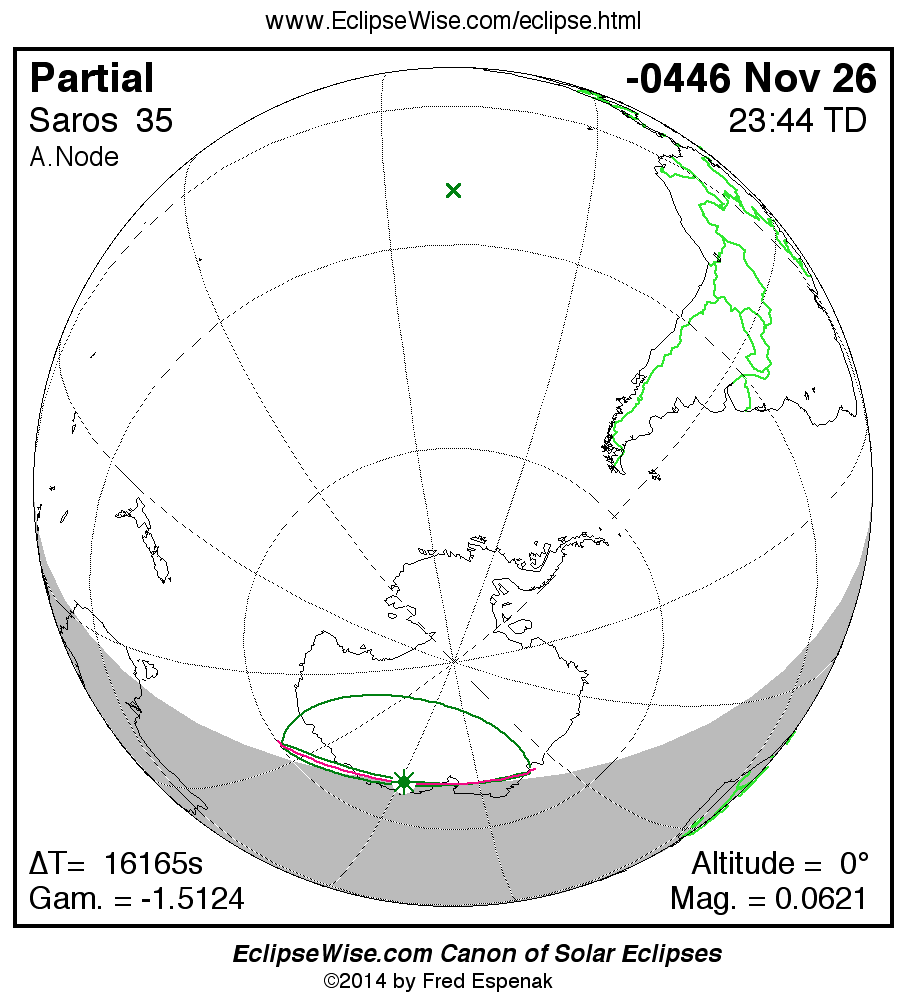
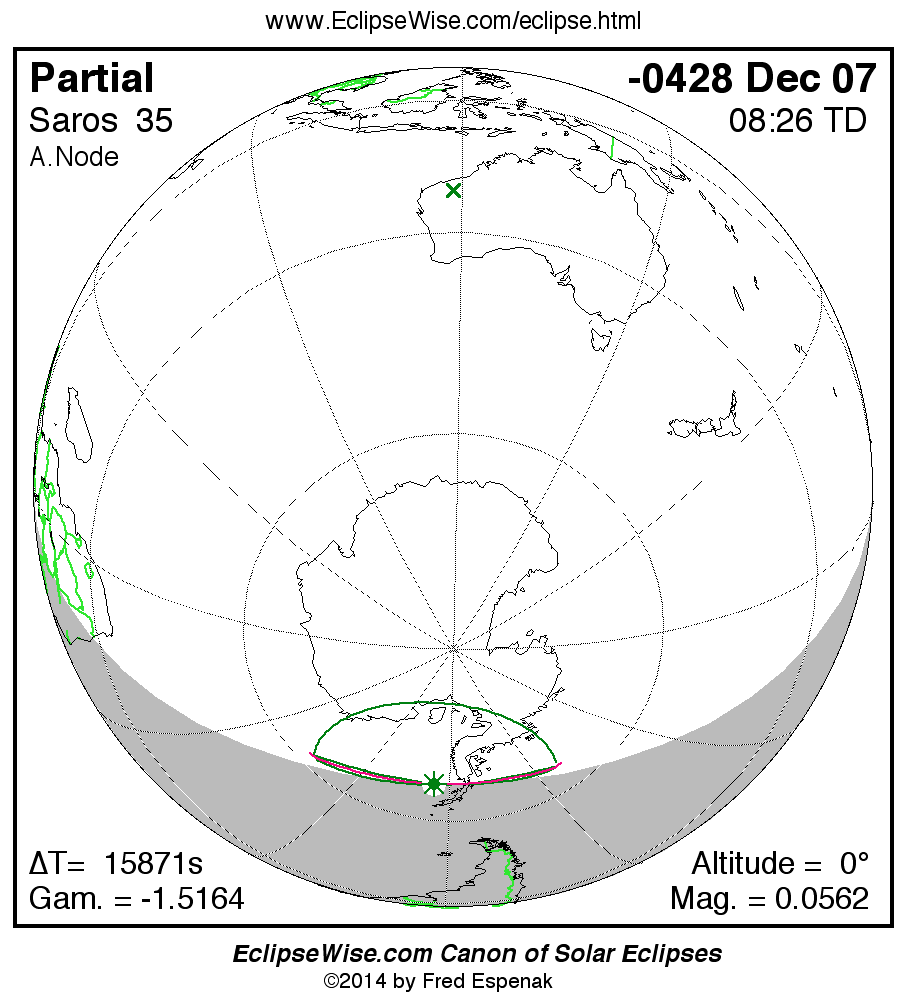
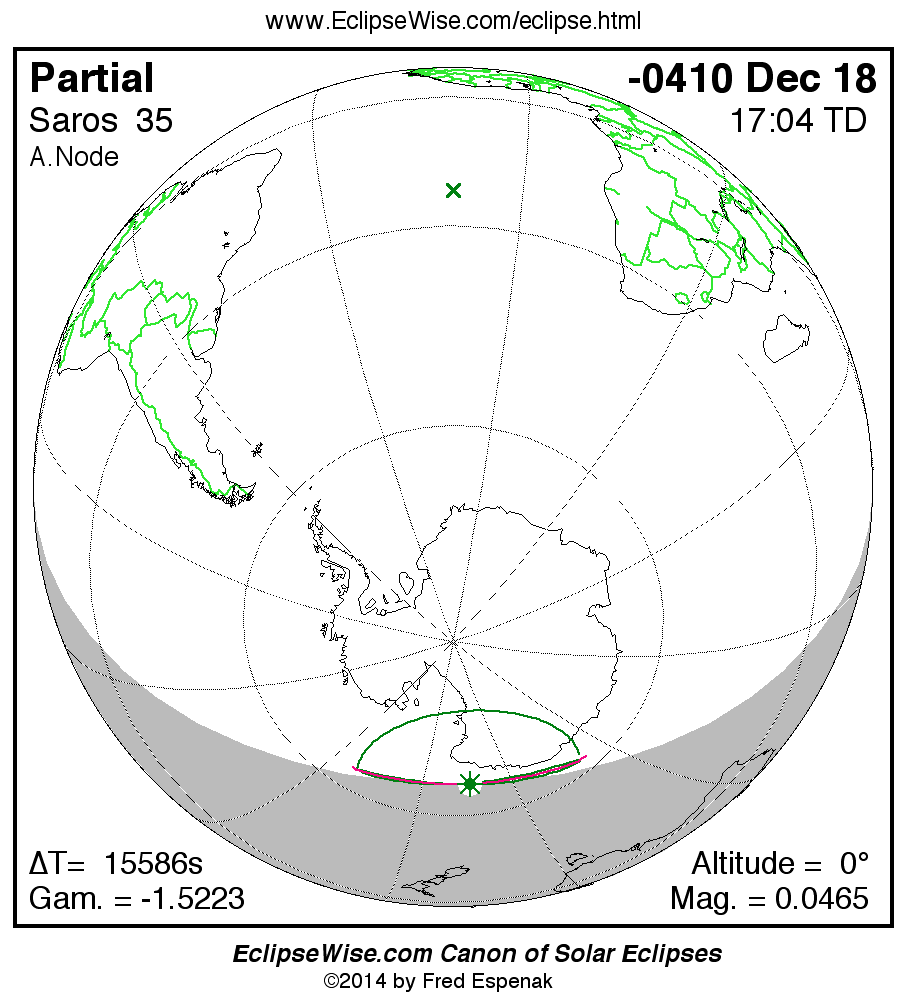
Saros 35
Panorama of Solar Eclipses of Saros 35
Fred Espenak
Introduction
A solar eclipse occurs whenever the Moon's shadow passes across Earth's surface. At least two solar eclipses and as many as five occur every year.
The periodicity and recurrence of solar eclipses is governed by the Saros cycle, a period of approximately 6,585.3 days (18 years 11 days 8 hours). When two eclipses are separated by a period of one Saros, they share a very similar geometry. The two eclipses occur at the same node with the Moon at nearly the same distance from Earth and the same time of year due to a harmonic in three cycles of the Moon's orbit. Thus, the Saros is useful for organizing eclipses into families or series. Each series typically lasts 12 to 13 centuries and contains 70 or more eclipses. Every saros series begins with a number of partial eclipses near one of Earth's polar regions. The series will then produce several dozen central eclipses before ending with a group of partial eclipses near the opposite pole. For more information, see Periodicity of Solar Eclipses.
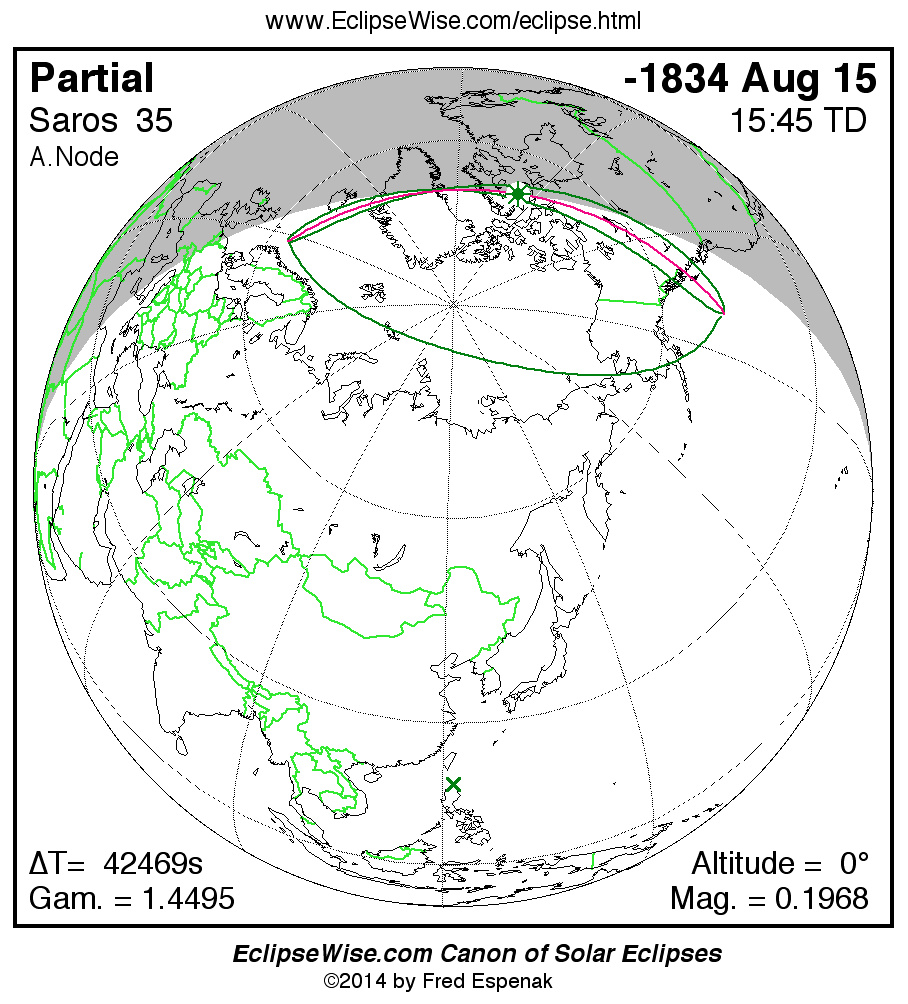
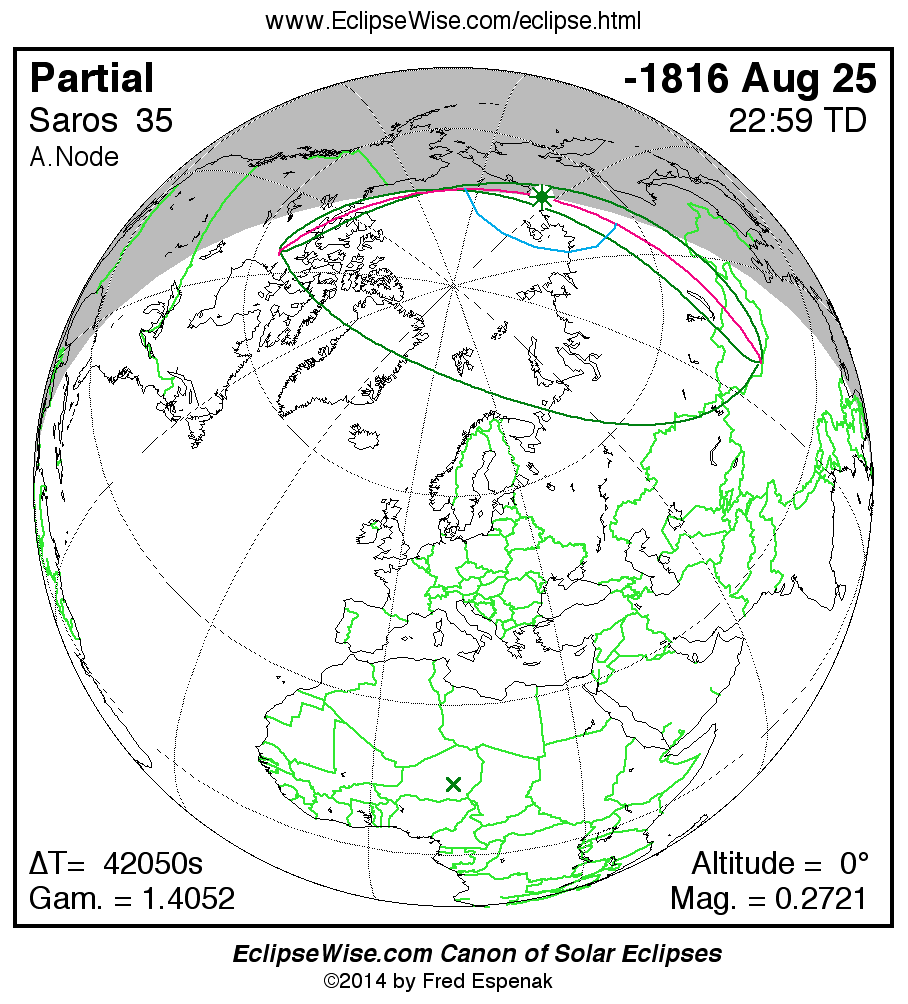
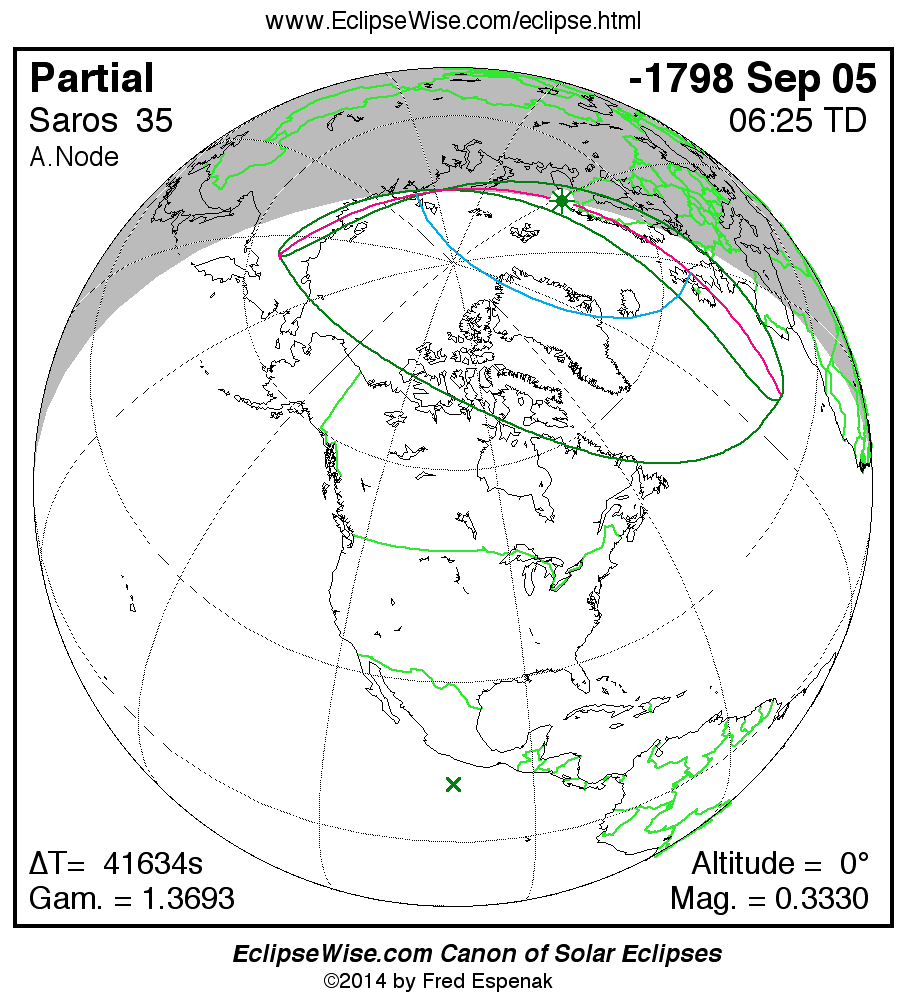
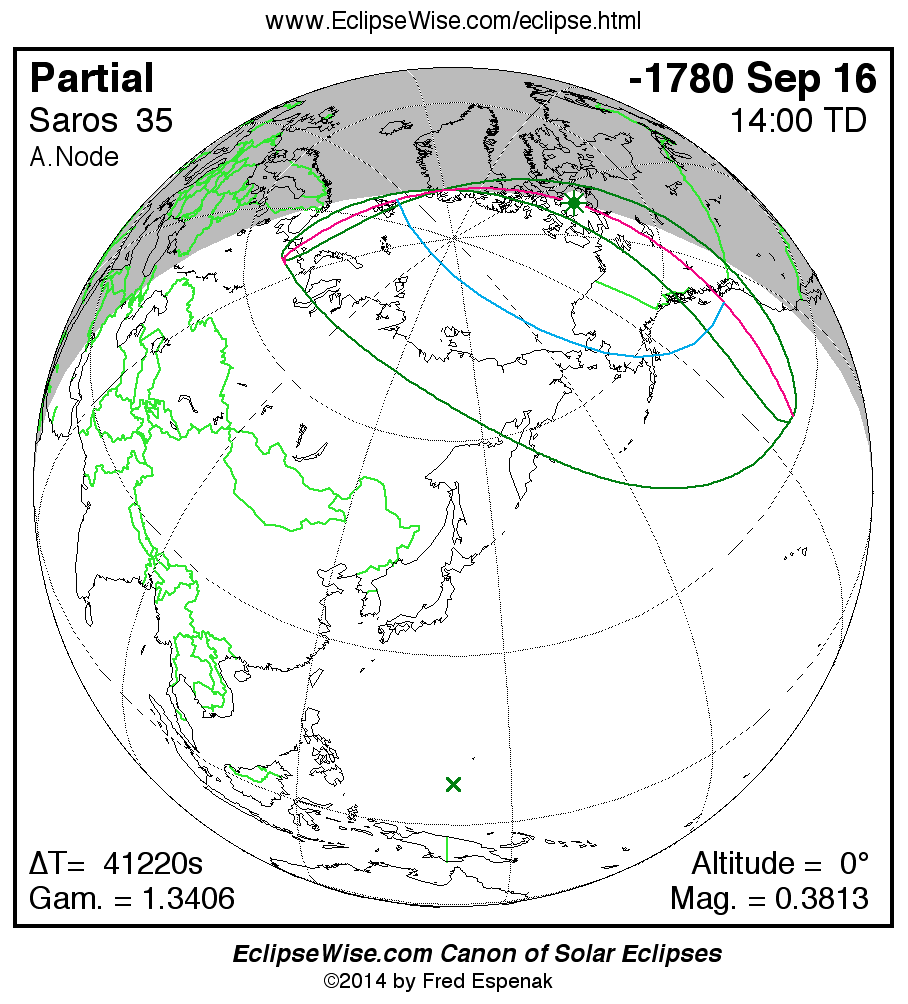
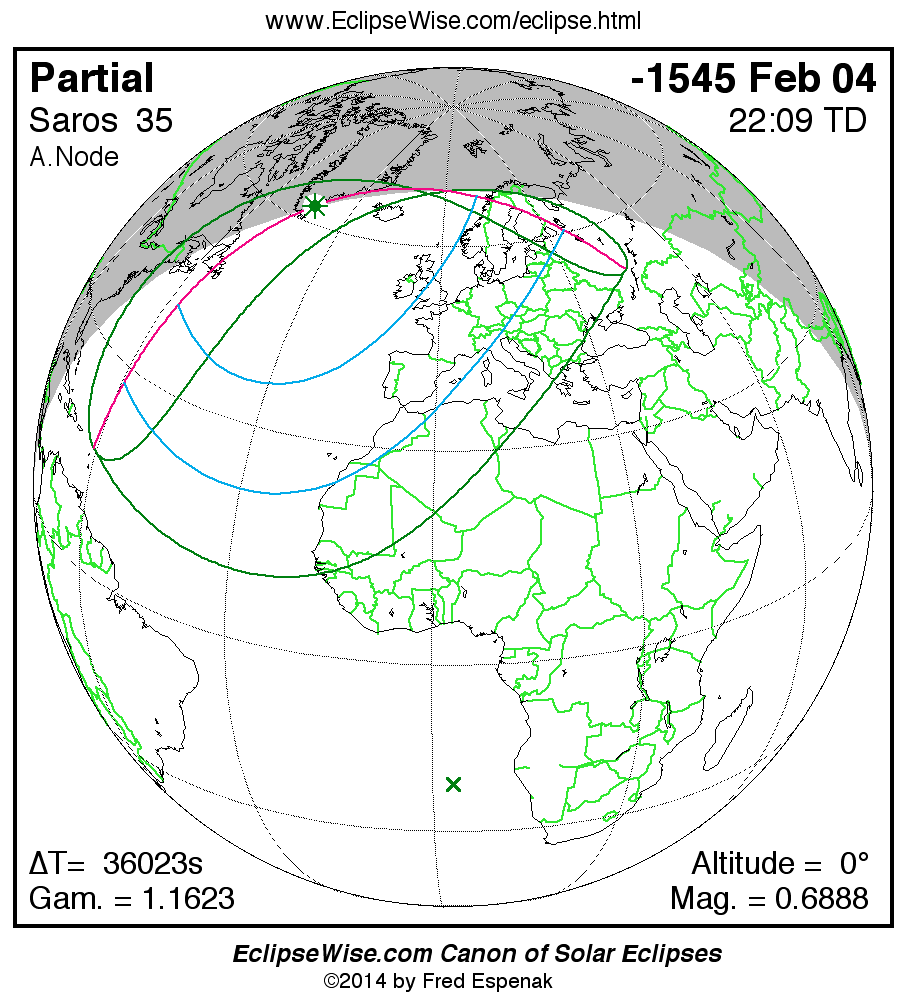
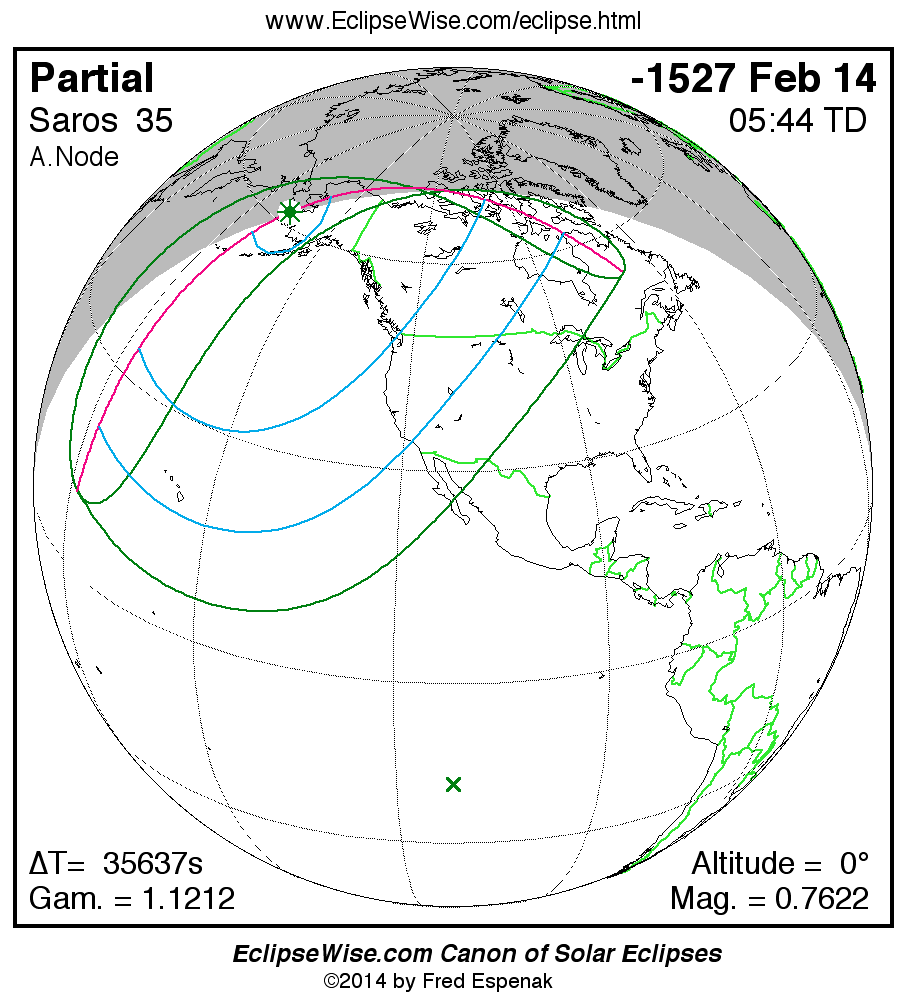
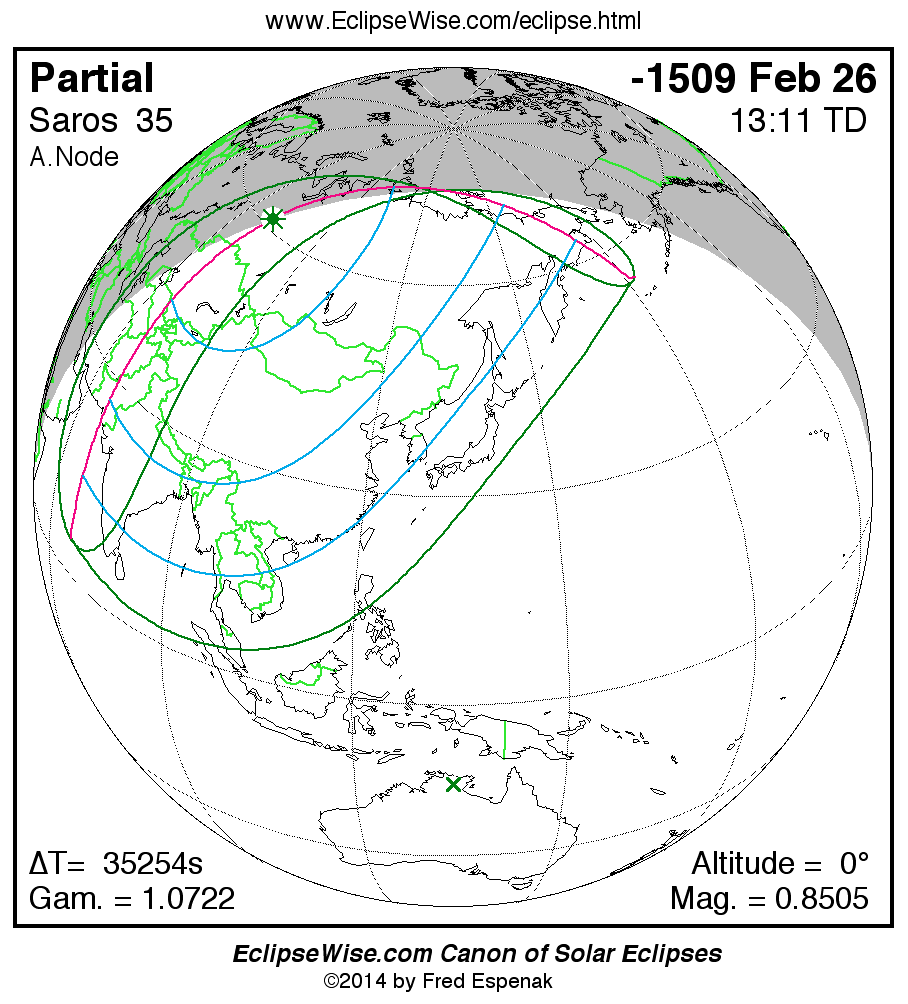
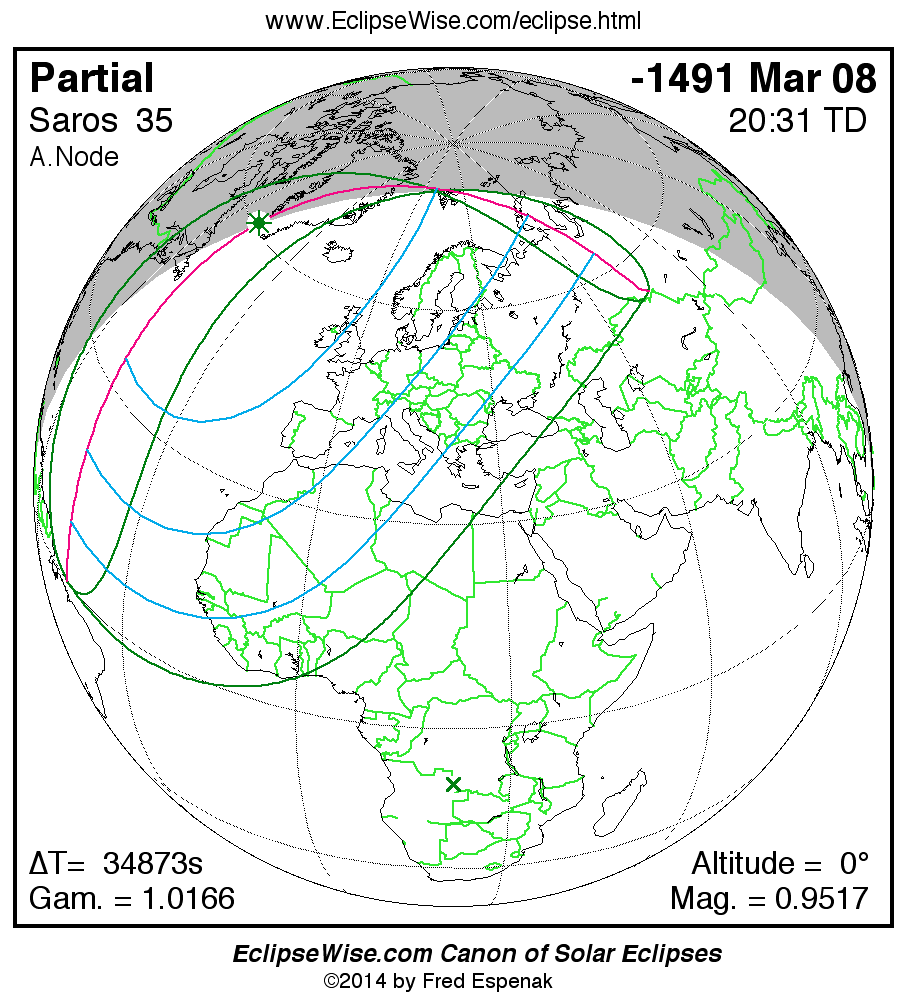
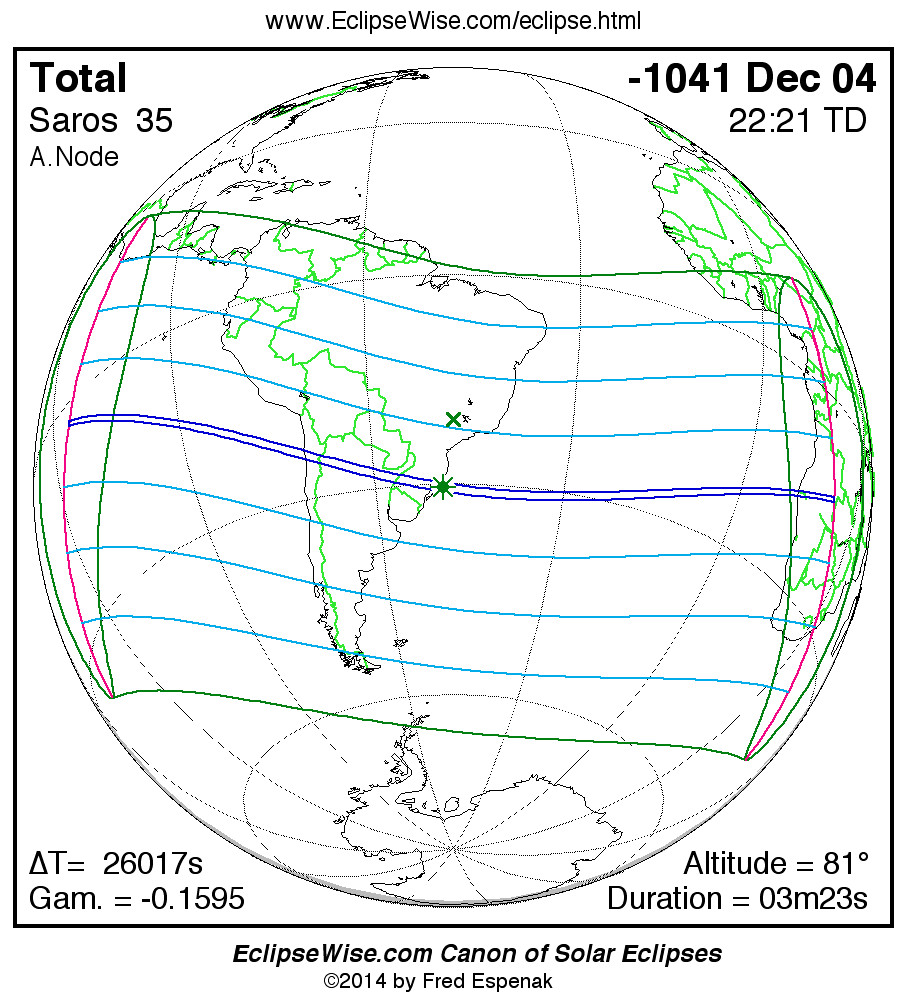
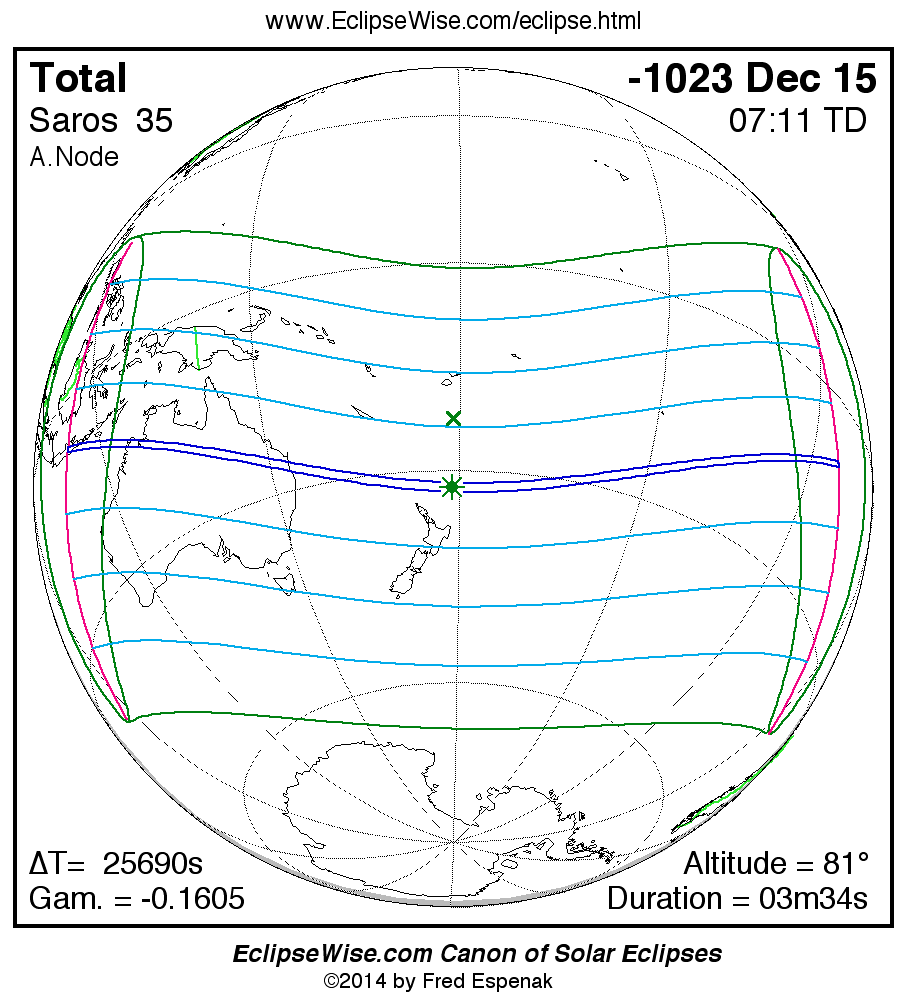
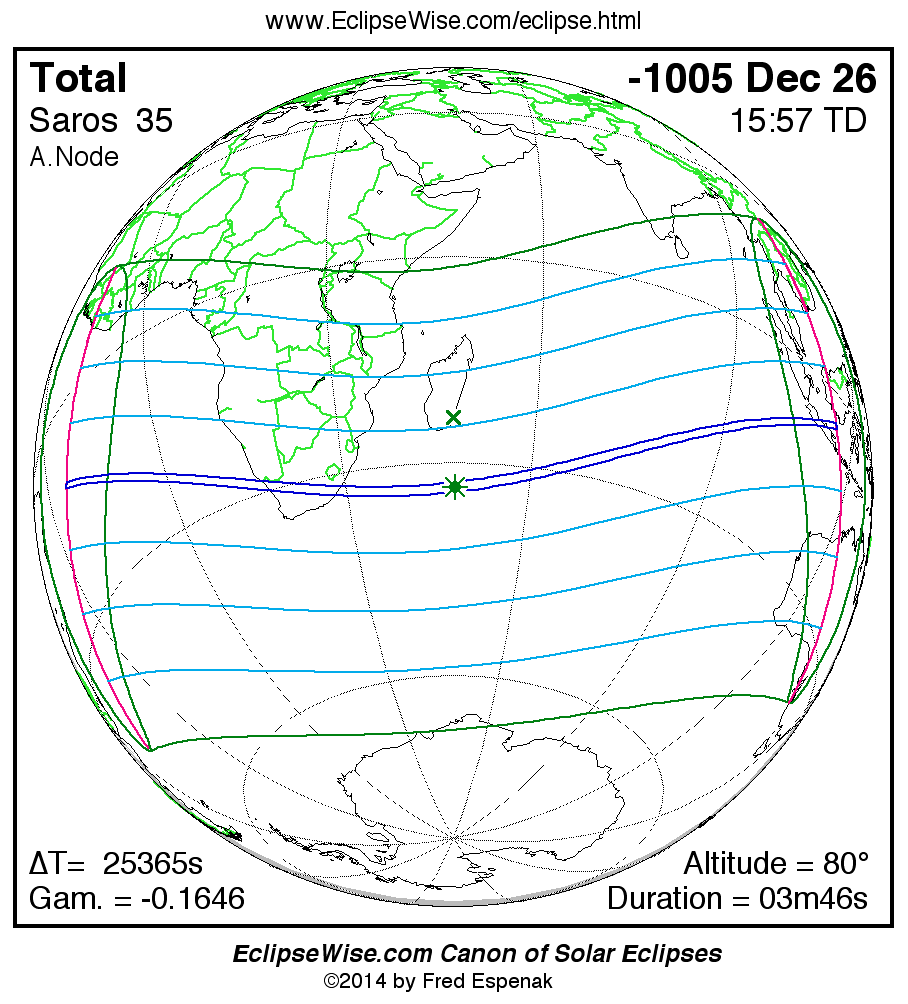
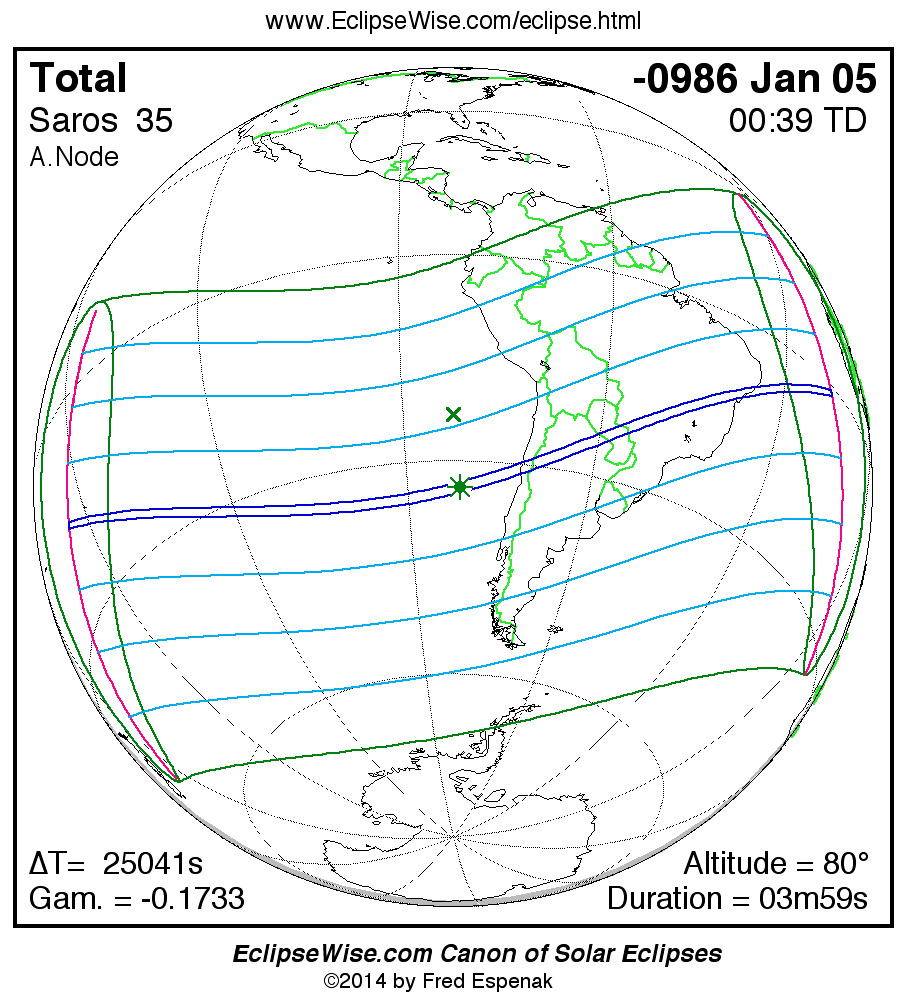
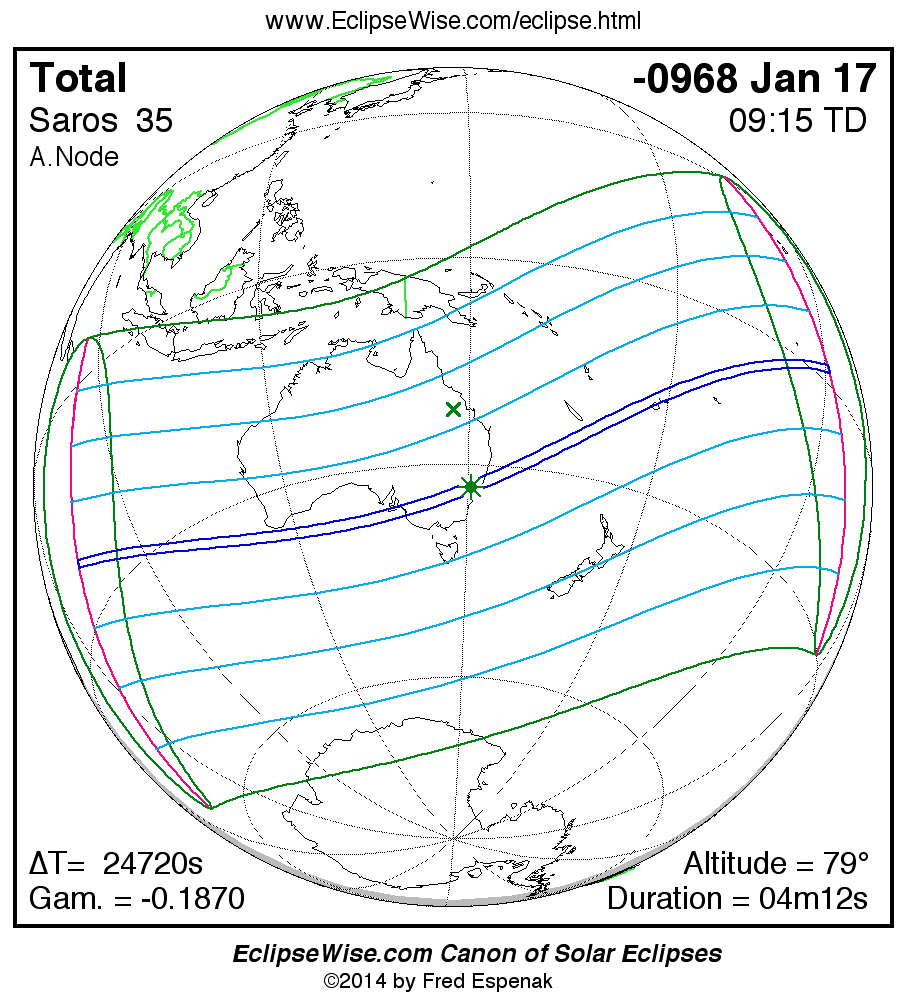
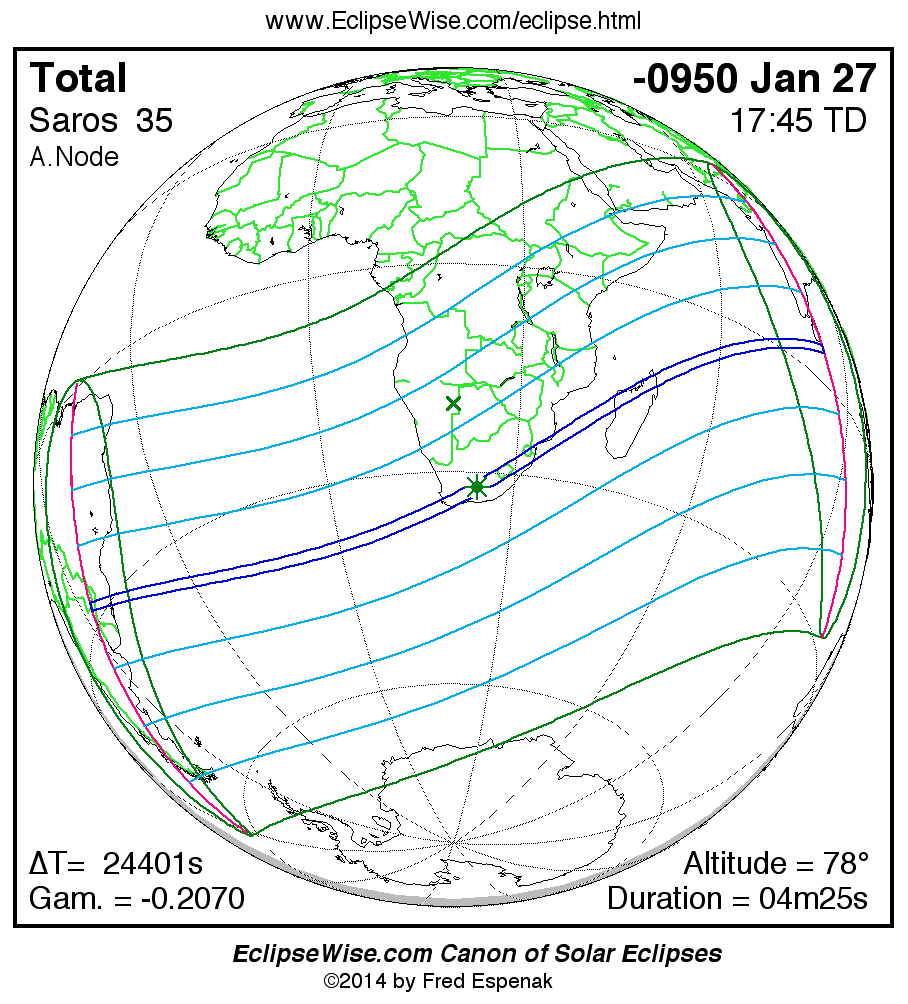
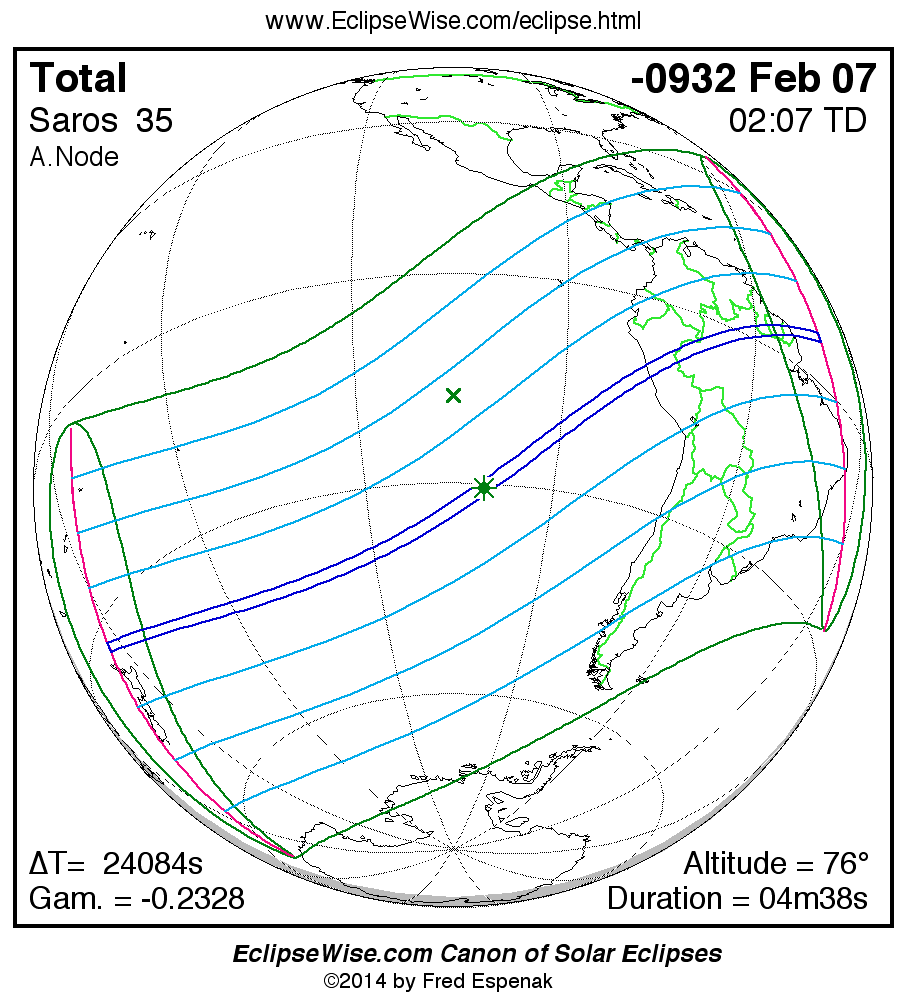
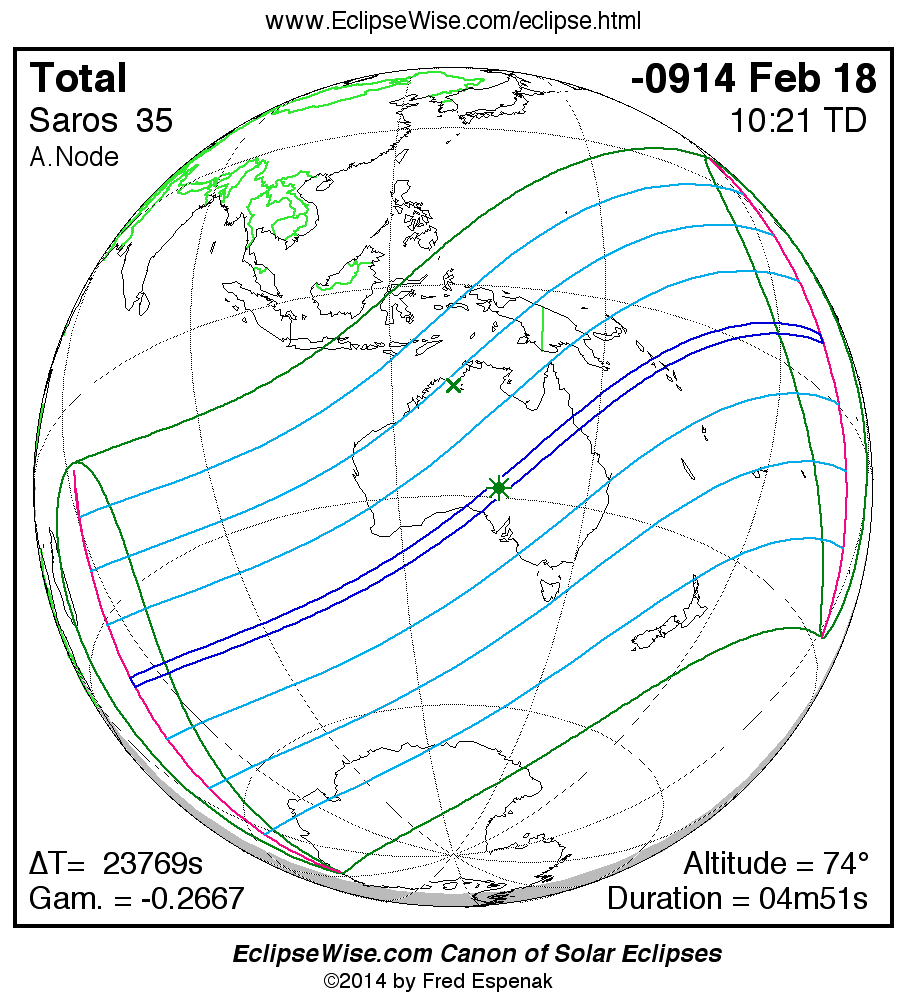
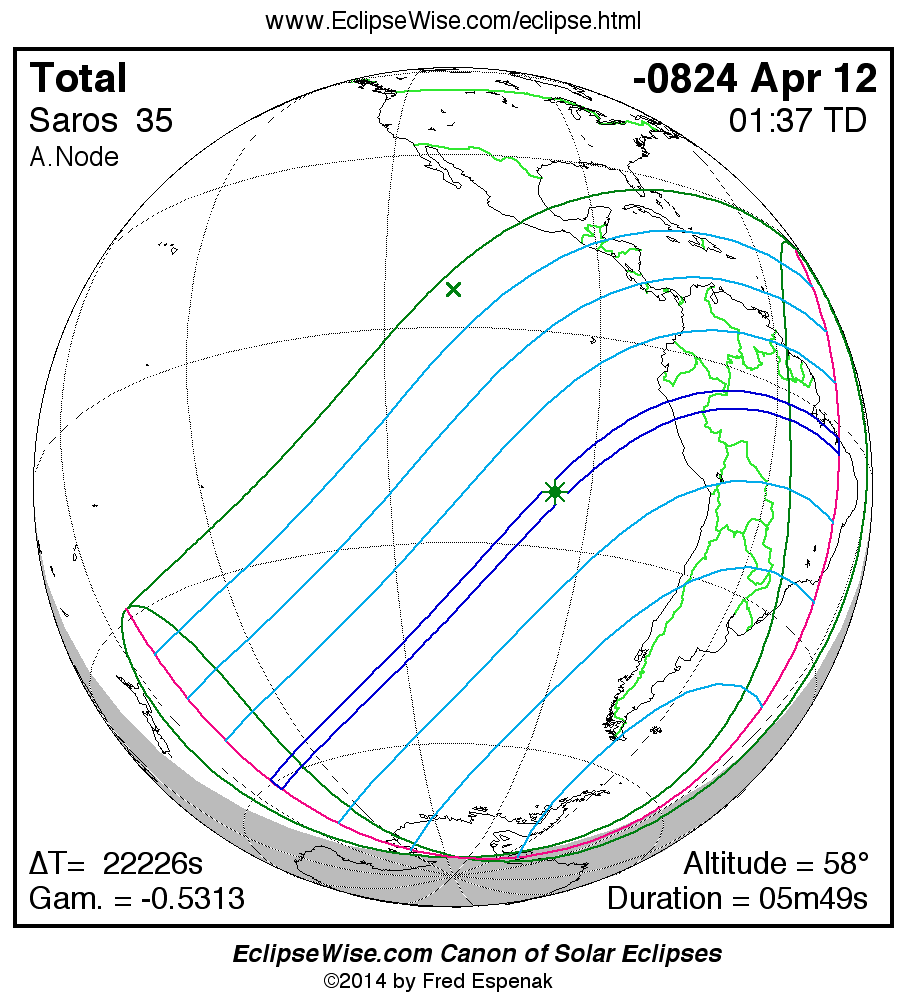
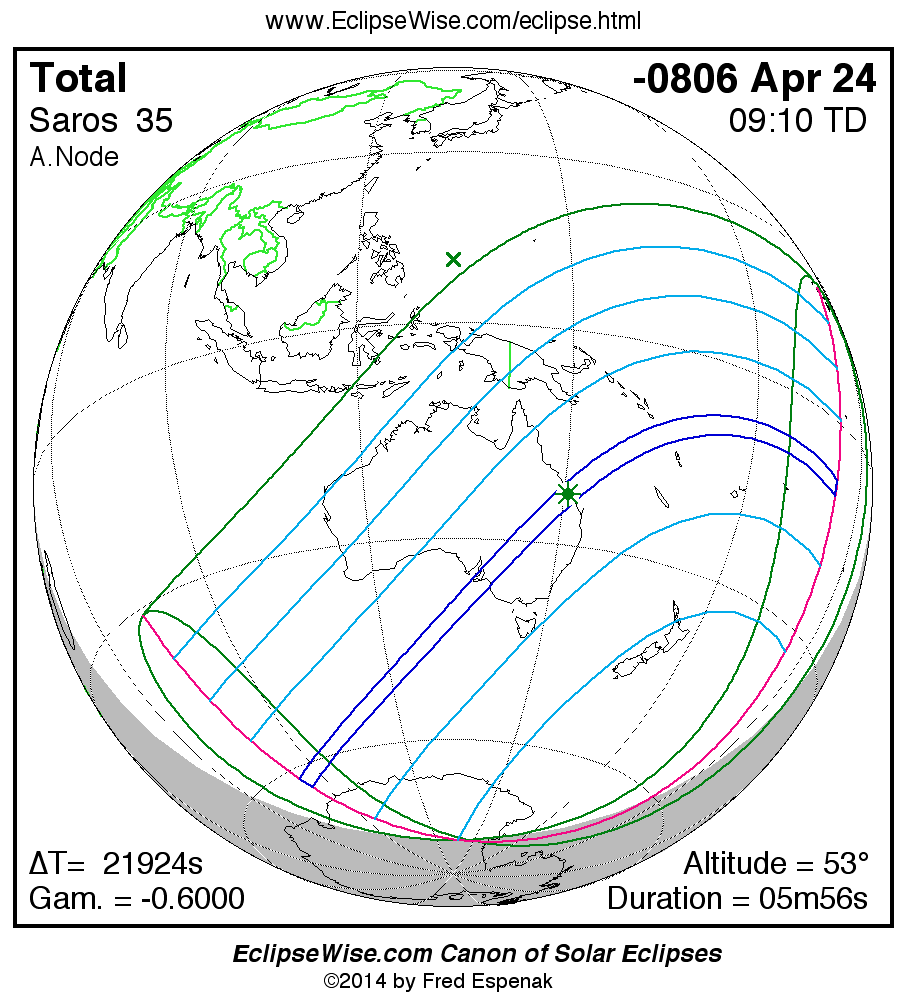
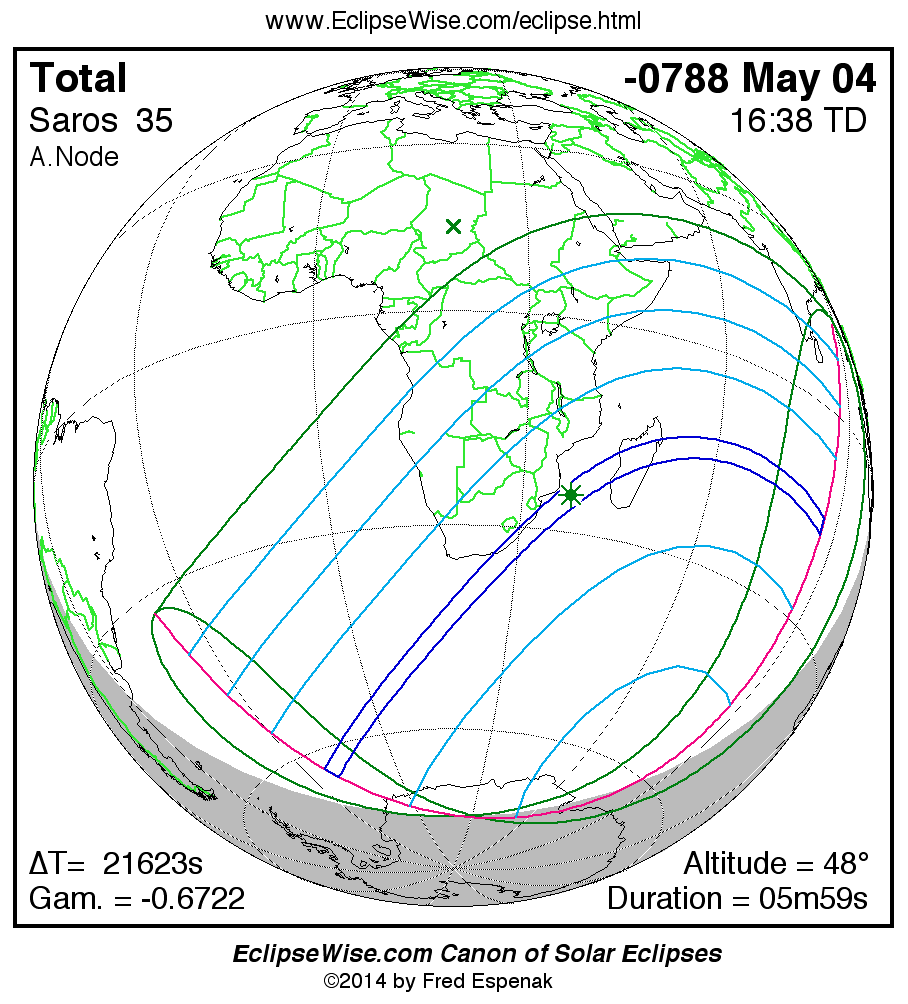
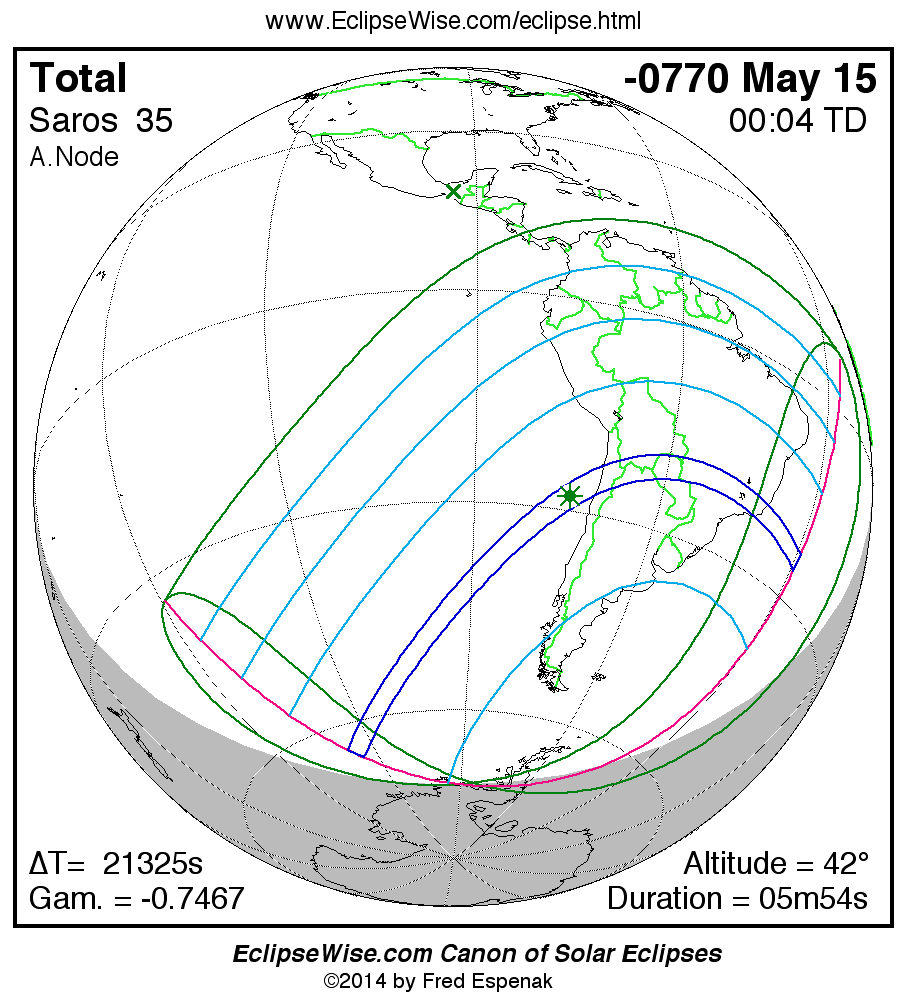
Panorama of Solar Eclipses of Saros 35
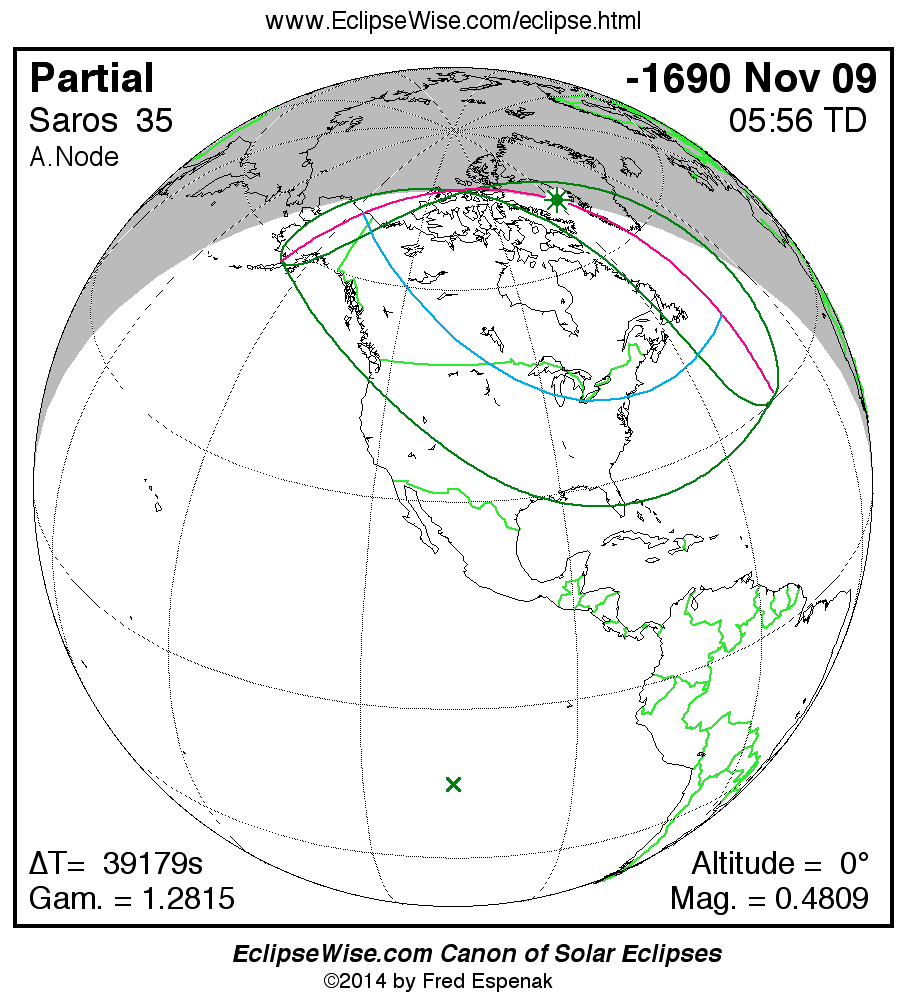
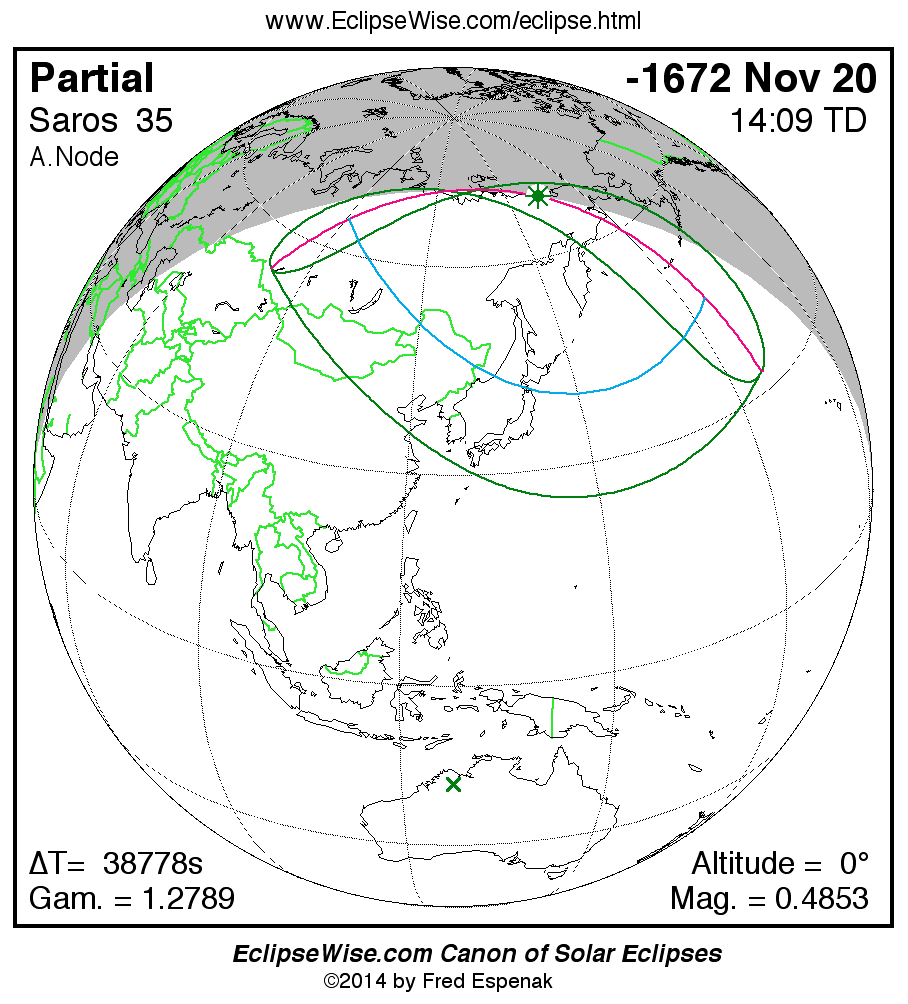
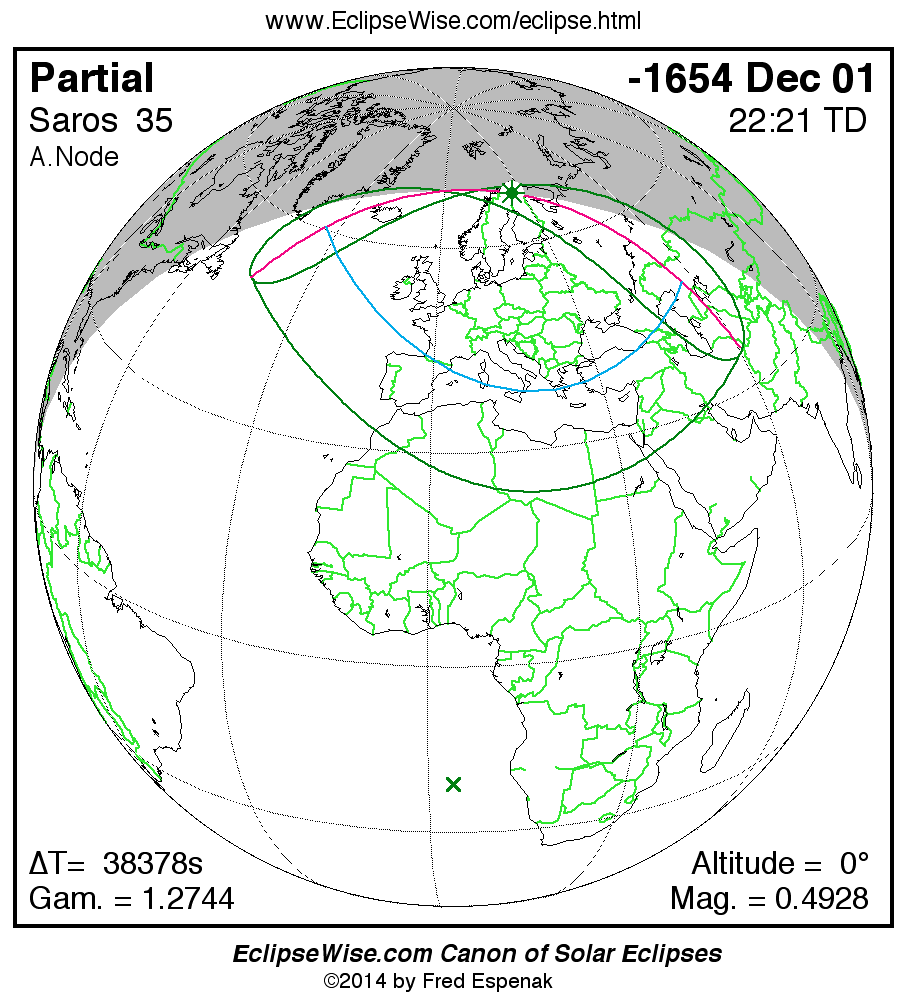
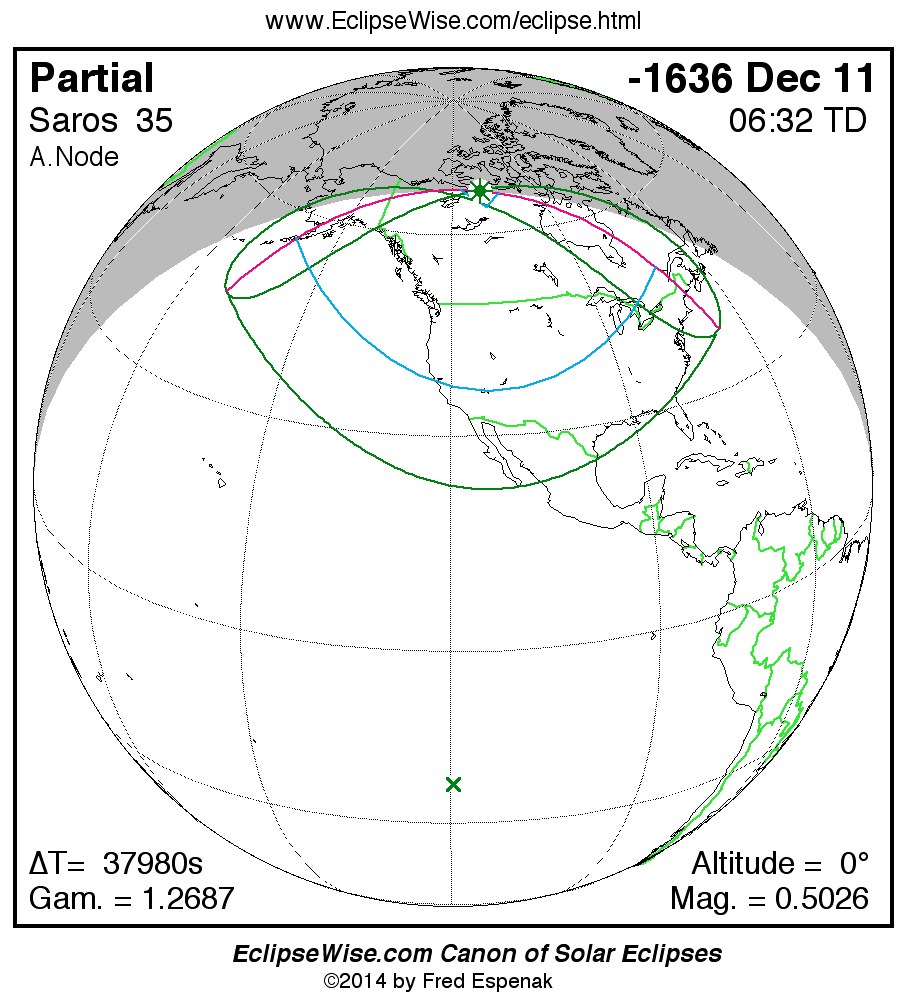
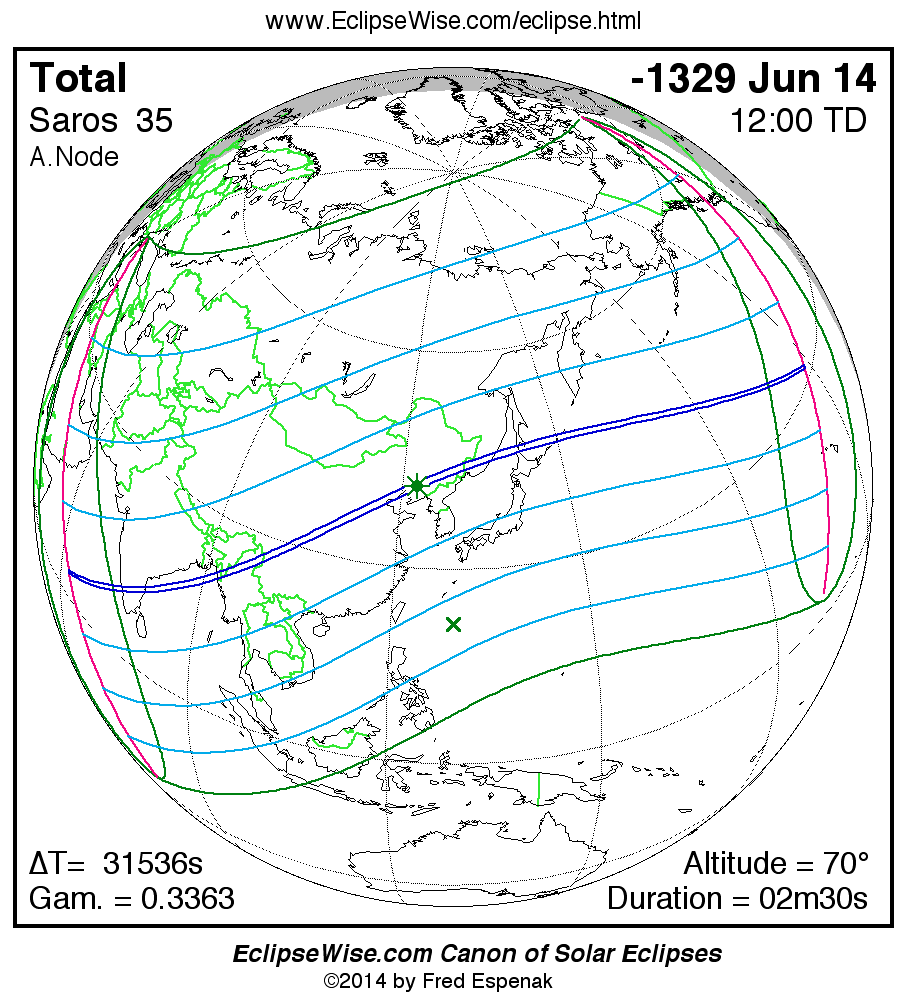
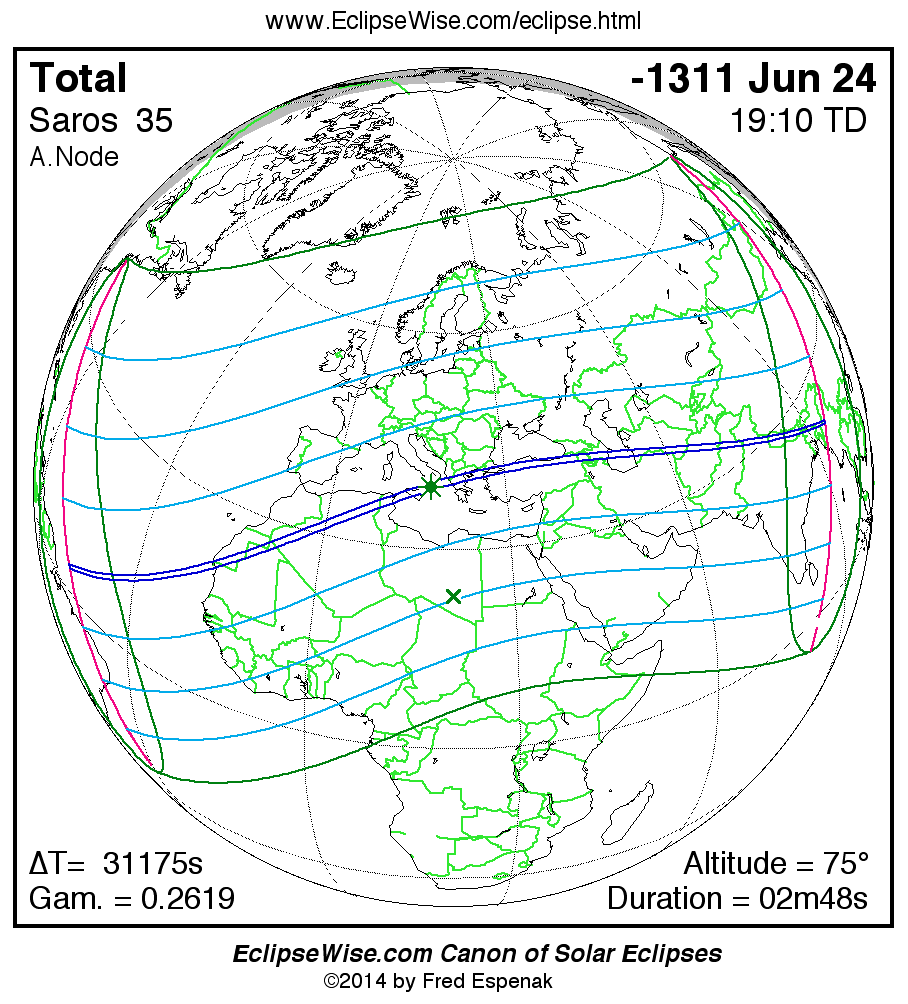
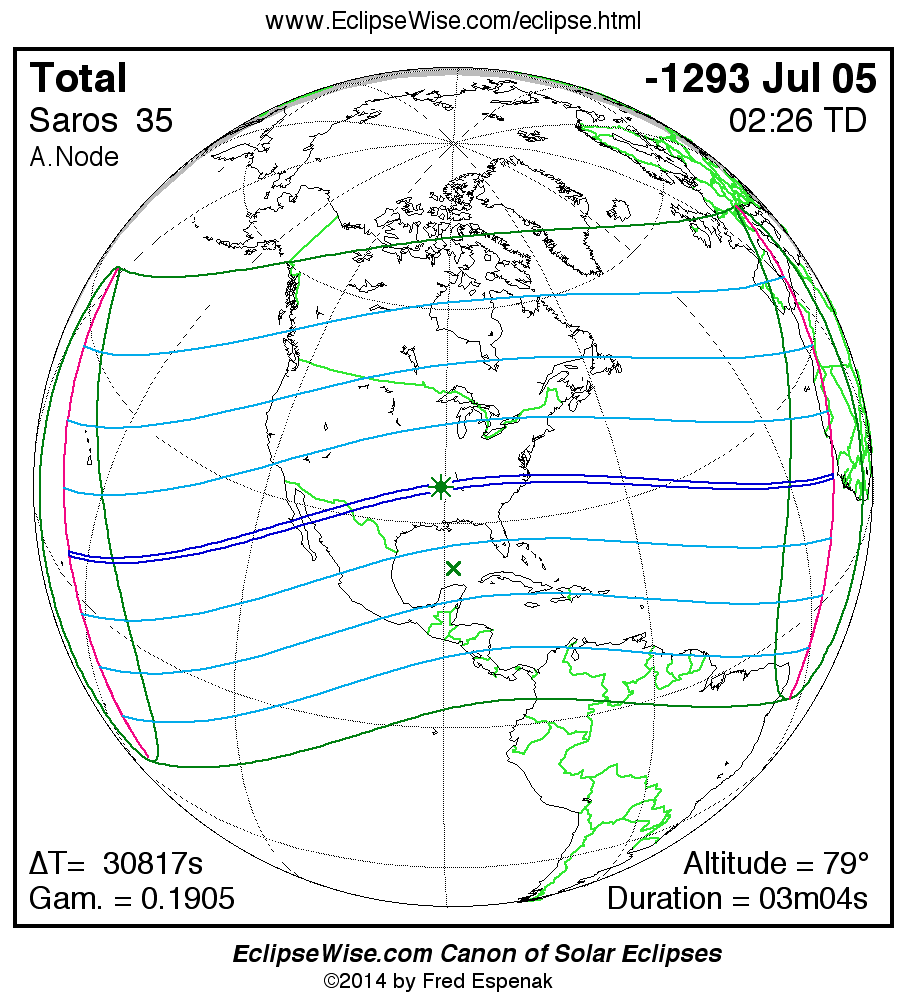
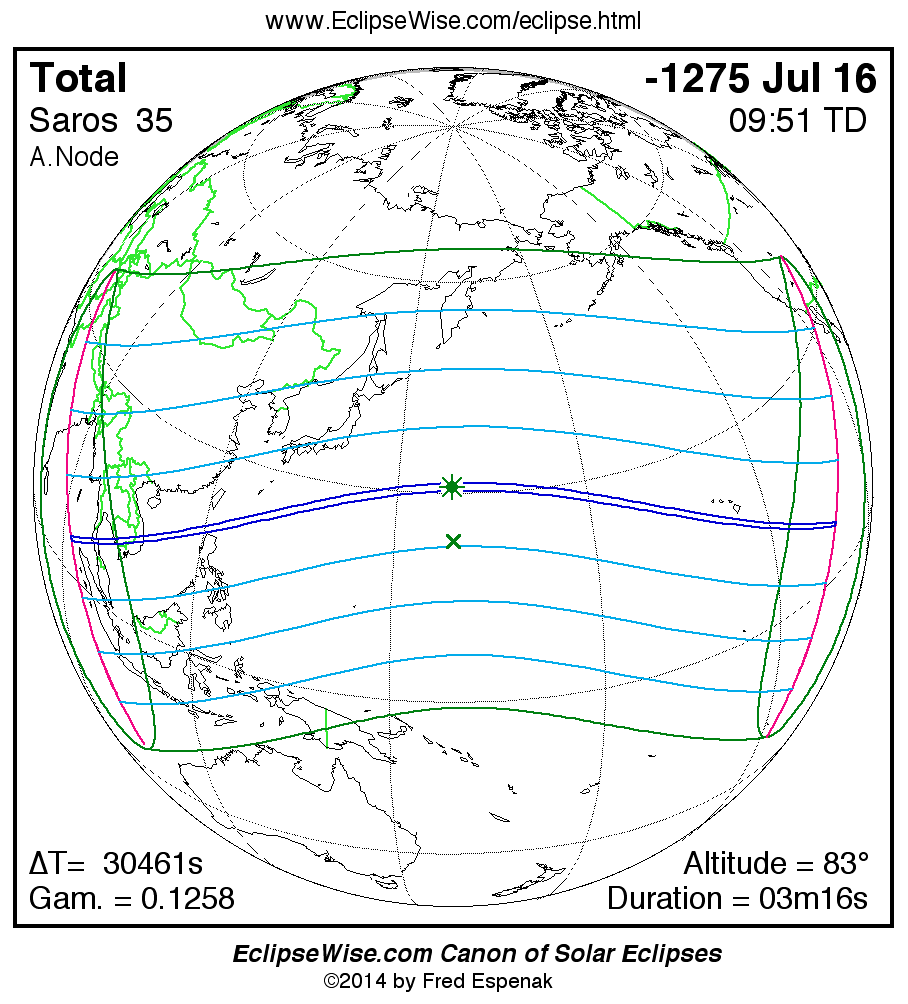
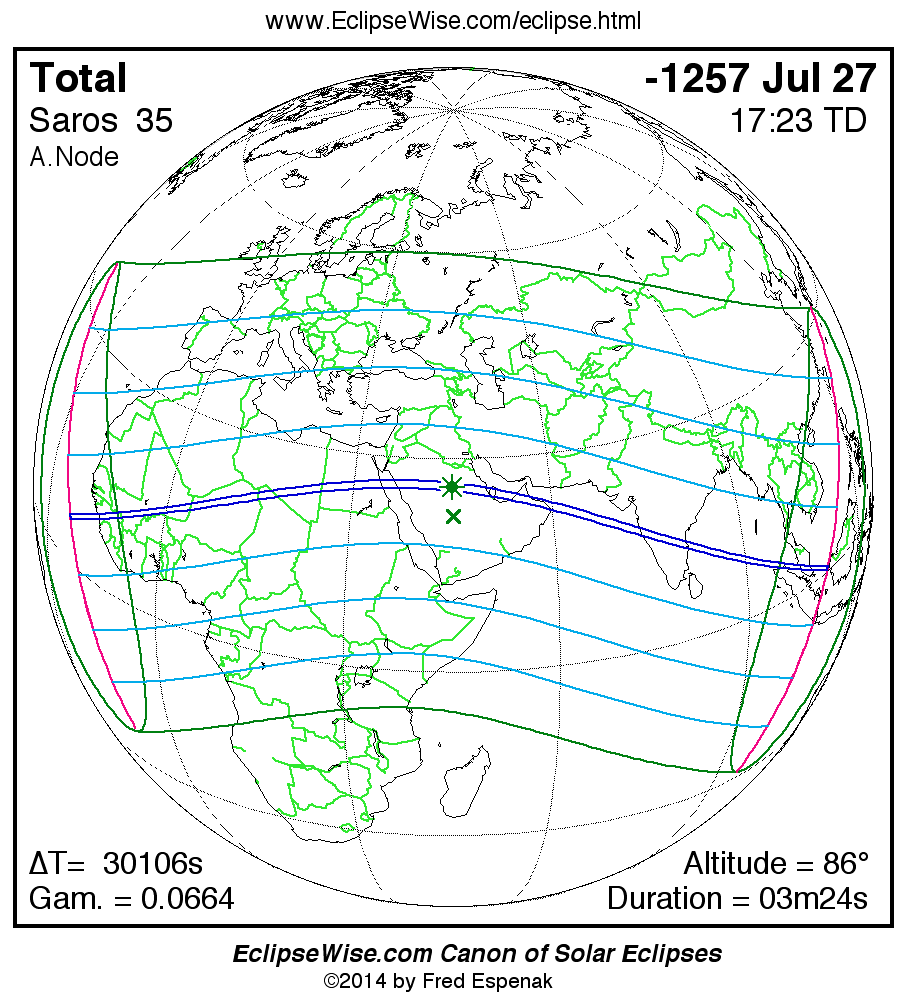
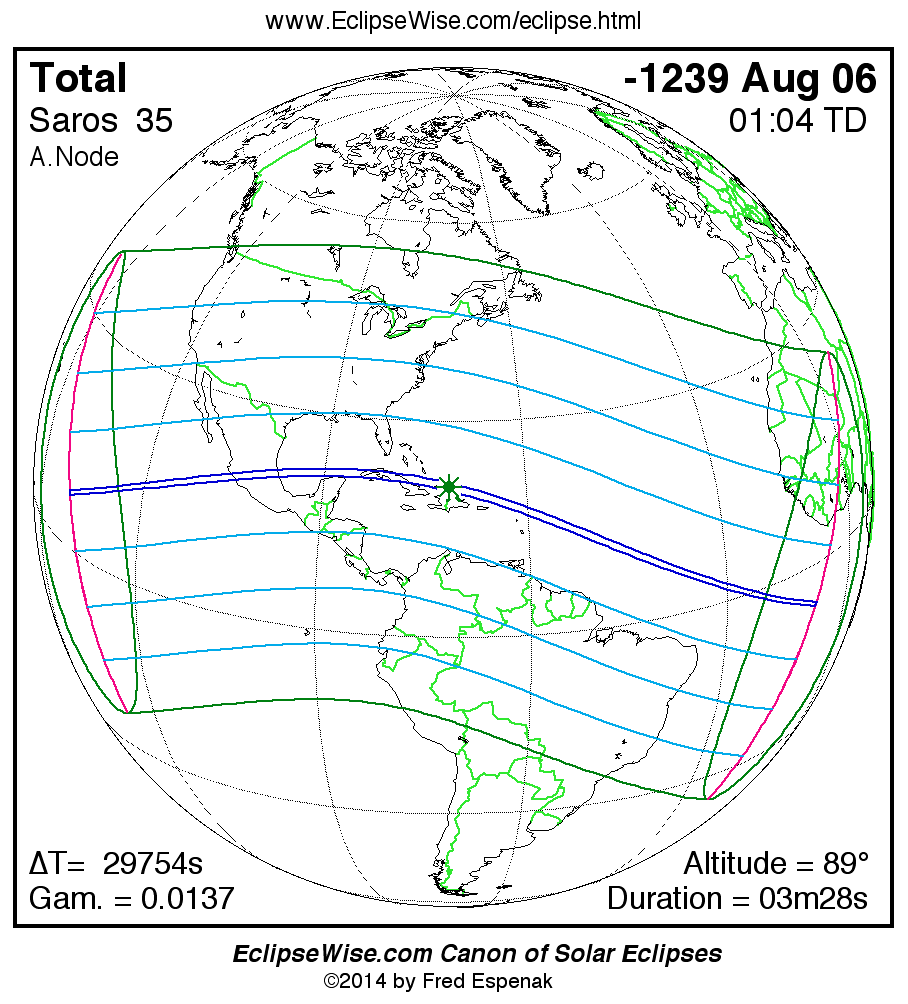
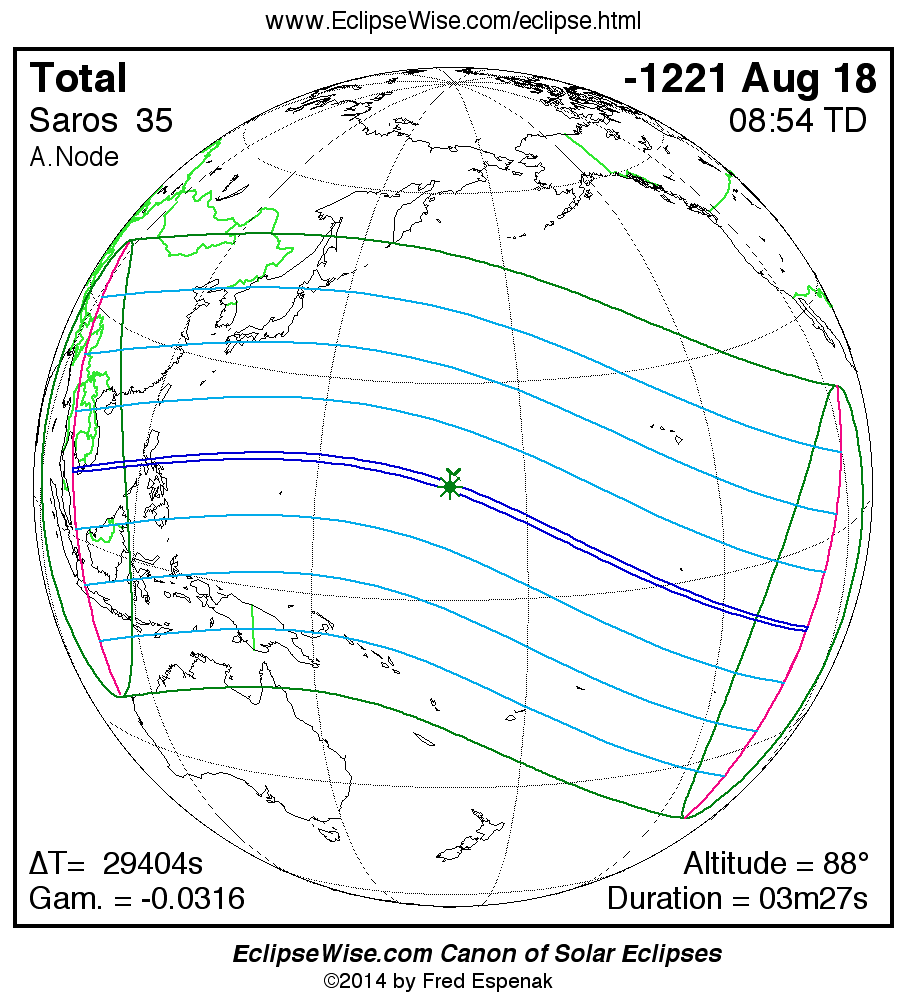
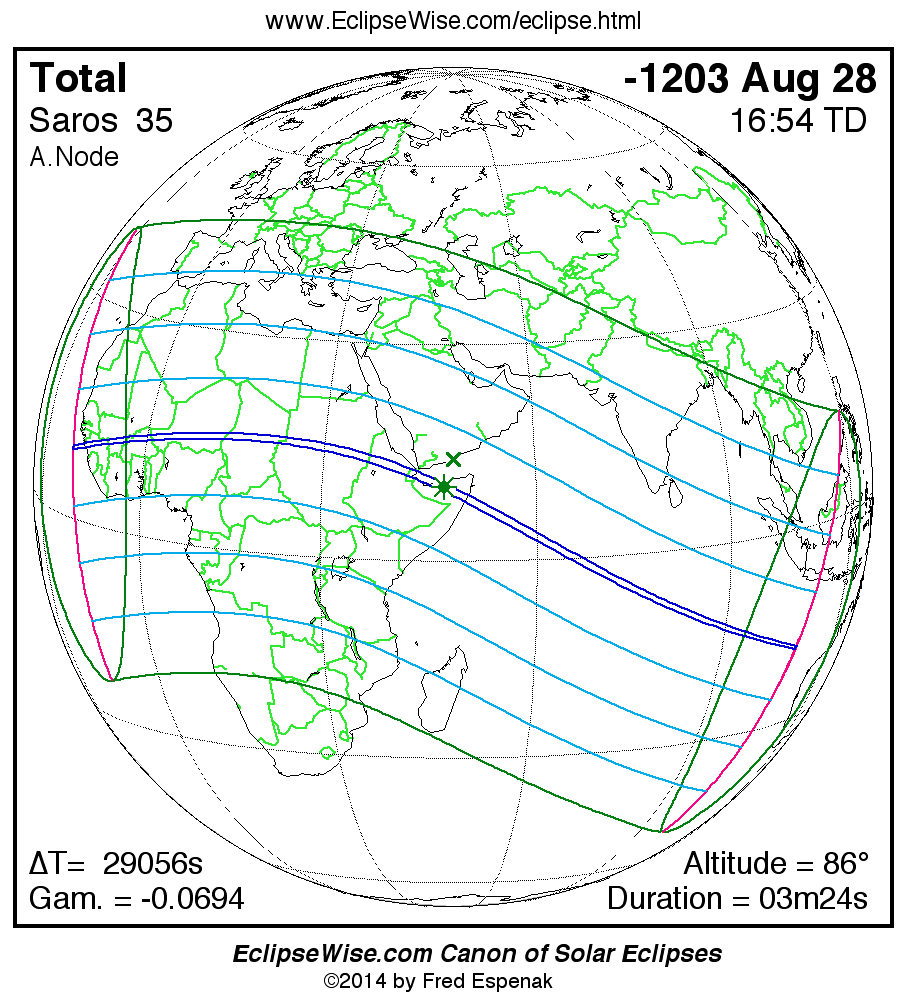
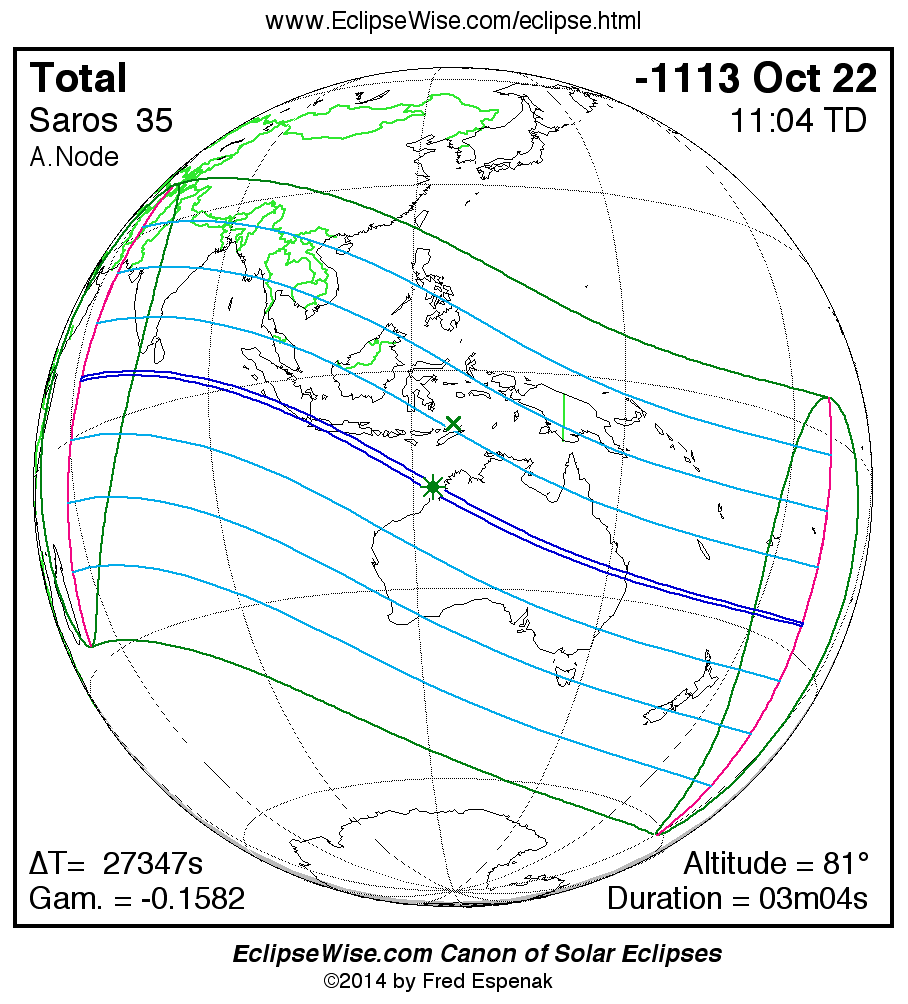
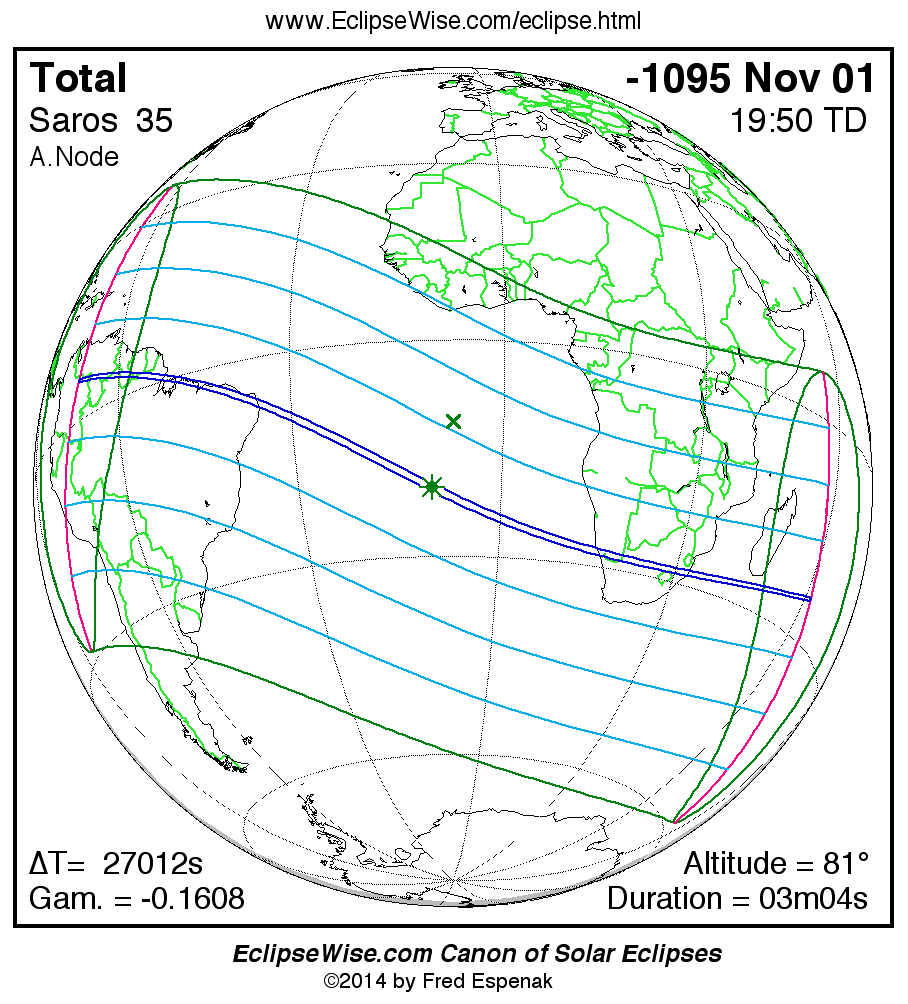
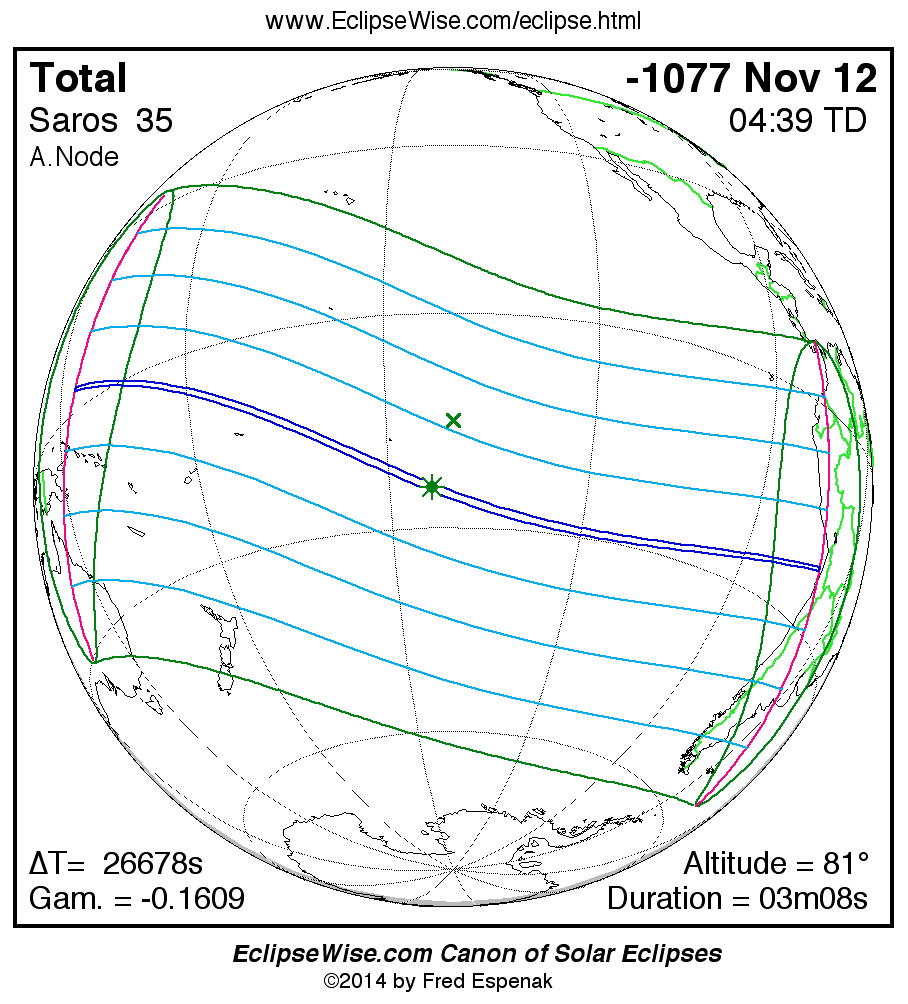
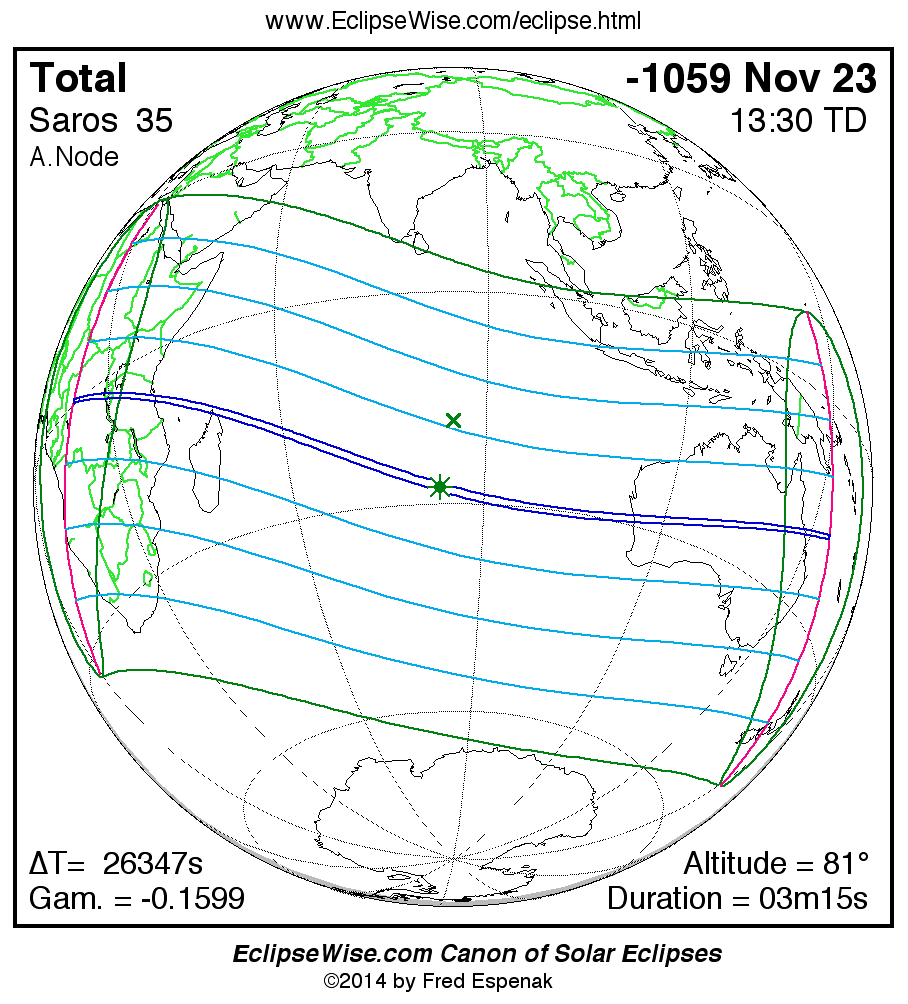
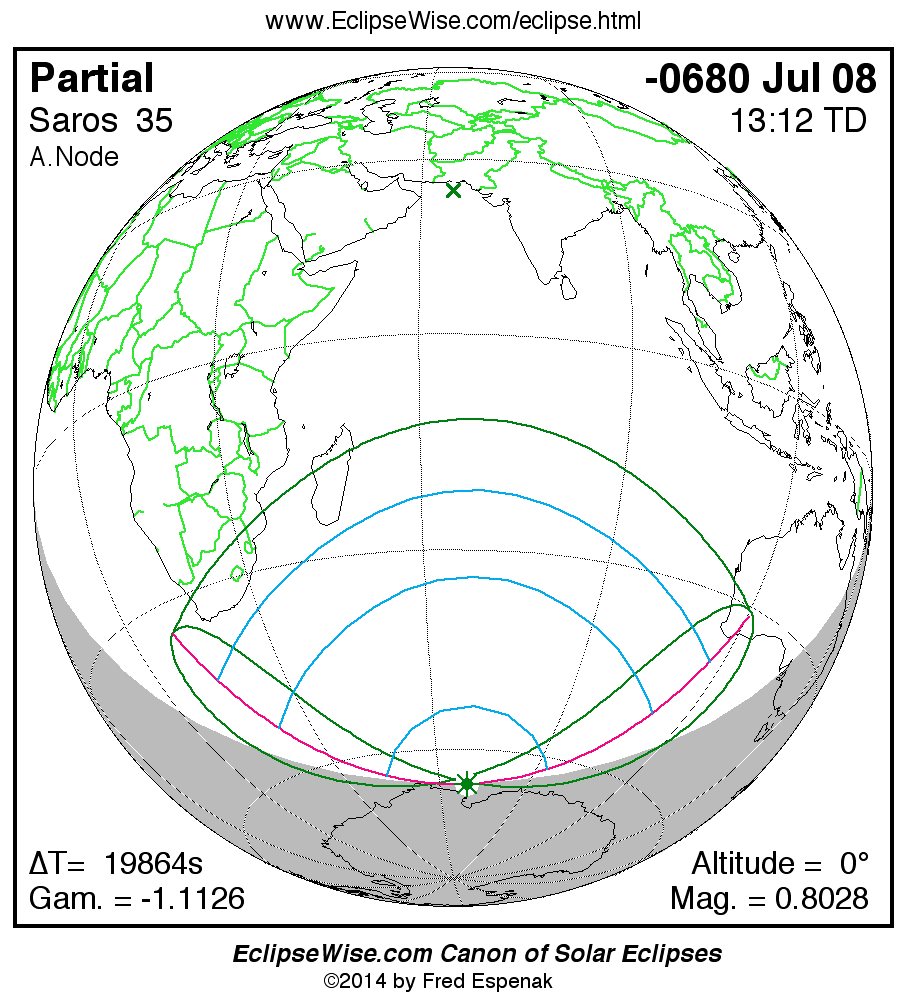
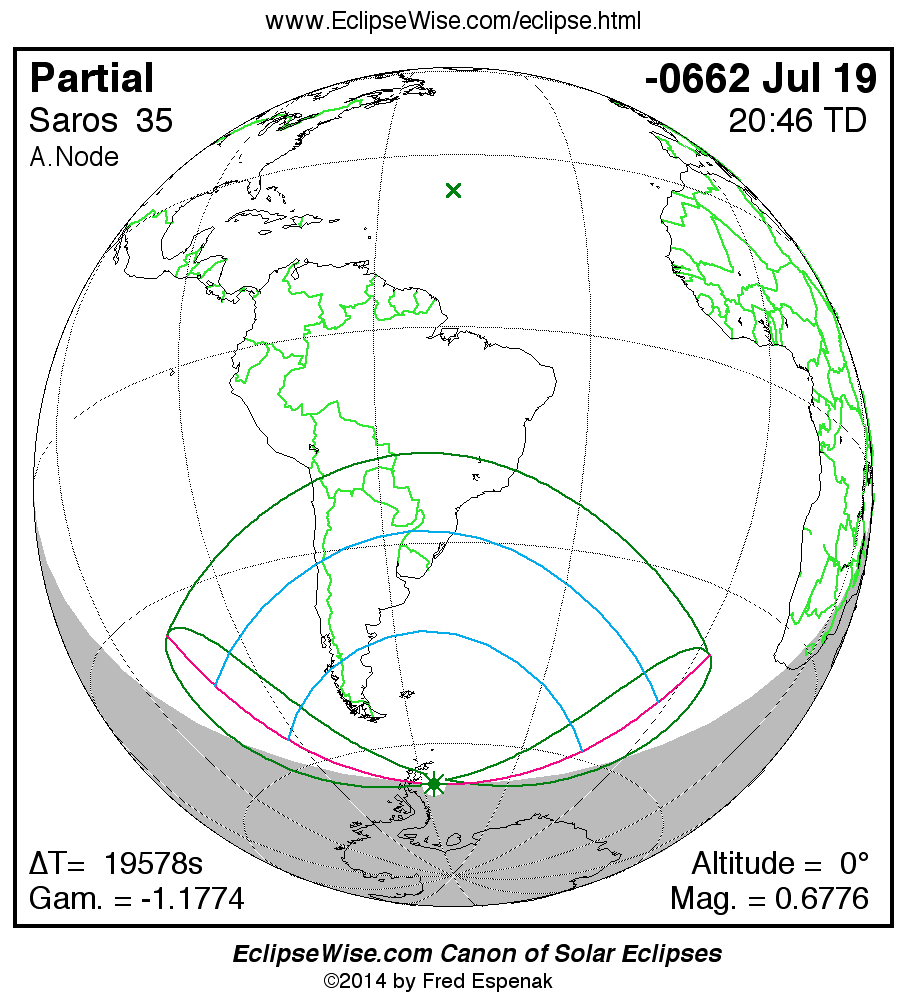
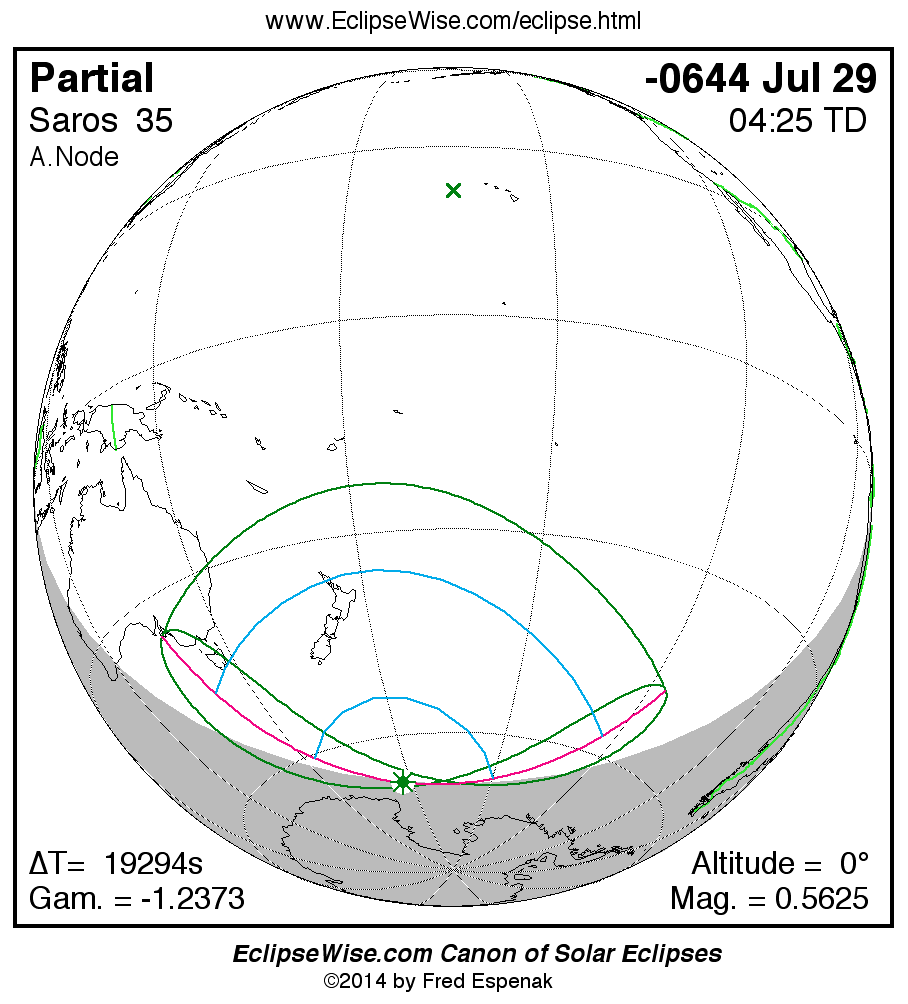
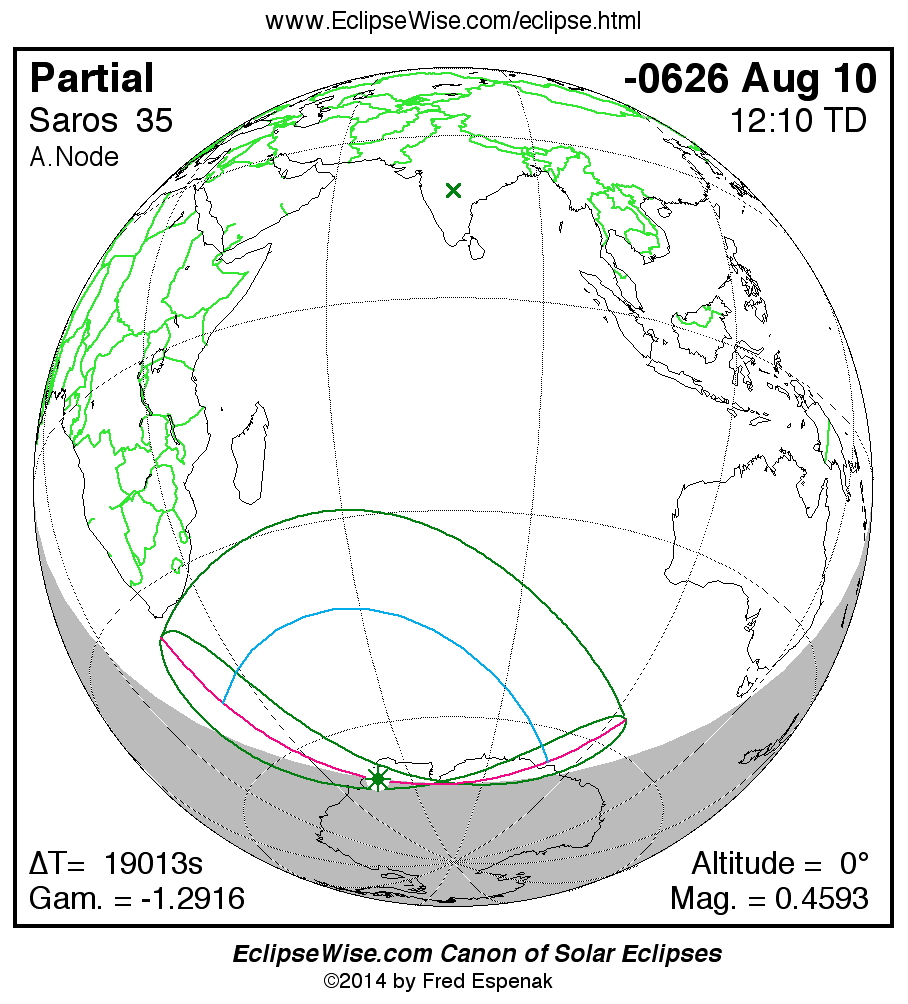
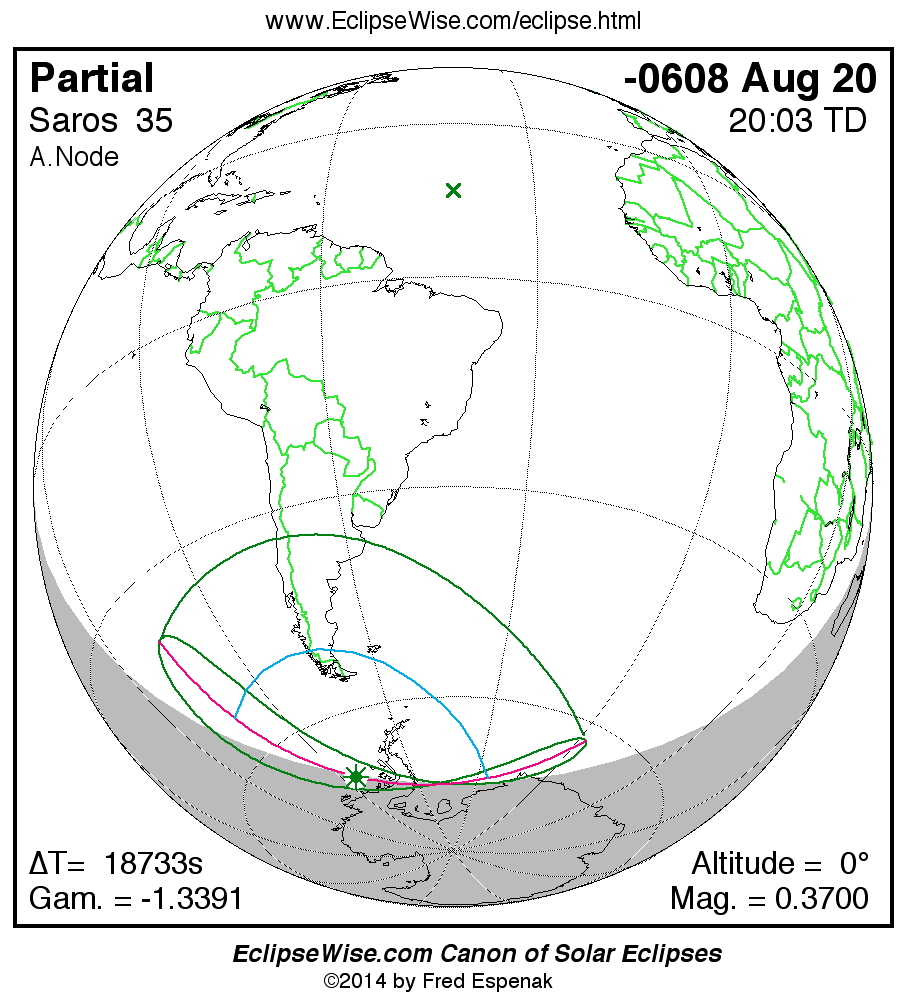
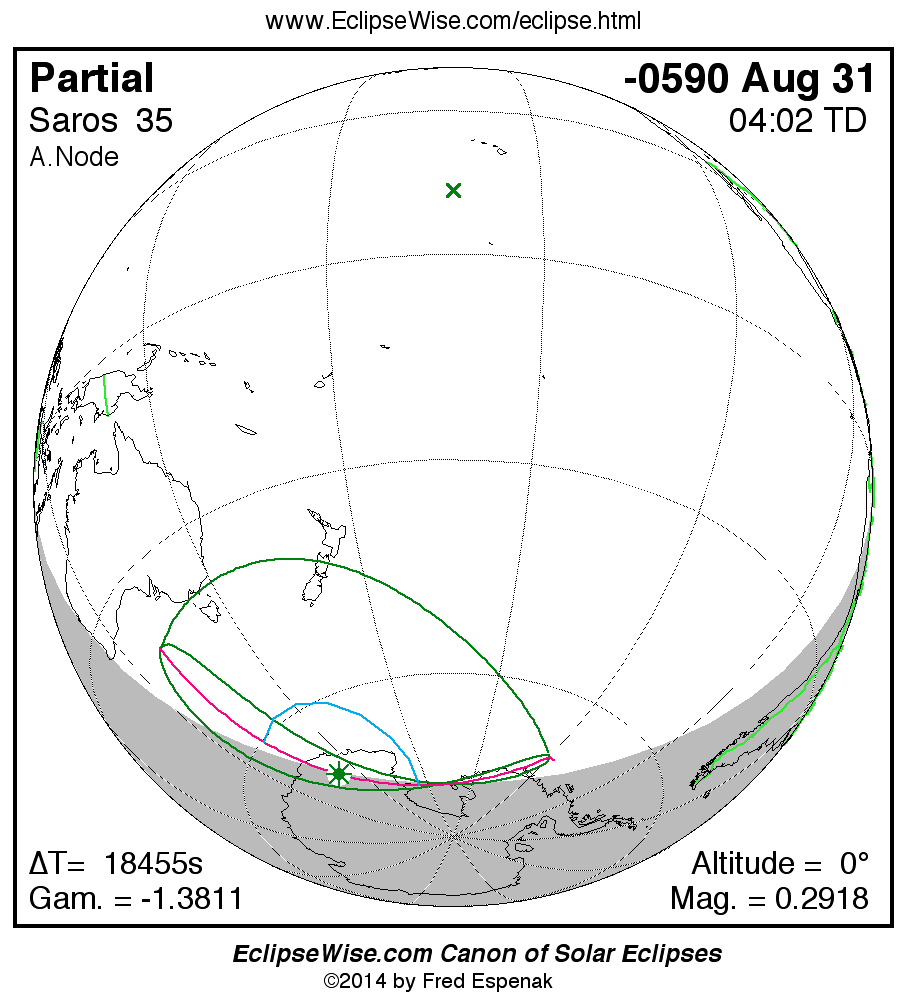
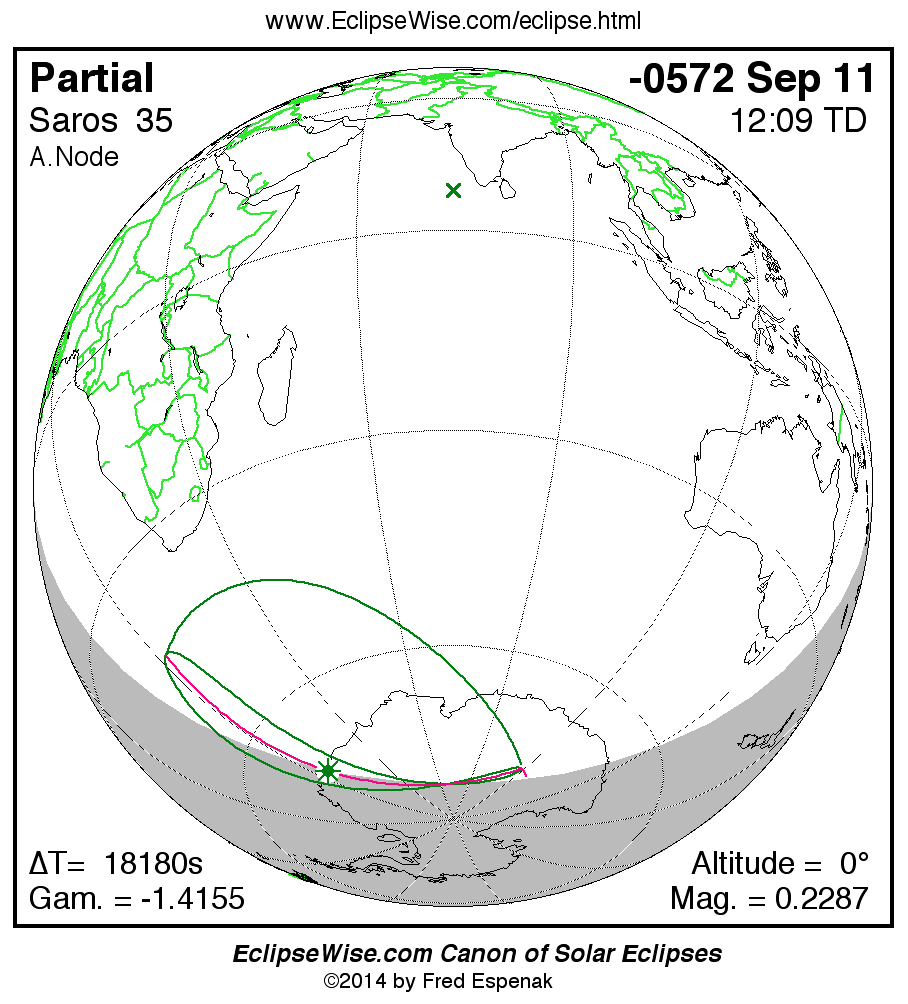
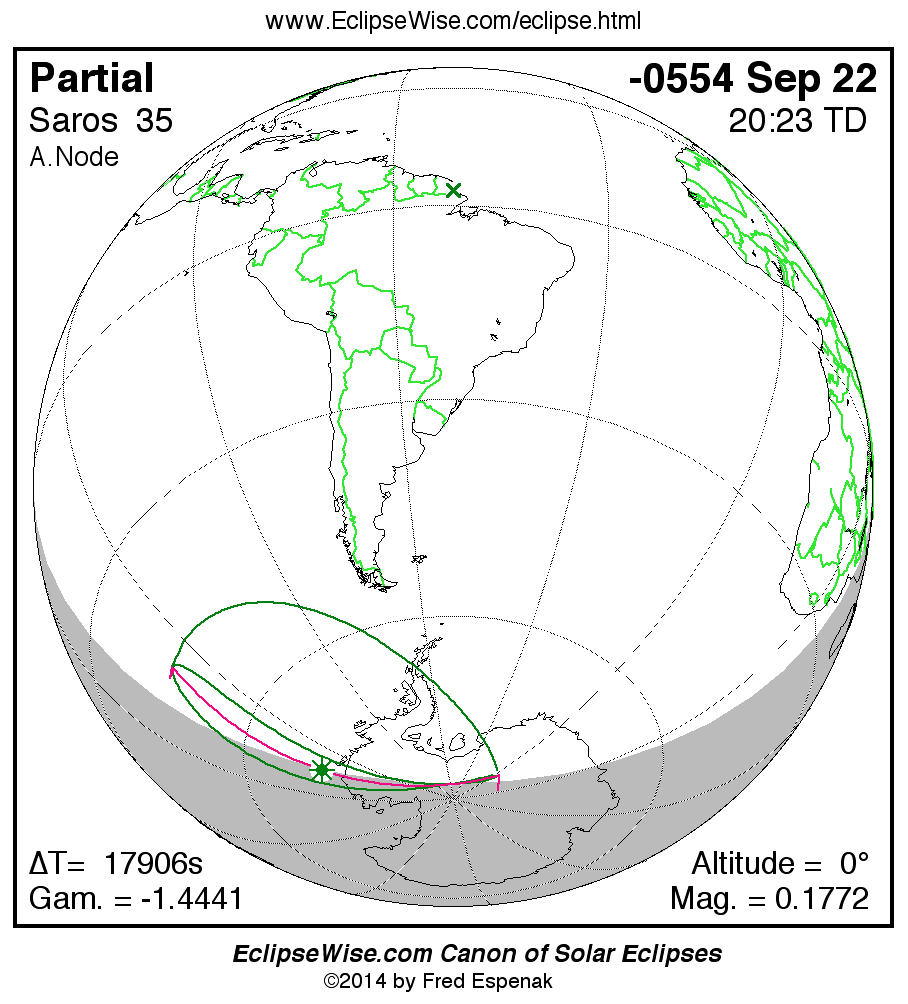
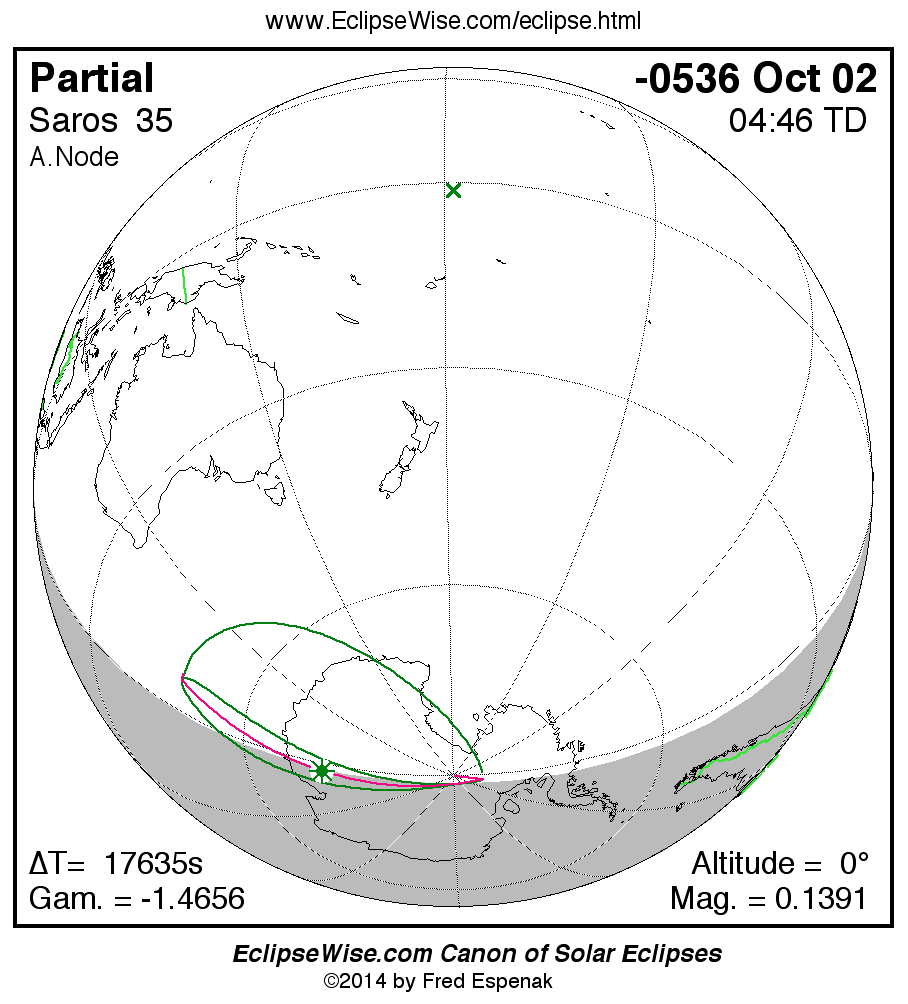
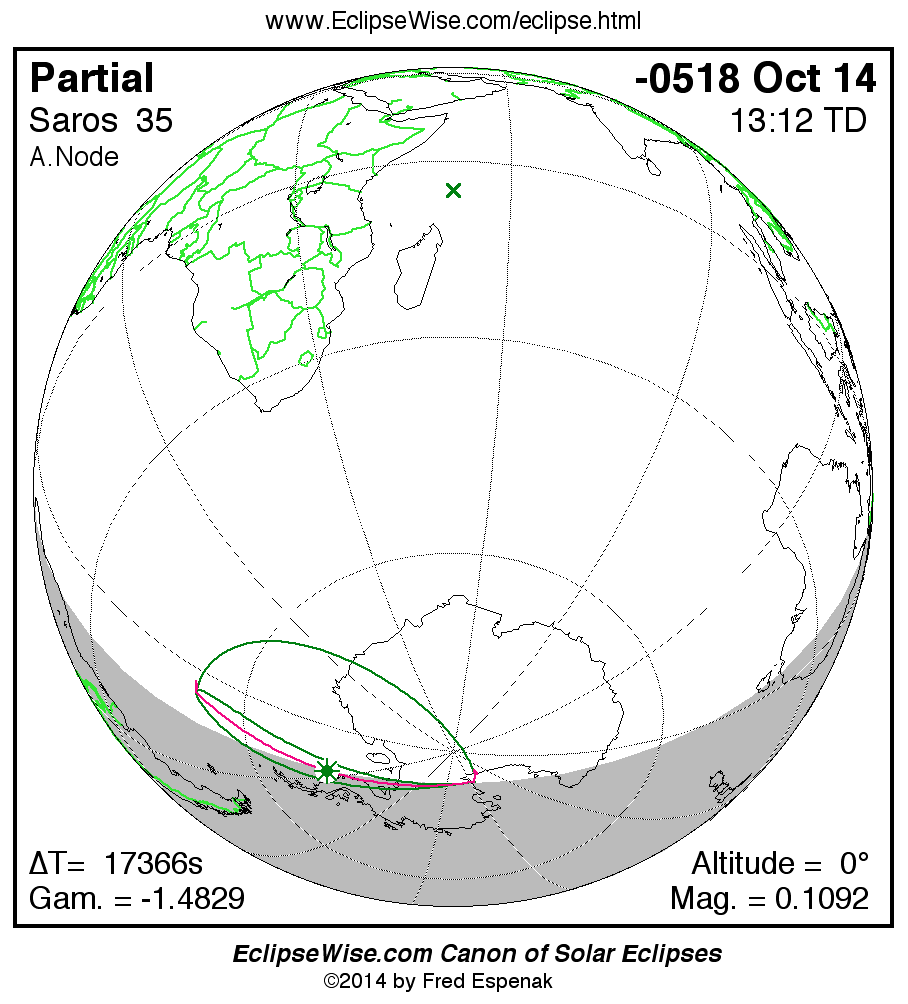
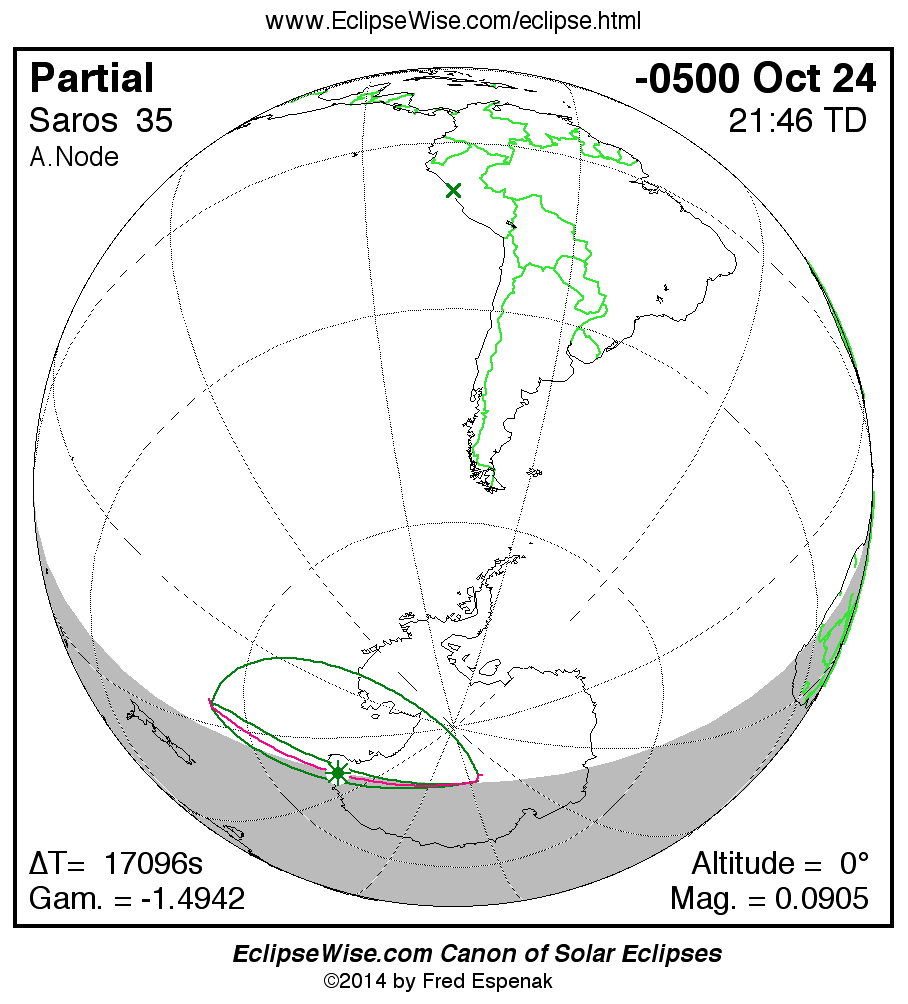
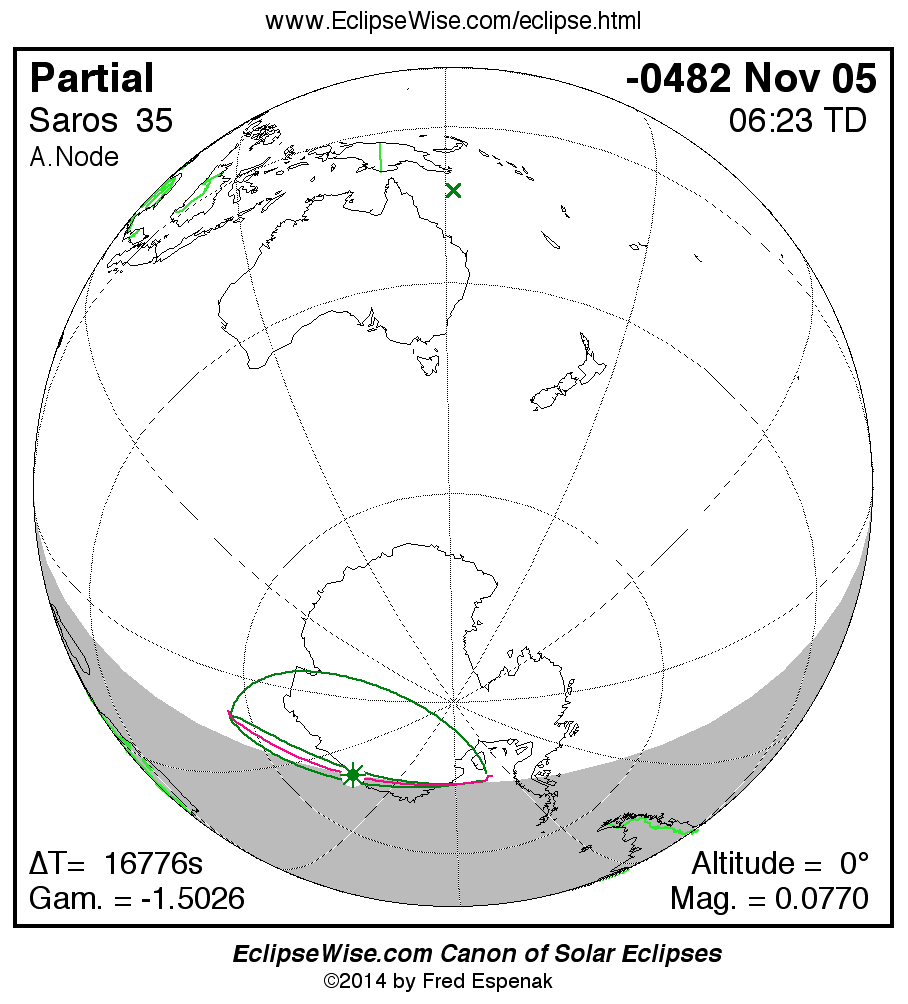
A panorama of all solar eclipses belonging to Saros 35 is presented here. Each map depicts the geographic region of visibility for a single eclipse. For central eclipses, the total or annular path is plotted in either blue (total) or red (annular). The date and time is given for the instant of Greatest Eclipse. Every map serves as a hyperlink to the EclipseWise Prime page for that eclipse where a larger map and complete details for the eclipse can be found. Visit the Key to Solar Eclipse Maps for a detailed explanation of these maps. Near the bottom of the page are a series of hyperlinks for more on solar eclipses.
The exeligmos is a period of three Saros cycles and is equal to approximately 54 years 33 days. Because it is nearly an integral number of days in length, two eclipses separated by 1 exeligmos (= 3 Saroses) not only share all the characterists of a Saros, but also take place in approximately the same geographic location.
The Saros panorama below is arranged in horizontal rows of 3 eclipses. So one eclipse to the left or right is a difference of 1 Saros cycle, and one eclipse above or below is a difference of 1 exeligmos. By scanning a column of the table, it reveals how the geographic visibility of eclipses separated by an exeligmos slowly changes.
- Click on any global map to go directly to the EclipseWise Prime Page for more information, tables, diagrams and maps. Key to Solar Eclipse Maps explains the features in these maps.
- Beneath each global eclipse map is a link Google Eclipse Map, that takes you to an interactive Google Map with the eclipse path plotted.
For more information on this series see Statistics for Solar Eclipses of Saros 35 .